Expression analysis of G Protein-Coupled Receptors in mouse macrophages - PubMed (original) (raw)
Expression analysis of G Protein-Coupled Receptors in mouse macrophages
Jane E Lattin et al. Immunome Res. 2008.
Abstract
Background: Monocytes and macrophages express an extensive repertoire of G Protein-Coupled Receptors (GPCRs) that regulate inflammation and immunity. In this study we performed a systematic micro-array analysis of GPCR expression in primary mouse macrophages to identify family members that are either enriched in macrophages compared to a panel of other cell types, or are regulated by an inflammatory stimulus, the bacterial product lipopolysaccharide (LPS).
Results: Several members of the P2RY family had striking expression patterns in macrophages; P2ry6 mRNA was essentially expressed in a macrophage-specific fashion, whilst P2ry1 and P2ry5 mRNA levels were strongly down-regulated by LPS. Expression of several other GPCRs was either restricted to macrophages (e.g. Gpr84) or to both macrophages and neural tissues (e.g. P2ry12, Gpr85). The GPCR repertoire expressed by bone marrow-derived macrophages and thioglycollate-elicited peritoneal macrophages had some commonality, but there were also several GPCRs preferentially expressed by either cell population.
Conclusion: The constitutive or regulated expression in macrophages of several GPCRs identified in this study has not previously been described. Future studies on such GPCRs and their agonists are likely to provide important insights into macrophage biology, as well as novel inflammatory pathways that could be future targets for drug discovery.
Figures
Figure 1
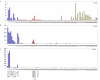
Macrophage-restricted GPCRs. Micro-array analysis of Gpr85 (A), P2ry6 (B) and Gpr84 (C) mRNA expression across a panel of 91 murine cell types and tissues. Data points show normalised values and similar cell types are grouped according to bar colour; blue indicates primary macrophage cell types, purple indicates bone-related cell types, red indicates other immune cell types, green indicates stem cell populations, orange indicates whole tissue samples, yellow indicates neuronal and retinal cell types and pink indicates cell lines. Additional file 3 gives details of the 91 cell types and tissues profiled.
Figure 2
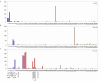
GPCRs differentially regulated in BMM and TEPM. Micro-array analysis of Calcrl (A), Gprc5b (B) and P2ry14 (C) mRNA expression across a panel of 91 murine cell types and tissues. Data points show normalised values and similar cell types are grouped according to bar colour; blue indicates primary macrophage cell types, purple indicates bone-related cell types, red indicates other immune cell types, green indicates stem cell populations, orange indicates whole tissue samples, yellow indicates neuronal and retinal cell types and pink indicates cell lines. Additional file 3 gives details of the 91 cell types and tissues profiled.
Figure 3
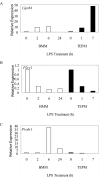
GPCRs regulated by LPS in macrophages. Micro-array expression analysis of Gpr84 (A), P2ry1 (B) and Prokr1 (C) mRNA in BMM and TEPM over a timecourse of 0, 2, 6, and 24 h, and 0, 1 and 7 h, respectively. Data points show gene expression relative to untreated control for each cell population (0 h).
Similar articles
- An mRNA atlas of G protein-coupled receptor expression during primary human monocyte/macrophage differentiation and lipopolysaccharide-mediated activation identifies targetable candidate regulators of inflammation.
Hohenhaus DM, Schaale K, Le Cao KA, Seow V, Iyer A, Fairlie DP, Sweet MJ. Hohenhaus DM, et al. Immunobiology. 2013 Nov;218(11):1345-53. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2013.07.001. Epub 2013 Jul 15. Immunobiology. 2013. PMID: 23948647 - Inducible expression of murine IP-10 mRNA varies with the state of macrophage inflammatory activity.
Narumi S, Hamilton TA. Narumi S, et al. J Immunol. 1991 May 1;146(9):3038-44. J Immunol. 1991. PMID: 1901891 - P2 receptors mRNA expression profiles in macrophages from ankylosing spondylitis patients and healthy individuals.
Akhtari M, Zargar SJ, Vojdanian M, Ashraf-Ganjouei A, Javinani A, Hamzeh E, Rezaiemanesh A, Jamshidi A, Mahmoudi M. Akhtari M, et al. Int J Rheum Dis. 2020 Mar;23(3):350-357. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.13783. Epub 2019 Dec 29. Int J Rheum Dis. 2020. PMID: 31884692 - Emerging Roles for G-protein Coupled Receptors in Development and Activation of Macrophages.
Wang X, Iyer A, Lyons AB, Körner H, Wei W. Wang X, et al. Front Immunol. 2019 Aug 27;10:2031. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02031. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31507616 Free PMC article. Review. - G-protein-coupled receptor expression, function, and signaling in macrophages.
Lattin J, Zidar DA, Schroder K, Kellie S, Hume DA, Sweet MJ. Lattin J, et al. J Leukoc Biol. 2007 Jul;82(1):16-32. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0107051. Epub 2007 Apr 24. J Leukoc Biol. 2007. PMID: 17456803 Review.
Cited by
- p53 Is a Host Cell Regulator during Herpes Simplex Encephalitis.
Maruzuru Y, Koyanagi N, Takemura N, Uematsu S, Matsubara D, Suzuki Y, Arii J, Kato A, Kawaguchi Y. Maruzuru Y, et al. J Virol. 2016 Jul 11;90(15):6738-6745. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00846-16. Print 2016 Aug 1. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 27170756 Free PMC article. - A gene expression atlas of the domestic pig.
Freeman TC, Ivens A, Baillie JK, Beraldi D, Barnett MW, Dorward D, Downing A, Fairbairn L, Kapetanovic R, Raza S, Tomoiu A, Alberio R, Wu C, Su AI, Summers KM, Tuggle CK, Archibald AL, Hume DA. Freeman TC, et al. BMC Biol. 2012 Nov 15;10:90. doi: 10.1186/1741-7007-10-90. BMC Biol. 2012. PMID: 23153189 Free PMC article. - Gpcpd1-GPC metabolic pathway is dysfunctional in aging and its deficiency severely perturbs glucose metabolism.
Cikes D, Leutner M, Cronin SJF, Novatchkova M, Pfleger L, Klepochová R, Lair B, Lac M, Bergoglio C, Viguerie N, Dürnberger G, Roitinger E, Grivej M, Rullman E, Gustafsson T, Hagelkruys A, Tavernier G, Bourlier V, Knauf C, Krebs M, Kautzky-Willer A, Moro C, Krssak M, Orthofer M, Penninger JM. Cikes D, et al. Nat Aging. 2024 Jan;4(1):80-94. doi: 10.1038/s43587-023-00551-6. Epub 2024 Jan 18. Nat Aging. 2024. PMID: 38238601 - Insm1 regulates mTEC development and immune tolerance.
Tao W, Ye Z, Wei Y, Wang J, Yang W, Yu G, Xiong J, Jia S. Tao W, et al. Cell Mol Immunol. 2023 Dec;20(12):1472-1486. doi: 10.1038/s41423-023-01102-0. Epub 2023 Nov 21. Cell Mol Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37990032 Free PMC article. - Genomic Analysis of Gastrointestinal Parasite Resistance in Akkaraman Sheep.
Arzik Y, Kizilaslan M, White SN, Piel LMW, Çınar MU. Arzik Y, et al. Genes (Basel). 2022 Nov 22;13(12):2177. doi: 10.3390/genes13122177. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36553445 Free PMC article.
References
- McKnight AJ, Macfarlane AJ, Dri P, Turley L, Willis AC, Gordon S. Molecular cloning of F4/80, a murine macrophage-restricted cell surface glycoprotein with homology to the G-protein-linked transmembrane 7 hormone receptor family. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:486–489. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.1.486. - DOI - PubMed
- Genomics Institute of the Novartis Research Foundation SA. Genomics Institute of the Novartis Research Foundation, [http://symatlas.gnf.org/SymAtlas]
- NCBIs Gene Expression Omnibus NCBIs Gene Expression Omnibus, [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/]
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases