Preclinical evaluation of dasatinib, a potent Src kinase inhibitor, in melanoma cell lines - PubMed (original) (raw)
Preclinical evaluation of dasatinib, a potent Src kinase inhibitor, in melanoma cell lines
Alex J Eustace et al. J Transl Med. 2008.
Abstract
Background: Metastatic melanoma is a highly chemotherapy resistant tumour. The use of newer targeted therapies alone and in combination with chemotherapy may offer new hope of improving response to treatment. Dasatinib, a multi-target kinase inhibitor, is currently approved for the treatment of chronic myeloid leukaemia and has shown promising results in preclinical studies in a number of solid tumours.
Methods: We examined the effects of dasatinib on proliferation, chemo-sensitivity, cell cycle arrest, apoptosis, migration and invasion in human melanoma cell lines. Expression and activation of Src kinase, FAK and EphA2 were also examined in the melanoma cells.
Results: Dasatinib inhibited growth of three of the five melanoma cell lines. Comparison with sorafenib showed that in these three cell lines dasatinib inhibited growth at lower concentrations than sorafenib. Dasatinib in combination with the chemotherapy drug temozolomide showed greater efficacy than either drug alone. Dasatinib induced cell cycle arrest and apoptosis and significantly inhibited cell migration and invasion of melanoma cells. Dasatinib inhibition of proliferation was associated with reduced phosphorylation of Src kinase, while decreased phosphorylation of FAK was implicated in dasatinib-mediated inhibition of migration and invasion in melanoma cells.
Conclusion: Dasatinib has both anti-proliferative and anti-invasive effects in melanoma cells and combined with chemotherapy may have clinical benefit in the treatment of malignant melanoma.
Figures
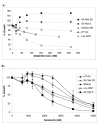
Figure 1
Percentage growth inhibition by A) dasatinib and B) sorafenib in a panel of melanoma cell lines. Error bars represent the standard deviation of triplicate experiments.
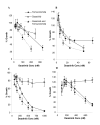
Figure 2
Combination assays testing dasatinib with temozolomide at the specified ratios in (A) HT144 (ratio 1:1500), (B) Lox-IMVI (ratio 1:3000), (C) Malme-3M (ratio 1:800) and (D) Sk-Mel-28 (ratio 1:800) cells. Concentrations of temozolomide are represented as a ratio of the dasatinib concentration. Error bars represent the standard deviation of triplicate experiments.
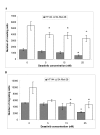
Figure 3
Measurement of dasatinib induced apoptosis in HT144, Lox-IMVI and Malme-3M using the TUNEL assay.
Figure 4
Effect of dasatinib on (A) invasion and (B) migration in HT144 and Sk-Mel-28 melanoma cell lines. Error bars represent the standard deviation of triplicate assays. '*' indicates p < 0.05.
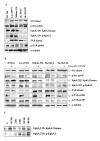
Figure 5
Western blotting for Src kinase, phospho-Src kinase py 418, FAK, phospho-FAK py 397 and py 861, immunoprecipitated (IP) EphA2, IP phospho-EphA2 and α-tubulin in (A) the panel of melanoma cell lines; and (B) HT144, Lox-IMVI, Malme-3M, Sk-Mel-5 and Sk-Mel-28 untreated (control) or treated with 100 nM dasatinib for 6 hours. (C) Western blotting for IP EphA2, IP phospho-EphA2 in Lox-IMVI untreated (control) and treated with 100 nM dasatinib for up to 48 hours.
Similar articles
- Inhibition of cell growth and up-regulation of MAD2 in human oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma after treatment with the Src/Abl inhibitor dasatinib.
Wang L, Guo B, Wang R, Jiang Y, Qin S, Liang S, Zhao Y, Guo W, Li K, Fan X. Wang L, et al. Clin Sci (Lond). 2012 Jan;122(1):13-24. doi: 10.1042/CS20110230. Clin Sci (Lond). 2012. PMID: 21751967 - Inhibition of Src family kinases with dasatinib blocks migration and invasion of human melanoma cells.
Buettner R, Mesa T, Vultur A, Lee F, Jove R. Buettner R, et al. Mol Cancer Res. 2008 Nov;6(11):1766-74. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-08-0169. Mol Cancer Res. 2008. PMID: 19010823 Free PMC article. - Inhibition of SRC family kinases and receptor tyrosine kinases by dasatinib: possible combinations in solid tumors.
Montero JC, Seoane S, Ocaña A, Pandiella A. Montero JC, et al. Clin Cancer Res. 2011 Sep 1;17(17):5546-52. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-2616. Epub 2011 Jun 13. Clin Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21670084 Review. - Dasatinib: a potent SRC inhibitor in clinical development for the treatment of solid tumors.
Araujo J, Logothetis C. Araujo J, et al. Cancer Treat Rev. 2010 Oct;36(6):492-500. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2010.02.015. Epub 2010 Mar 11. Cancer Treat Rev. 2010. PMID: 20226597 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Dasatinib inhibits primary melanoma cell proliferation through morphology-dependent disruption of Src-ERK signaling.
Wu J, Liao X, Yu B, Su B. Wu J, et al. Oncol Lett. 2013 Feb;5(2):527-532. doi: 10.3892/ol.2012.1066. Epub 2012 Dec 10. Oncol Lett. 2013. PMID: 23420605 Free PMC article. - Combined inhibition of PI3K and Src kinases demonstrates synergistic therapeutic efficacy in clear-cell renal carcinoma.
Roelants C, Giacosa S, Pillet C, Bussat R, Champelovier P, Bastien O, Guyon L, Arnoux V, Cochet C, Filhol O. Roelants C, et al. Oncotarget. 2018 Jul 10;9(53):30066-30078. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.25700. eCollection 2018 Jul 10. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 30046388 Free PMC article. - Targeting c-Met in triple negative breast cancer: preclinical studies using the c-Met inhibitor, Cpd A.
Breen L, Gaule PB, Canonici A, Walsh N, Collins DM, Cremona M, Hennessy BT, Duffy MJ, Crown J, Donovan NO, Eustace AJ. Breen L, et al. Invest New Drugs. 2020 Oct;38(5):1365-1372. doi: 10.1007/s10637-020-00937-y. Epub 2020 Apr 22. Invest New Drugs. 2020. PMID: 32318883 - Novel biomolecules in targeted cancer therapy: a new approach towards precision medicine.
Kannampuzha S, Murali R, Gopalakrishnan AV, Mukherjee AG, Wanjari UR, Namachivayam A, George A, Dey A, Vellingiri B. Kannampuzha S, et al. Med Oncol. 2023 Oct 7;40(11):323. doi: 10.1007/s12032-023-02168-6. Med Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37804361 Review. - Potential therapeutic targets of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in melanoma.
Pearlman RL, Montes de Oca MK, Pal HC, Afaq F. Pearlman RL, et al. Cancer Lett. 2017 Apr 10;391:125-140. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2017.01.029. Epub 2017 Jan 25. Cancer Lett. 2017. PMID: 28131904 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous