Concomitant inhibition of Mdm2-p53 interaction and Aurora kinases activates the p53-dependent postmitotic checkpoints and synergistically induces p53-mediated mitochondrial apoptosis along with reduced endoreduplication in acute myelogenous leukemia - PubMed (original) (raw)
Concomitant inhibition of Mdm2-p53 interaction and Aurora kinases activates the p53-dependent postmitotic checkpoints and synergistically induces p53-mediated mitochondrial apoptosis along with reduced endoreduplication in acute myelogenous leukemia
Kensuke Kojima et al. Blood. 2008.
Abstract
Aberrant expression of Aurora kinases and inactivation of wild-type p53 by Mdm2 overexpression are frequent molecular events in acute myelogenous leukemia (AML), and preclinical data for inhibition of Aurora kinases or Mdm2 are promising. However, it remains largely unknown whether the viability of cells exposed to Aurora kinase inhibitors depends on the p53 status. We investigated the interaction of Aurora kinases and p53 pathways after their simultaneous blockades using a small-molecule pan-Aurora kinase inhibitor, MK-0457, and a selective small-molecule antagonist of Mdm2, Nutlin-3. We found that MK-0457, which itself activates p53 signaling, acts synergistically with Nutlin-3 to induce apoptosis in wild-type p53 AML cell lines OCI-AML-3 and MOLM-13 but not in p53-null HL-60 cells. MK-0457 and Nutlin-3 showed synergism in inducing p53, conformational change of Bax and Deltapsi(m) loss, suggesting an involvement of p53-mediated mitochondrial apoptosis. Nutlin-3 constrained endoreduplication after Aurora inhibition via activation of a p53-dependent postmitotic checkpoint and p21 induction in pseudo-G1 cells. Our findings provide the molecular rationale for concomitant targeting of Aurora kinases and Mdm2 in AML where TP53 mutations are rare and downstream p53 signaling is mostly intact.
Figures
Figure 1
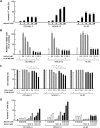
Inhibition of Aurora kinase activity induces endoreduplication in AML cells. (A) AML cells were treated for the indicated time with 10 nM MK-0457 or 2.5 μM Nutlin-3. MK-0457 induced time-dependent endoreduplication of the cells irrespective of the p53 status. Nutlin-3 caused G1-phase cell-cycle arrest only in wild-type p53 OCI-AML-3 and MOLM-13 cells. Results are representative of 3 independent experiments. (B) Expression of phosphorylated histone H3 in AML cells after 24 hours of treatment with 10 nM MK-0457. MK-0457 abrogated histone H3 phosphorylation on Ser. Results are representative of 3 independent experiments.
Figure 2
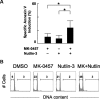
Inhibition of Aurora kinase activity enhances p53-dependent apoptosis in AML cells. (A) AML cells were incubated with the indicated concentrations of MK-0457 for 48 hours, and the annexin V–positive fractions were measured by flow cytometry. Data are mean plus or minus SD. A dose-response relationship ranging from 5 to 100 nM was seen in MOLM-13 cells, whereas the effect reached the maximum at 10 nM in OCI-AML-3 and HL-60 cells. (B) Effects of MK-0457 and Nutlin-3 on viable cell number. Cells were incubated with a range of concentrations of Nutlin-3 in the absence or presence of 10 nM MK-0457 for 48 hours, and the cell viability was determined by the trypan blue exclusion method. Results are expressed as the percentage of the viable cell number in an untreated group and represent the average of triplicate cultures. (C) MK-0457 enhanced Nutlin-induced cytotoxicity in wild-type p53 OCI-AML-3 and MOLM-13 cells. Cells were incubated with a range of concentrations of Nutlin-3 in the absence or presence of 10 nM MK-0457 for 48 hours, and the cell viability was determined by the trypan blue exclusion method. Data are mean plus or minus SD. (D) MK-0457 enhanced Nutlin-induced apoptosis in wild-type p53 OCI-AML-3 and MOLM-13 cells but not in mutant p53 HL-60 cells. Cells were incubated with the indicated concentrations of MK-0457 or Nutlin-3, and the annexin V–positive fractions were measured by flow cytometry at 24 hours. Data are mean plus or minus SD.
Figure 3
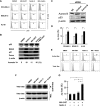
Aurora kinase inhibition induces p53 and enhances p53-mediated mitochondrial apoptosis. (A) Cells were treated for 12 hours with 10 nM MK-0457 and 2.5 μM Nutlin-3 (1 μM in MOLM-13 cells), either as individual agents or in combination. DMSO-treated cells served as control. (B) Expression of p53-related proteins in OCI-AML-3 cells, which were treated for 24 hours with 2.5 μM Nutlin-3 and 10 nM MK-0457, either as individual agents or in combination. MK-0457 as well as Nutlin-3 induced increased protein expression of Mdm2, p21, and a BH3-only member of the Bcl-2 family protein Puma in OCI-AML-3 cells. The intensity of the p53 signals was quantified by densitometry using ImageJ 1.38x software, and the relative intensity compared with β-actin was calculated. (C) Western blot analysis of OCI-AML-3 cells electroporated with either control or Aurora B siRNA. Twenty-four hours after siRNA electroporation, Aurora B, p53, and β-actin levels were determined. (D) AML cells were cultured for 12 hours in the absence (□) or presence (■) of 10 nM MK-0457. Δψm was assessed by flow cytometry. Data are mean plus or minus SD of triplicate measurements. Comparable results were obtained in 2 other independent experiments. *P ≤ .01. (E) MK-0457 and Nutlin-3 synergistically induce Bax conformational change. MOLM-13 cells were treated with 10 nM MK-0457 and 2.5 μM Nutlin-3 for 6 hours, either as individual agents or in combination, and Bax conformational change was determined by staining with the active conformation-specific anti-Bax antibody YTH-6A7 (shaded histogram) or a corresponding isotype control (open histogram). To block caspase activation-mediated conformational change of Bax, cells were preincubated for 1 hour with 50 μM Z-VAD-FMK. Results are representative of 3 independent experiments. (F) After 1 hour of preincubation with 50 μM Z-VAD-FMK, MOLM-13 cells were treated with 10 nM MK-0457 and 2.5 μM Nutlin-3 for 6 hours, either as individual agents or in combination. Active Bax was immunoprecipitated (IP) from total cell lysates with the conformation-specific antibody YTH-6A7. The amount of immunoprecipitated Bax and the levels of Bax and β-actin in whole-cell lysates (WCL) were determined by Western blot analysis. (G) MK-0457 and Nutlin-3 synergistically induce Δψm loss. MOLM-13 cells were cultured for 6 hours in the presence of DMSO, 10 nM MK-0457, 2.5 μM Nutlin-3, or a combination of MK-0457 and Nutlin-3. Δψm was assessed by flow cytometry. Data are mean plus or minus SD of triplicate measurements. Comparable results were obtained in 2 other independent experiments. *P ≤ .01.
Figure 4
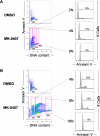
Cells with higher DNA content are resistant to MK-0457–induced apoptosis. MOLM-13 cells were treated with 10 nM MK-0457 for 36 hours (A) or 48 hours (B). The annexin V–positive fractions in correlation with DNA content were measured by flow cytometry. Data were gated on the FL2-area versus FL2-width cytogram to exclude doublets. DMSO-treated cells served as control. Results are representative of 3 independent experiments.
Figure 5
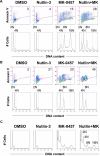
Nutlin-induced p53 blocks endoreduplication and enhances apoptosis in wild-type p53 AML cells treated with MK-0457. (A,B) OCI-AML-3 cells (A) or MOLM-13 cells (B) were treated for 48 hours with 2.5 μM Nutlin-3 and 10 nM of MK-0457, either as individual agents or in combination. Data were gated on the FL2-area versus FL2-width cytogram to exclude doublets. DMSO-treated cells served as control. Combination treatment results in reduced endoreduplication with increased percentage of annexin V–positive, apoptotic cell fraction. (C) HL-60 cells were treated for 48 hours with 2.5 μM Nutlin-3 and 10 nM MK-0457, either as individual agents or in combination. Nutlin-3 did not influence the degree of endoreduplication after MK-0457 treatment. Results are representative of 3 independent experiments.
Figure 6
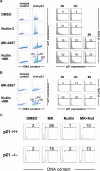
Nutlin-3 induces p21 in pseudo-G1 cells when combined with MK-0457. (A) OCI-AML-3 cells were treated for 24 hours with 2.5 μM Nutlin-3 and 10 nM MK-0457, either as individual agents or in combination. p21 expression levels and DNA content were measured by flow cytometry. Open histograms show staining with isotype controls. Data were gated on the FL2-area versus FL2-width cytogram to exclude doublets. Results are representative of 3 independent experiments. (B) After 48 hours of treatment, aberrant p21 expression was observed in cells with 8N as well as 4N DNA content. (C) Parental HCT116 cells (p21+/+) or p21-deficient HCT116 cells (p21−/−) were treated for 48 hours with 10 nM MK-0457 and 10 μM Nutlin-3, either as individual agents or in combination. Nutlin-3 caused G1-phase cell- cycle arrest and inhibited MK-0457-induced endoreduplication more prominently in p21+/+ cells than p21−/− cells. Results are representative of 3 independent experiments.
Figure 7
Nutlin-induced apoptosis is enhanced by combination with MK-0457 in primary AML cells. (A) Primary AML cells from 8 patients were incubated for 48 hours with 10 nM MK-0457 and 1 μM Nutlin-3, either as individual agents or in combination, and the annexin V–positive fractions were measured by flow cytometry. Data are mean plus or minus SD. *P ≤ .01. (B) Representative cell-cycle distribution patterns in primary AML cells after treatment. Cells were treated for 48 hours with 10 nM MK-0457 and 1 μM Nutlin-3, either as individual agents or in combination. Data were gated on the FL2-area versus FL2-width cytogram to exclude doublets. DMSO-treated cells served as control. MK-0457 did not induce significant increase in percentages of cells with more than or equal to 4N DNA content, whereas the MK-0457/Nutlin-3 combination treatment results in increased percentage of sub-G1 cells.
Similar articles
- Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase inhibition enhances nuclear proapoptotic function of p53 in acute myelogenous leukemia cells.
Kojima K, Konopleva M, Samudio IJ, Ruvolo V, Andreeff M. Kojima K, et al. Cancer Res. 2007 Apr 1;67(7):3210-9. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-2712. Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17409429 - Concomitant inhibition of MDM2 and Bcl-2 protein function synergistically induce mitochondrial apoptosis in AML.
Kojima K, Konopleva M, Samudio IJ, Schober WD, Bornmann WG, Andreeff M. Kojima K, et al. Cell Cycle. 2006 Dec;5(23):2778-86. doi: 10.4161/cc.5.23.3520. Epub 2006 Dec 1. Cell Cycle. 2006. PMID: 17172851 - The dual PI3 kinase/mTOR inhibitor PI-103 prevents p53 induction by Mdm2 inhibition but enhances p53-mediated mitochondrial apoptosis in p53 wild-type AML.
Kojima K, Shimanuki M, Shikami M, Samudio IJ, Ruvolo V, Corn P, Hanaoka N, Konopleva M, Andreeff M, Nakakuma H. Kojima K, et al. Leukemia. 2008 Sep;22(9):1728-36. doi: 10.1038/leu.2008.158. Epub 2008 Jun 12. Leukemia. 2008. PMID: 18548093 - Beyond BCL-2 Inhibition in Acute Myloid Leukemia: Other Approaches to Leverage the Apoptotic Pathway.
Maiti A, Carter BZ, Andreeff M, Konopleva MY. Maiti A, et al. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2022 Sep;22(9):652-658. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2022.04.001. Epub 2022 Apr 6. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2022. PMID: 35490155 Review. - The role of the MDM2/p53 axis in antitumor immune responses.
Brummer T, Zeiser R. Brummer T, et al. Blood. 2024 Jun 27;143(26):2701-2709. doi: 10.1182/blood.2023020731. Blood. 2024. PMID: 37467495 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Dynamin inhibitors induce caspase-mediated apoptosis following cytokinesis failure in human cancer cells and this is blocked by Bcl-2 overexpression.
Joshi S, Braithwaite AW, Robinson PJ, Chircop M. Joshi S, et al. Mol Cancer. 2011 Jun 28;10:78. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-10-78. Mol Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21708043 Free PMC article. - HDAC inhibition by SNDX-275 (Entinostat) restores expression of silenced leukemia-associated transcription factors Nur77 and Nor1 and of key pro-apoptotic proteins in AML.
Zhou L, Ruvolo VR, McQueen T, Chen W, Samudio IJ, Conneely O, Konopleva M, Andreeff M. Zhou L, et al. Leukemia. 2013 Jun;27(6):1358-68. doi: 10.1038/leu.2012.366. Epub 2012 Dec 18. Leukemia. 2013. PMID: 23247046 Free PMC article. - Simultaneous activation of p53 and inhibition of XIAP enhance the activation of apoptosis signaling pathways in AML.
Carter BZ, Mak DH, Schober WD, Koller E, Pinilla C, Vassilev LT, Reed JC, Andreeff M. Carter BZ, et al. Blood. 2010 Jan 14;115(2):306-14. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-03-212563. Epub 2009 Nov 6. Blood. 2010. PMID: 19897582 Free PMC article. - Inhibition of Bcl-xL overcomes polyploidy resistance and leads to apoptotic cell death in acute myeloid leukemia cells.
Zhou W, Xu J, Gelston E, Wu X, Zou Z, Wang B, Zeng Y, Wang H, Liu A, Xu L, Liu Q. Zhou W, et al. Oncotarget. 2015 Aug 28;6(25):21557-71. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.4306. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26188358 Free PMC article. - A phase I trial of the human double minute 2 inhibitor (MK-8242) in patients with refractory/recurrent acute myelogenous leukemia (AML).
Ravandi F, Gojo I, Patnaik MM, Minden MD, Kantarjian H, Johnson-Levonas AO, Fancourt C, Lam R, Jones MB, Knox CD, Rose S, Patel PS, Tibes R. Ravandi F, et al. Leuk Res. 2016 Sep;48:92-100. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2016.07.004. Epub 2016 Jul 25. Leuk Res. 2016. PMID: 27544076 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
- Carmena M, Earnshaw WC. The cellular geography of aurora kinases. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2003;4:842–854. - PubMed
- Marumoto T, Zhang D, Saya H. Aurora A: a guardian of poles. Nat Rev Cancer. 2005;5:42–50. - PubMed
- Murata-Hori M, Wang YL. The kinase activity of aurora B is required for kinetochore-microtubule interactions during mitosis. Curr Biol. 2002;12:894–899. - PubMed
- Yan X, Cao L, Li Q, et al. Aurora C is directly associated with Survivin and required for cytokinesis. Genes Cells. 2005;10:617–626. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- CA89346/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA016672/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA49639/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA16672/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA089346/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA55164/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA049639/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA055164/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous