Multiple Nod-like receptors activate caspase 1 during Listeria monocytogenes infection - PubMed (original) (raw)
Multiple Nod-like receptors activate caspase 1 during Listeria monocytogenes infection
Sarah E Warren et al. J Immunol. 2008.
Abstract
Listeria monocytogenes escapes from the phagosome of macrophages and replicates within the cytosolic compartment. The macrophage responds to L. monocytogenes through detection pathways located on the cell surface (TLRs) and within the cytosol (Nod-like receptors) to promote inflammatory processes aimed at clearing the pathogen. Cytosolic L. monocytogenes activates caspase 1, resulting in post-translational processing of the cytokines IL-1beta and IL-18 as well as caspase 1-dependent cell death (pyroptosis). We demonstrate that the presence of L. monocytogenes within the cytosolic compartment induces caspase 1 activation through multiple Nod-like receptors, including Ipaf and Nalp3. Flagellin expression by cytosolic L. monocytogenes was detected through Ipaf in a dose-dependent manner. Concordantly, detection of flagellin promoted bacterial clearance in a murine infection model. Finally, we provide evidence that suggests cytosolic L. monocytogenes activates caspase 1 through a third pathway, which signals through the adaptor protein ASC. Thus, L. monocytogenes activates caspase 1 in macrophages via multiple pathways, all of which detect the presence of bacteria within the cytosol.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures
The authors have no financial conflict of interest.
Figures
FIGURE 1
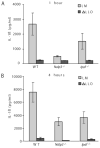
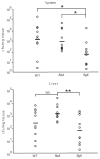
Cytosolic Listeria monocytogenes in macrophages induces IL-1_β_ secretion, which is partially dependent upon the NLRs Nalp3 and Ipaf. WT, Nalp3−/−, or Ipaf−/− BMM were stimulated with LPS to induce proIL-1_β_ expression before infection with WT or LLO-deficient L. monocytogenes (MOI 6). IL-1_β_ secretion was assessed by ELISA as a measure of caspase 1 activation at (A) 1 h or (B) 4 h post infection. Error bars, SD. Representative of three independent experiments.
FIGURE 2
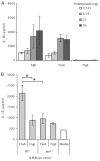
Ipaf is activated in response to cytosolic L. monocytogenes flagellin. A, LPS stimulated macrophages were transfected with purified flagellin from S. typhimurium (FljB) or L. monocytogenes (FlaA) or hook protein (FlgE) (negative control). IL-1_β_ secretion was assessed after 1 h by ELISA. B, LPS stimulated WT or Ipaf_−/− BMM were transfected with 31 ng of either FlaA or FlgE and IL-1_β secretion was assessed after 2 h. Representative of three independent experiments.*, p < 0.05.
FIGURE 3
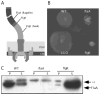
flgK L. monocytogenes are amotile and secrete increased amounts of flagellin into the environment. A, Schematic of the structure of L. monocytogenes flagella. CM, Cell membrane; and PGN, peptidoglycan. B, Motility plate demonstrating that WT and LLO L. monocytogenes are motile but flaA and flgK L. monocytogenes are not. C, Proteins were precipitated from bacterial pellets and supernatants and run on western blot to assess flagellin expression and secretion. P, Pellet (bacteria associated); and S, supernatant (secreted). **, Nonspecific band.
FIGURE 4
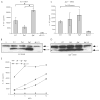
Flagellin-dependent variation in caspase 1 processing in L. monocytogenes_-infected macrophages is dependent on Ipaf. A, LPS-primed WT macrophages were infected with WT, flaA, flgK, or ΔLLO L. monocytogenes at MOI 6. IL-1_β secretion from supernatants was assessed 4 h post infection. *, p < 0.05. B, WT macrophages were infected at MOI 6 for 4 h then proteins precipitated from supernatants and combined with cell lysates. Samples were Western blotted then probed for the p10 fragment of caspase 1. U, Uninfected; and **, nonspecific band. L. monocytogenes infected Ipaf_−/− macrophages were analyzed for (C) IL-1_β secretion and (D) caspase 1 processing as in A and B above. Error bars, SD. Representative of three experiments. E, LPS-primed WT macrophages were infected with WT, flaA, flgK, or ΔLLO L. monocytogenes at MOI 1, 3, 6, or 12. IL-1_β_ secretion from supernatants was assessed 4 h post infection.
FIGURE 5
Detection of flagellin enhances bacterial clearance. C57BL/6 mice were injected with 104 L. monocytogenes i.v. Five days later, bacterial clearance was assessed by plating organ homogenates and counting CFUs. Geometric mean of 10 mice per strain is shown (−).*, p < 0.05 and **, p < 0.01. NS, Not significant. Ten mice per cohort.
FIGURE 6
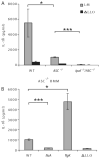
Ipaf signaling and flagellin detection is independent of ASC. Macrophages were infected with L. monocytogenes strains (MOI 6) for 4 h before IL-1_β_ secretion was determined by ELISA. A) WT, _ASC_−/−, or Ipaf_−/−/ASC_−/− macrophages infected with WT or ΔLLO mutant L. monocytogenes B) _ASC_−/− macrophages infected with WT, flaA, flgK, or ΔLLO L. monocytogenes. Error bars, s.d. Representative of three experiments. *p = 0.05; ***p < 0.001.
FIGURE 7
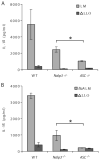
A third receptor activates inflammasome following L. monocytogenes infection. Macrophages were infected with L. monocytogenes strains (MOI 6) and IL-1_β_ secretion determined after four hours. A) WT, _Nalp3_−/−, and _ASC_−/− macrophages infected with WT or ΔLLO mutant L. monocytogenes. B) WT, _Nalp3_−/−, and _ASC_−/− macrophages were infected with either flaA or ΔLLO mutant L. monocytogenes. Error bars, s.d. Representative of three experiments. *p = 0.05.
Similar articles
- Involvement of the AIM2, NLRC4, and NLRP3 inflammasomes in caspase-1 activation by Listeria monocytogenes.
Wu J, Fernandes-Alnemri T, Alnemri ES. Wu J, et al. J Clin Immunol. 2010 Sep;30(5):693-702. doi: 10.1007/s10875-010-9425-2. Epub 2010 May 20. J Clin Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20490635 Free PMC article. - Involvement of absent in melanoma 2 in inflammasome activation in macrophages infected with Listeria monocytogenes.
Tsuchiya K, Hara H, Kawamura I, Nomura T, Yamamoto T, Daim S, Dewamitta SR, Shen Y, Fang R, Mitsuyama M. Tsuchiya K, et al. J Immunol. 2010 Jul 15;185(2):1186-95. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1001058. Epub 2010 Jun 21. J Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20566831 - Asc and Ipaf Inflammasomes direct distinct pathways for caspase-1 activation in response to Legionella pneumophila.
Case CL, Shin S, Roy CR. Case CL, et al. Infect Immun. 2009 May;77(5):1981-91. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01382-08. Epub 2009 Feb 23. Infect Immun. 2009. PMID: 19237518 Free PMC article. - Inflammasomes: guardians of cytosolic sanctity.
Lamkanfi M, Dixit VM. Lamkanfi M, et al. Immunol Rev. 2009 Jan;227(1):95-105. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2008.00730.x. Immunol Rev. 2009. PMID: 19120479 Review. - The inflammasome: a caspase-1-activation platform that regulates immune responses and disease pathogenesis.
Franchi L, Eigenbrod T, Muñoz-Planillo R, Nuñez G. Franchi L, et al. Nat Immunol. 2009 Mar;10(3):241-7. doi: 10.1038/ni.1703. Nat Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19221555 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Inflammasome-dependent pyroptosis and IL-18 protect against Burkholderia pseudomallei lung infection while IL-1β is deleterious.
Ceballos-Olvera I, Sahoo M, Miller MA, Del Barrio L, Re F. Ceballos-Olvera I, et al. PLoS Pathog. 2011 Dec;7(12):e1002452. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002452. Epub 2011 Dec 29. PLoS Pathog. 2011. PMID: 22241982 Free PMC article. - Resveratrol inhibits inflammation induced by heat-killed Listeria monocytogenes.
Park DW, Kim JS, Chin BR, Baek SH. Park DW, et al. J Med Food. 2012 Sep;15(9):788-94. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2012.2194. Epub 2012 Aug 2. J Med Food. 2012. PMID: 22857612 Free PMC article. - A Yersinia effector protein promotes virulence by preventing inflammasome recognition of the type III secretion system.
Brodsky IE, Palm NW, Sadanand S, Ryndak MB, Sutterwala FS, Flavell RA, Bliska JB, Medzhitov R. Brodsky IE, et al. Cell Host Microbe. 2010 May 20;7(5):376-87. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2010.04.009. Cell Host Microbe. 2010. PMID: 20478539 Free PMC article. - Innate immune detection of the type III secretion apparatus through the NLRC4 inflammasome.
Miao EA, Mao DP, Yudkovsky N, Bonneau R, Lorang CG, Warren SE, Leaf IA, Aderem A. Miao EA, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Feb 16;107(7):3076-80. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0913087107. Epub 2010 Feb 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20133635 Free PMC article.
References
- Kawai T, Akira S. TLR signaling. Cell Death Differ. 2006;13:816–825. - PubMed
- Franchi L, Park JH, Shaw MH, Marina-Garcia N, Chen G, Kim YG, Nunez G. Intracellular NOD-like receptors in innate immunity, infection and disease. Cell Microbiol. 2008;10:1–8. - PubMed
- Takeuchi O, Akira S. Recognition of viruses by innate immunity. Immunol Rev. 2007;220:214–224. - PubMed
- Seveau S, Pizarro-Cerda J, Cossart P. Molecular mechanisms exploited by Listeria monocytogenes during host cell invasion. Microbes Infect. 2007;9:1167–1175. - PubMed
- Schnupf P, Portnoy DA. Listeriolysin O: a phagosome-specific lysin. Microbes Infect. 2007;9:1176–1187. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AI032972/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI025032/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K08 AI065878-04/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI025032-19/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI025032-24/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K08 AI065878/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI052286/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI032972-15/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI065878/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI032972/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI052286-10/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI052286/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI032972-20/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI025032/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA009537/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32CA009537/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI025032/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 56005710/HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous