Elevated levels of pro-apoptotic p53 and its oxidative modification by the lipid peroxidation product, HNE, in brain from subjects with amnestic mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease - PubMed (original) (raw)
Elevated levels of pro-apoptotic p53 and its oxidative modification by the lipid peroxidation product, HNE, in brain from subjects with amnestic mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease
Giovanna Cenini et al. J Cell Mol Med. 2008 Jun.
Abstract
Oxidative stress has been implicated in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Both AD and arguably its earlier form, mild cognitive impairment (MCI), have elevated membrane oxidative damage in brain. The tumor suppressor and transcription factor p53 plays a pivotal function in neuronal apoptosis triggered by oxidative stress. Apoptosis contributes to neuronal death in many neurological disorders, including AD. In this study, we investigated p53 expression in a specific region of the cerebral cortex, namely the inferior parietal lobule (IPL), in MCI and AD brain, to test the hypothesis that alterations of this pro-apoptotic protein may be involved in neuronal death in the progression of AD. By immunoprecipitation assay, we also investigated whether 4-hydroxy-2-transnonenal (HNE), an aldehydic product of lipid peroxidation, was bound in excess to p53 in IPL from subjects with MCI and AD compared to control. Overall, the data provide evidence that p53 is involved in the neuronal death in both MCI and AD, suggesting that the observed alterations are early events in the progression of AD. In addition, HNE may be a novel non-protein mediator of oxidative stress-induced neuronal apoptosis.
Figures
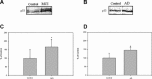
1
(A) and (B) represent blots of the levels of p53 in the IPL from MCI, AD and control, respectively.(C) and (D) represent densitometric analysis of (A) and (B), respectively. Equal amounts of protein (75 mg/lane) were electrophoresed using SDS-PAGE. Proteins were transferred to nitrocellulose membranes and probed with the primary anti-p53 antibody. (A) is a representative blot of data obtained from seven control and MCI samples, and (B) is a representative blot of data obtained from five control and AD samples, respectively. The control value was set to 100%, to which experimental values were compared.*P < 0.04;AD, #P < 0.015.
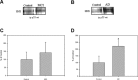
2
(A) and (B) represent blots of p53-HNE adduction studied from MCI, AD and control, respectively.(C) and (D) represent densitometric analysis of (A) and (B), respectively. Equal amount of protein (150 mg/lane) were immunoprecipitated by anti-p53 antibody, and immunoprecipitates were analyzed for HNE immunoreactivity by Western blotting.(A) is a representative blot of data obtained from seven control and MCI samples, and (B) is representative blot of data obtained from five control and AD samples, respectively. The control value was set to 100%, to which experimental values were compared. AD, #P < 0.004.
Similar articles
- Effects of oxidative and nitrosative stress in brain on p53 proapoptotic protein in amnestic mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer disease.
Cenini G, Sultana R, Memo M, Butterfield DA. Cenini G, et al. Free Radic Biol Med. 2008 Jul 1;45(1):81-5. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2008.03.015. Epub 2008 Apr 8. Free Radic Biol Med. 2008. PMID: 18439434 Free PMC article. - Loss of phospholipid asymmetry and elevated brain apoptotic protein levels in subjects with amnestic mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer disease.
Bader Lange ML, Cenini G, Piroddi M, Abdul HM, Sultana R, Galli F, Memo M, Butterfield DA. Bader Lange ML, et al. Neurobiol Dis. 2008 Mar;29(3):456-64. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2007.11.004. Epub 2007 Nov 12. Neurobiol Dis. 2008. PMID: 18077176 Free PMC article. - Elevated levels of 3-nitrotyrosine in brain from subjects with amnestic mild cognitive impairment: implications for the role of nitration in the progression of Alzheimer's disease.
Butterfield DA, Reed TT, Perluigi M, De Marco C, Coccia R, Keller JN, Markesbery WR, Sultana R. Butterfield DA, et al. Brain Res. 2007 May 7;1148:243-8. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2007.02.084. Epub 2007 Mar 7. Brain Res. 2007. PMID: 17395167 Free PMC article. - Oxidative damage in mild cognitive impairment and early Alzheimer's disease.
Lovell MA, Markesbery WR. Lovell MA, et al. J Neurosci Res. 2007 Nov 1;85(14):3036-40. doi: 10.1002/jnr.21346. J Neurosci Res. 2007. PMID: 17510979 Review. - Role of by-products of lipid oxidation in Alzheimer's disease brain: a focus on acrolein.
Singh M, Dang TN, Arseneault M, Ramassamy C. Singh M, et al. J Alzheimers Dis. 2010;21(3):741-56. doi: 10.3233/JAD-2010-100405. J Alzheimers Dis. 2010. PMID: 20634576 Review.
Cited by
- PQM130, a Novel Feruloyl-Donepezil Hybrid Compound, Effectively Ameliorates the Cognitive Impairments and Pathology in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease.
Morroni F, Sita G, Graziosi A, Ravegnini G, Molteni R, Paladini MS, Dias KST, Dos Santos AF, Viegas C Jr, Camps I, Pruccoli L, Tarozzi A, Hrelia P. Morroni F, et al. Front Pharmacol. 2019 Jun 12;10:658. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00658. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31244664 Free PMC article. - Caspase-dependent degradation of MDMx/MDM4 cell cycle regulatory protein in amyloid β-induced neuronal damage.
Colacurcio DJ, Zyskind JW, Jordan-Sciutto KL, Espinoza CA. Colacurcio DJ, et al. Neurosci Lett. 2015 Nov 16;609:182-8. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2015.10.031. Epub 2015 Oct 22. Neurosci Lett. 2015. PMID: 26477779 Free PMC article. - Effects of Smoking on Regional Homogeneity in Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Resting-State Functional MRI Study.
Zhang T, Luo X, Zeng Q, Fu Y, Li Z, Li K, Liu X, Huang P, Chen Y, Zhang M, Liu Z; Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI). Zhang T, et al. Front Aging Neurosci. 2020 Nov 19;12:572732. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2020.572732. eCollection 2020. Front Aging Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 33328955 Free PMC article. - Ferroptosis: A Regulated Cell Death Nexus Linking Metabolism, Redox Biology, and Disease.
Stockwell BR, Friedmann Angeli JP, Bayir H, Bush AI, Conrad M, Dixon SJ, Fulda S, Gascón S, Hatzios SK, Kagan VE, Noel K, Jiang X, Linkermann A, Murphy ME, Overholtzer M, Oyagi A, Pagnussat GC, Park J, Ran Q, Rosenfeld CS, Salnikow K, Tang D, Torti FM, Torti SV, Toyokuni S, Woerpel KA, Zhang DD. Stockwell BR, et al. Cell. 2017 Oct 5;171(2):273-285. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.09.021. Cell. 2017. PMID: 28985560 Free PMC article. Review. - Dynamic Interplay between Copper Toxicity and Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Alzheimer's Disease.
Tassone G, Kola A, Valensin D, Pozzi C. Tassone G, et al. Life (Basel). 2021 Apr 24;11(5):386. doi: 10.3390/life11050386. Life (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33923275 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Katzman R, Saitoh T. Advances in Alzheimer's disease. FASEB J. 1991;5:278–86. - PubMed
- Khachaturian ZS. Diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease. Arch Neurol. 1985;42:1097–105. - PubMed
- Barcikowska M, Wisniewski HM, Bancher C, Grundke-Iqbal I. About the presence of paired helical filaments in dystrophic neurites participating in the plaque formation. Acta Neuropathol. 1989;78:225–31. - PubMed
- Terry RD, Hansen LA, DeTeresa R, Davies P, Tobias H, Katzman R. Senile dementia of the Alzheimer type without neocortical neurofibrillary tangles. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1987;46:262–8. - PubMed
- Mattson MP. Apoptosis in neurodegenerative disorders. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2000;1:120–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous