Integrins in angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Integrins in angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis
Christie J Avraamides et al. Nat Rev Cancer. 2008 Aug.
Abstract
Blood vessels promote tumour growth, and both blood and lymphatic vessels facilitate tumour metastasis by serving as conduits for the transport of tumour cells to new sites. Angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis are regulated by integrins, which are members of a family of cell surface receptors whose ligands are extracellular matrix proteins and immunoglobulin superfamily molecules. Select integrins promote endothelial cell migration and survival during angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis, whereas other integrins promote pro-angiogenic macrophage trafficking to tumours. Several integrin-targeted therapeutic agents are currently in clinical trials for cancer therapy. Here, we review the evidence implicating integrins as a family of fundamental regulators of angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis.
Figures
FIG. Box 1
FIG. Box 2
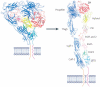
Figure 1. Mechanisms regulating angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis
(A) Tumor cells near pre-existing blood vessels secrete growth factors and chemokines such as VEGF-A, bFGF, and TNFα that stimulate quiescent vascular endothelium to enter the cell cycle. Tumors also secrete factors such as VEGF-C, VEGF-A or HGF that stimulate the growth of new lymphatic vessels in the peritumoral space. (B) These growth factors activate or upregulate expression of integrins such as α1β1, α2β1, α4β1, α5β1 and αvβ3 on blood vessels and α4β1, α9β1, α2β1 and α1β1 on lymphatic vessels. Tumor derived VEGF-C also promotes new lymphatic vessel growth in draining lymph nodes. (C) These integrins then promote endothelial cell migration and survival during invasion of tumor tissue, resulting in the creation of new vessels sprouts. The new blood vessels promote tumor growth by removing waste products and providing nutrients. These new blood and lymphatic vessels also provide an avenue for tumor metastasis. (D) Lymphangiogenesis promotes metastasis to lymph nodes and, sometimes, more distant tissues such as lung, while angiogenesis promotes metastasis to local and distant sites, such as lung.
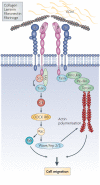
Figure 2. Myeloid cells promote angiogenesis
Myeloid precursor cells adhere to angiogenic endothelium via activated α4β1 or β2 integrins. A variety of tumor or stromal derived factors, including stromal derived factor 1 (SDF-1), colony stimulating factors (CSF), and others mobilize myeloid cells and activate integrins, promoting extravasation into the tumor environment. In the presence of other cytokines and growth factors, these cells differentiate into macrophages, which support tumor growth by expressing VEGF, other pro-angiogenic factors and proteases.
Similar articles
- Integrins in tumor angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis.
Foubert P, Varner JA. Foubert P, et al. Methods Mol Biol. 2012;757:471-86. doi: 10.1007/978-1-61779-166-6_27. Methods Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 21909928 Free PMC article. - New insights into the role of co-receptor neuropilins in tumour angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis and targeted therapy strategies.
Zhao L, Chen H, Lu L, Wang L, Zhang X, Guo X. Zhao L, et al. J Drug Target. 2021 Feb;29(2):155-167. doi: 10.1080/1061186X.2020.1815210. Epub 2020 Sep 3. J Drug Target. 2021. PMID: 32838575 Review. - Roles of integrins in tumor angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis.
Garmy-Susini B, Varner JA. Garmy-Susini B, et al. Lymphat Res Biol. 2008;6(3-4):155-63. doi: 10.1089/lrb.2008.1011. Lymphat Res Biol. 2008. PMID: 19093788 Free PMC article. Review. - Endothelial cell integrins and COX-2: mediators and therapeutic targets of tumor angiogenesis.
Rüegg C, Dormond O, Mariotti A. Rüegg C, et al. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004 Mar 4;1654(1):51-67. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2003.09.003. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004. PMID: 14984767 Review. - Angiopoietin-2: development of inhibitors for cancer therapy.
Hu B, Cheng SY. Hu B, et al. Curr Oncol Rep. 2009 Mar;11(2):111-6. doi: 10.1007/s11912-009-0017-3. Curr Oncol Rep. 2009. PMID: 19216842 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Assessing the carcinogenic potential of low-dose exposures to chemical mixtures in the environment: focus on the cancer hallmark of tumor angiogenesis.
Hu Z, Brooks SA, Dormoy V, Hsu CW, Hsu HY, Lin LT, Massfelder T, Rathmell WK, Xia M, Al-Mulla F, Al-Temaimi R, Amedei A, Brown DG, Prudhomme KR, Colacci A, Hamid RA, Mondello C, Raju J, Ryan EP, Woodrick J, Scovassi AI, Singh N, Vaccari M, Roy R, Forte S, Memeo L, Salem HK, Lowe L, Jensen L, Bisson WH, Kleinstreuer N. Hu Z, et al. Carcinogenesis. 2015 Jun;36 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S184-202. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgv036. Carcinogenesis. 2015. PMID: 26106137 Free PMC article. Review. - Imaging key biomarkers of tumor angiogenesis.
Backer MV, Backer JM. Backer MV, et al. Theranostics. 2012;2(5):502-15. doi: 10.7150/thno.3623. Epub 2012 May 17. Theranostics. 2012. PMID: 22737188 Free PMC article. - Developing an Injectable Nanofibrous Extracellular Matrix Hydrogel With an Integrin αvβ3 Ligand to Improve Endothelial Cell Survival, Engraftment and Vascularization.
Hao D, Liu R, Gao K, He C, He S, Zhao C, Sun G, Farmer DL, Panitch A, Lam KS, Wang A. Hao D, et al. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020 Jul 29;8:890. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2020.00890. eCollection 2020. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32850742 Free PMC article. - Age-related macular degeneration: current treatment and future options.
Moutray T, Chakravarthy U. Moutray T, et al. Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2011 Sep;2(5):325-31. doi: 10.1177/2040622311415895. Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2011. PMID: 23251758 Free PMC article. - The αvβ6 integrin in cancer cell-derived small extracellular vesicles enhances angiogenesis.
Krishn SR, Salem I, Quaglia F, Naranjo NM, Agarwal E, Liu Q, Sarker S, Kopenhaver J, McCue PA, Weinreb PH, Violette SM, Altieri DC, Languino LR. Krishn SR, et al. J Extracell Vesicles. 2020 May 20;9(1):1763594. doi: 10.1080/20013078.2020.1763594. eCollection 2020. J Extracell Vesicles. 2020. PMID: 32595914 Free PMC article.
References
- Carmeliet P. Angiogenesis in life, disease and medicine. Nature. 2005;42:932–936. - PubMed
- Adams RH, Alitalo K. Molecular regulation of angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007;8:464–478. - PubMed
- Lyden D, et al. Impaired recruitment of bone-marrow-derived endothelial and hematopoietic precursor cells blocks tumor angiogenesis and growth. Nat. Med. 2001;11:1194–1201.This article established the concept that bone marrow derived cells in lung and other tissues could help create an environment that attracts metastatic tumor cells.
- Lin EY, Pollard JW. Tumor-associated macrophages press the angiogenic switch in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2007;67:5064–5066.This article shows that macrophages play critical roles in altering the fate of tumors by secreting pro-angiogenic growth factors.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources