Expression of a bacterial flagellin gene triggers plant immune responses and confers disease resistance in transgenic rice plants - PubMed (original) (raw)
Expression of a bacterial flagellin gene triggers plant immune responses and confers disease resistance in transgenic rice plants
Yoshimitsu Takakura et al. Mol Plant Pathol. 2008 Jul.
Abstract
Flagellin is a component of bacterial flagella and acts as a proteinaceous elicitor of defence responses in organisms. Flagellin from a phytopathogenic bacterium, Acidovorax avenae strain N1141, induces immune responses in suspension-cultured rice cells. To analyse the function of flagellin in rice, we fused the N1141 flagellin gene to the cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter and introduced it into rice. Many of the resulting transgenic rice plants accumulated flagellin at various levels. The transgenic rice developed pale spots in the leaves. The expression of a defence-related gene for phenylalanine ammonia-lyase was induced in the transgenic plants, and H(2)O(2) production and cell death were observed in some plants with high levels of gene expression, suggesting that the flagellin triggers immune responses in the transgenic rice. Transgenic plants inoculated with Magnaporthe grisea, the causal agent of rice blast, showed enhanced resistance to blast, suggesting that the flagellin production confers disease resistance in the transgenic rice.
Figures
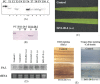
Figure 1
Analysis of flagellin production and the immune response. (A) Detection of N1141 flagellin production in transgenic rice. Thirty micrograms of soluble proteins from the leaves of the primary transgenic plants (T) and ‘Koshihikari’ (C) were subjected to immunoblot analysis . As a reference (positive control, PC), 30 ng of histidine‐tagged N1141 flagellin was used. Results: –, not detected; +, 0.015–0.05% of total soluble leaf proteins; ++, more than 0.05% of total soluble leaf proteins. (B) Localization of flagellin production. S, total soluble leaf protein fractions; IF, intercellular fluid fractions. (C) Chlorotic spots observed on the leaves of a transgenic plant that accumulated flagellin. (D) Northern blot analysis of the expression of the PAL gene. Ten micrograms of total RNA from leaves of primary transgenic plants was used for RNA blotting. (E) Detection of H2O2 (left) and cell death (right) in transgenic rice. H2O2 was detected as brown spots among the main veins of a leaf of the transgenic plant. Cell death was detected as blue spots along the veins of the leaves of transgenic plants. In panels C, D and E, a transgenic plant harbouring pSB24 was used as a control and parentheses indicate the level of flagellin production.
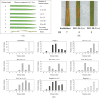
Figure 2
Analysis of resistance to M. grisea in transgenic rice. (A) An illustration of the disease indices used in this experiment. Disease indices were judged based on the number of disease lesions on the leaves. Disease index (1 to 10) in parentheses indicates small dark brownish lesions that are difficult to be judged as representing disease lesions. (B) Photographs of typical disease symptoms on the leaves of the transgenic rice 7 days following infection. DI, disease index. (C) The results of the inoculation test with M. grisea. The frequency distributions of the resulting DI values in various lines are shown. Asterisks (**) represent distributions of DI that differ significantly from that of ‘Koshihikari’ (Steel–Dwass test, P < 0.01). The distributions of DI values for plants that produced flagellin [Flagellin (+/++)] and those that did not [Flagellin (–)] are also shown. In B and C, parentheses indicate the level of flagellin production.
References
- Asai, T. , Tena, G. , Plotnikova, J. , Willmann, M.R. , Chiu, W.L. , Gomez‐Gomez, L. , Boller, T. , Ausubel, F.M. and Sheen, J. (2002) MAP kinase signalling cascade in Arabidopsis innate immunity. Nature, 415, 977–983. - PubMed
- Che, F.S. , Iwano, M. , Tanaka, N. , Takayama, S. , Minami, E. , Shibuya, N. , Kadota, I. and Isogai, A. (1999) Biochemical and morphological features of rice cell death induced by Pseudomonas avenae . Plant Cell Physiol. 40, 1036–1045.
- Che, F.S. , Nakajima, Y. , Tanaka, N. , Iwano, M. , Yoshida, T. , Takayama, S. , Kadota, I. and Isogai, A. (2000) Flagellin from an incompatible strain of Pseudomonas avenae induces a resistance response in cultured rice cells. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 32347–32356. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials