Novel functions of Ect2 in polar lamellipodia formation and polarity maintenance during "contractile ring-independent" cytokinesis in adherent cells - PubMed (original) (raw)
Novel functions of Ect2 in polar lamellipodia formation and polarity maintenance during "contractile ring-independent" cytokinesis in adherent cells
Masamitsu Kanada et al. Mol Biol Cell. 2008 Jan.
Abstract
Some mammalian cells are able to divide via both the classic contractile ring-dependent method (cytokinesis A) and a contractile ring-independent, adhesion-dependent method (cytokinesis B). Cytokinesis A is triggered by RhoA, which, in HeLa cells, is activated by the guanine nucleotide-exchange factor Ect2 localized at the central spindle and equatorial cortex. Here, we show that in HT1080 cells undergoing cytokinesis A, Ect2 does not localize in the equatorial cortex, though RhoA accumulates there. Moreover, Ect2 depletion resulted in only modest multinucleation of HT1080 cells, enabling us to establish cell lines in which Ect2 was constitutively depleted. Thus, RhoA is activated via an Ect2-independent pathway during cytokinesis A in HT1080 cells. During cytokinesis B, Ect2-depleted cells showed narrower accumulation of RhoA at the equatorial cortex, accompanied by compromised pole-to-equator polarity, formation of ectopic lamellipodia in regions where RhoA normally would be distributed, and delayed formation of polar lamellipodia. Furthermore, C3 exoenzyme inhibited equatorial RhoA activation and polar lamellipodia formation. Conversely, expression of dominant active Ect2 in interphase HT1080 cells enhanced RhoA activity and suppressed lamellipodia formation. These results suggest that equatorial Ect2 locally suppresses lamellipodia formation via RhoA activation, which indirectly contributes to restricting lamellipodia formation to polar regions during cytokinesis B.
Figures
Figure 1.
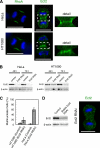
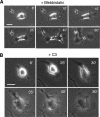
Localization of RhoA and Ect2 during cytokinesis and the effects of Ect2 depletion on cytokinesis in HeLa cells and HT1080 cells. (A) Confocal microscopic images of mitotic HeLa and HT1080 cells showing the distributions of RhoA (green), Ect2 (green), and DNA (blue); scale bars, 10 μm. Magnified views of the Ect2 staining (dashed boxes) are provided on the right. (B) Depletion of Ect2 in HeLa and HT1080 cells was confirmed by immunoblotting using anti-Ect2 antibodies 48 and 72 h after transfection. β-actin was detected as a loading control. (C) Frequencies of multinucleate cells. In each of three independent experiments, 200 cells were examined. Values are shown as mean (%) ± SD. (D) Persistent depletion of Ect2 in a stably transfected HT1080 cell line was confirmed by immunoblotting (left) and by confocal immunofluorescence microscopy (right) using anti-Ect2 antibodies; scale bar, 10 μm.
Figure 2.
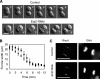
Effects of Ect2 depletion on cytokinesis A. (A) Cytokinesis A in control and Ect2-depleted HT1080 cells. Numbers indicate the time in minutes after onset of anaphase; scale bars, 20 μm. (B) Changes in the widths of the furrows in control (♦) and Ect2-depleted (■) cells after anaphase onset. Values are shown as means ± SD (n = 6). (C) Confocal microscopic images of control and Ect2-depleted mitotic HT1080 cells showing the distributions of RhoA and DNA; scale bars, 10 μm.
Figure 3.
Effects of Ect2 depletion on cytokinesis B. (A) Cytokinesis B in control HT1080 cells on collagen coated substrates in the presence of 30 μM blebbistatin. (B–D) Three representative patterns of cytokinesis B in Ect2-depleted cells cultured as in A. See text for details. Numbers indicate the time in minutes after anaphase onset; scale bars, 20 μm. (E) Growth of the distance from pole to pole in control (diamonds) and Ect2-depleted (squares) daughter cells after anaphase onset in the presence of blebbistatin. Values are shown as means ± SEM (n = 8). The differences between the two cell lines are statistically significant (p < 0.05) at 4 and 8 min after anaphase onset (Mann-Whitney test).
Figure 4.
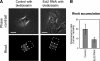
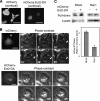
Effects of Ect2 depletion on RhoA localization during cytokinesis B. (A) Phase-contrast and conventional epifluorescence micrographs of control and Ect2-depleted HT1080 cells undergoing cytokinesis B on collagen-coated substrates in the presence of 30 μM blebbistatin. The cells were stained by anti-RhoA antibodies. Dashed boxes (20 × 25 μm) represent regions in which relative RhoA levels were measured; scale bars, 20 μm. (B) Levels of RhoA present in the equatorial region are expressed as ratios of the total fluorescence in the equatorial region over that in the region where lamellipodia were formed. RhoA accumulation is significantly reduced (p < 0.01) in the equatorial region of Ect2-depleted cells (Mann-Whitney test). Values are means ± SEM (n = 14 and 12 for control cells and Ect2-depleted cells, respectively).
Figure 5.
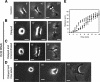
Effects of the cell permeable derivative of C3 exoenzyme on cytokinesis B. (A) Cytokinesis B in an HT1080 cell on a collagen-coated substrate in the presence of 30 μM blebbistatin. (B) Failed cytokinesis B in a C3-loaded cell on a collagen-coated substrate. Numbers indicate the time in minutes after onset of anaphase; scale bars, 20 μm.
Figure 6.
Activation of RhoA and inhibition of lamellipodia formation by mCherry-tagged Ect2-DA. (A) HT1080 cells were transfected with plasmids encoding either mCherry-Ect2-DA or mCherry. Twenty-four hours later the cells were transferred to glass-bottomed dishes for confocal microscopic observation; scale bars, 20 μm. (B) Behavior of interphase HT1080 cells expressing mCherry or mCherry-Ect2-DA on collagen-coated substrates. The expression of each protein was identified by red fluorescence (left). Arrows show a newly formed lamellipodium in an mCherry-expressing cell; numbers indicate elapsed time in minutes; scale bars, 20 μm. (C) mCherry-expressing (−) or mCherry-Ect2-DA–expressing (+) cells on collagen-coated substrates were assayed for RhoA activity using a GST-Rhotekin pulldown assay and for Rac1 activity using a GST-PAK binding domain pulldown assay. Typical immunoblots and the results of quantitative analysis (means ± SD, n = 3 and 4 for RhoA and Rac1, respectively) are shown.
Figure 7.
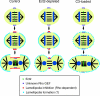
A model of Rho-dependent polar lamellipodia formation during cytokinesis B. Ect2 and an unidentified Rho GEF accumulate at the central spindle and the equatorial cortex to activate RhoA, respectively (top and middle in Control). The two GEFs then induce broad RhoA accumulation at the equatorial cortex, which contributes to recruitment of the elements involved in lamellipodia formation to the polar peripheries (bottom in Control). Ect2-depleted cells are unable to form the broad RhoA accumulation as in Control cells, so that ectopic lamellipodia form near the equatorial region (bottom in Ect2-depleted). In C3-loaded cells, equatorial RhoA accumulation is completely inhibited, so that lamellipodia form all around the cell periphery (bottom in C3-loaded). In addition to this, a basal level of active RhoA seems necessary for lamellipodia formation during the first half hour after the anaphase onset, but that aspect of RhoA activity is not included in this scheme.
Similar articles
- An ECT2-centralspindlin complex regulates the localization and function of RhoA.
Yüce O, Piekny A, Glotzer M. Yüce O, et al. J Cell Biol. 2005 Aug 15;170(4):571-82. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200501097. J Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 16103226 Free PMC article. - Polo-like kinase 1 triggers the initiation of cytokinesis in human cells by promoting recruitment of the RhoGEF Ect2 to the central spindle.
Petronczki M, Glotzer M, Kraut N, Peters JM. Petronczki M, et al. Dev Cell. 2007 May;12(5):713-25. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2007.03.013. Dev Cell. 2007. PMID: 17488623 - Targeting of the RhoGEF Ect2 to the equatorial membrane controls cleavage furrow formation during cytokinesis.
Su KC, Takaki T, Petronczki M. Su KC, et al. Dev Cell. 2011 Dec 13;21(6):1104-15. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2011.11.003. Dev Cell. 2011. PMID: 22172673 - Spatiotemporal Regulation of RhoA during Cytokinesis.
Basant A, Glotzer M. Basant A, et al. Curr Biol. 2018 May 7;28(9):R570-R580. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2018.03.045. Curr Biol. 2018. PMID: 29738735 Free PMC article. Review. - Cytokinesis and cancer: Polo loves ROCK'n' Rho(A).
Li J, Wang J, Jiao H, Liao J, Xu X. Li J, et al. J Genet Genomics. 2010 Mar;37(3):159-72. doi: 10.1016/S1673-8527(09)60034-5. J Genet Genomics. 2010. PMID: 20347825 Review.
Cited by
- Protein kinase Cι promotes UBF1-ECT2 binding on ribosomal DNA to drive rRNA synthesis and transformed growth of non-small-cell lung cancer cells.
Justilien V, Lewis KC, Meneses KM, Jamieson L, Murray NR, Fields AP. Justilien V, et al. J Biol Chem. 2020 Jun 12;295(24):8214-8226. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.013175. Epub 2020 Apr 29. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32350115 Free PMC article. - Ect2 links the PKCiota-Par6alpha complex to Rac1 activation and cellular transformation.
Justilien V, Fields AP. Justilien V, et al. Oncogene. 2009 Oct 15;28(41):3597-607. doi: 10.1038/onc.2009.217. Epub 2009 Jul 20. Oncogene. 2009. PMID: 19617897 Free PMC article. - Mechanics and regulation of cytokinetic abscission.
Andrade V, Echard A. Andrade V, et al. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Nov 24;10:1046617. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.1046617. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36506096 Free PMC article. Review. - Phosphorylation of myosin II-interacting guanine nucleotide exchange factor (MyoGEF) at threonine 544 by aurora B kinase promotes the binding of polo-like kinase 1 to MyoGEF.
Wu D, Asiedu M, Matsumura F, Wei Q. Wu D, et al. J Biol Chem. 2014 Mar 7;289(10):7142-7150. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.510388. Epub 2014 Jan 30. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24482237 Free PMC article. - Oncogenic activity of Ect2 is regulated through protein kinase C iota-mediated phosphorylation.
Justilien V, Jameison L, Der CJ, Rossman KL, Fields AP. Justilien V, et al. J Biol Chem. 2011 Mar 11;286(10):8149-8157. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.196113. Epub 2010 Dec 28. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21189248 Free PMC article.
References
- Amano M., Ito M., Kimura K., Fukata Y., Chihara K., Nakano T., Matsuura Y., Kaibuchi K. Phosphorylation and activation of myosin by Rho-associated kinase (Rho-kinase) J. Biol. Chem. 1996;271:20246–20249. - PubMed
- Benard V., Bokoch G. M. Assay of Cdc42, Rac, and Rho GTPase activation by affinity methods. Methods Enzymol. 2002;345:349–359. - PubMed
- Burridge K., Wennerberg K. Rho and Rac take center stage. Cell. 2004;116:167–179. - PubMed
- Burton K., Taylor D. L. Traction forces of cytokinesis measured with optically modified elastic substrata. Nature. 1997;385:450–454. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous