Acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor kinase inhibitors associated with a novel T854A mutation in a patient with EGFR-mutant lung adenocarcinoma - PubMed (original) (raw)
Case Reports
Acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor kinase inhibitors associated with a novel T854A mutation in a patient with EGFR-mutant lung adenocarcinoma
James Bean et al. Clin Cancer Res. 2008.
Abstract
Purpose: Somatic mutations in the tyrosine kinase domain of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) gene are associated with sensitivity of lung adenocarcinomas to the EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors, gefitinib and erlotinib. Acquired drug resistance is frequently associated with a secondary somatic mutation that leads to the substitution of methionine for threonine at position 790 (T790M). We aimed to identify additional second-site alterations associated with acquired resistance.
Experimental design: Tumor samples were obtained from 48 patients with acquired resistance. Tumor cell DNA was analyzed for EGFR kinase domain mutations. Molecular analyses were then done to characterize the biological properties of a novel mutant EGFR allele.
Results: A previously unreported mutation in exon 21 of EGFR, which leads to substitution of alanine for threonine at position 854 (T854A), was identified in one patient with a drug-sensitive EGFR L858R-mutant lung adenocarcinoma after long-term treatment with tyrosine kinase inhibitors. The T854A mutation was not detected in a pretreatment tumor sample. The crystal structure analyses of EGFR suggest that the T854 side chain is within contact distance of gefitinib and erlotinib. Surrogate kinase assays show that the EGFR T854A mutation abrogates the inhibition of tyrosine phosphorylation by erlotinib. Such resistance seems to be overcome by a new irreversible dual EGFR/HER2 inhibitor, BIBW 2992.
Conclusions: The T854A mutation is the second reported second-site acquired resistance mutation that is within contact distance of gefitinib and erlotinib. These data suggest that acquired resistance to ATP-mimetic EGFR kinase inhibitors may often be associated with amino acid substitutions that alter drug contact residues in the EGFR ATP-binding pocket.
Figures
Figure 1. Identification of a novel EGFR mutation in a patient with acquired resistance to EGFR inhibitors
Sequencing chromatograms showing presence of the EGFR T854A mutation along with the L858R mutation in pleural fluid cells collected from the index patient after prolonged treatment with gefitinib and erlotinib. Only the L858R mutation was detected in a pretreatment metastatic brain tumor specimen.
Figure 2. T854A mutation reduces inhibition of autophosphorylation of EGFR by erlotinib
Lysates from 293T cells transiently transfected with cDNAs encoding either EGFR WT, T854A, L858R, or L858R plus T854A and treated with different concentrations of erlotinib were immunoblotted for phospho-EGFR (Y1092), total EGFR, and Actin. T854A reduced the degree of inhibition of phospho-EGFR by erlotinib relative to WT or L858R EGFR. Actin is shown as a loading control.
Figure 3. T854A mutation is not analogous to other known kinase mutations and is located at a drug contact site
A) Alignment of the kinase domain of EGFR with other tyrosine kinases adapted from the Mutagrator Tool reveals no other identified mutations (highlighted in orange) at analogous residues. Overall the EGFR T854 position is not highly conserved among other kinases. B) Crystal structure of the L858R EGFR mutant bound to gefitinib (adapted from (18)) reveals the T854 residue is at the “bottom” of the ATP-binding site, on the C-lobe. Residues with known mutations associated with acquired resistance in patients are shown in red.
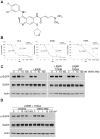
Figure 4. BIBW 2992 more potently inhibits both sensitive and resistant EGFR mutants, including T854A
A) Chemical structure of BIBW 2992. Adapted from (21). B) Cell growth inhibition assays of three EGFR mutant cell lines treated with various does of erlotinib (dashed line) or BIBW 2992 (solid line). PC-9 cells have a drug-sensitive exon 19 deletion in EGFR, H3255 cells have the drug-sensitive L858R mutation, and H1975 cells have both L858R and the T790M resistance mutation. All plots are relative to a DMSO-only control and error bars indicate one standard deviation from six replicates. All assays were performed three independent times and representative plots are shown. IC50 values were calculated using BioDataFit 1.02. C) Lysates from 293T cells transiently transfected with cDNAs encoding either EGFR WT, L858R, L858R plus T790M, or L858R plus T854A and treated with different concentrations of BIBW 2992 were immunoblotted for phospho-EGFR, total EGFR, and actin. Actin is shown as a loading control. D) Lysates from 293T cells transiently transfected with L858R plus T854A EGFR cDNA and treated with different concentrations of erlotinib or BIBW 2992 were immunoblotted for phospho-EGFR, total EGFR, and actin.
Similar articles
- Acquired resistance of lung adenocarcinomas to gefitinib or erlotinib is associated with a second mutation in the EGFR kinase domain.
Pao W, Miller VA, Politi KA, Riely GJ, Somwar R, Zakowski MF, Kris MG, Varmus H. Pao W, et al. PLoS Med. 2005 Mar;2(3):e73. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0020073. Epub 2005 Feb 22. PLoS Med. 2005. PMID: 15737014 Free PMC article. - Novel D761Y and common secondary T790M mutations in epidermal growth factor receptor-mutant lung adenocarcinomas with acquired resistance to kinase inhibitors.
Balak MN, Gong Y, Riely GJ, Somwar R, Li AR, Zakowski MF, Chiang A, Yang G, Ouerfelli O, Kris MG, Ladanyi M, Miller VA, Pao W. Balak MN, et al. Clin Cancer Res. 2006 Nov 1;12(21):6494-501. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-1570. Clin Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 17085664 - Acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in non-small-cell lung cancers dependent on the epidermal growth factor receptor pathway.
Nguyen KS, Kobayashi S, Costa DB. Nguyen KS, et al. Clin Lung Cancer. 2009 Jul;10(4):281-9. doi: 10.3816/CLC.2009.n.039. Clin Lung Cancer. 2009. PMID: 19632948 Free PMC article. Review. - MET amplification occurs with or without T790M mutations in EGFR mutant lung tumors with acquired resistance to gefitinib or erlotinib.
Bean J, Brennan C, Shih JY, Riely G, Viale A, Wang L, Chitale D, Motoi N, Szoke J, Broderick S, Balak M, Chang WC, Yu CJ, Gazdar A, Pass H, Rusch V, Gerald W, Huang SF, Yang PC, Miller V, Ladanyi M, Yang CH, Pao W. Bean J, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Dec 26;104(52):20932-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0710370104. Epub 2007 Dec 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 18093943 Free PMC article. - Activating and resistance mutations of EGFR in non-small-cell lung cancer: role in clinical response to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors.
Gazdar AF. Gazdar AF. Oncogene. 2009 Aug;28 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S24-31. doi: 10.1038/onc.2009.198. Oncogene. 2009. PMID: 19680293 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Saturation profiling of drug-resistant genetic variants using prime editing.
Kim Y, Oh HC, Lee S, Kim HH. Kim Y, et al. Nat Biotechnol. 2024 Nov 12. doi: 10.1038/s41587-024-02465-z. Online ahead of print. Nat Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39533107 - Multimodal scanning of genetic variants with base and prime editing.
Belli O, Karava K, Farouni R, Platt RJ. Belli O, et al. Nat Biotechnol. 2024 Nov 12. doi: 10.1038/s41587-024-02439-1. Online ahead of print. Nat Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39533106 - Overcoming EGFR-TKI resistance by targeting the tumor microenvironment.
Zhang J, Vokes N, Li M, Xu J, Bai H, Wang J, Wang Z, Zhang J. Zhang J, et al. Chin Med J Pulm Crit Care Med. 2024 Sep 16;2(3):151-161. doi: 10.1016/j.pccm.2024.08.002. eCollection 2024 Sep. Chin Med J Pulm Crit Care Med. 2024. PMID: 39403414 Free PMC article. Review. - Mechanisms of resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitor-targeted therapy and overcoming strategies.
Ou X, Gao G, Habaz IA, Wang Y. Ou X, et al. MedComm (2020). 2024 Aug 24;5(9):e694. doi: 10.1002/mco2.694. eCollection 2024 Sep. MedComm (2020). 2024. PMID: 39184861 Free PMC article. Review. - Identification of potential inhibitors for drug-resistant EGFR mutations in non-small cell lung cancer using whole exome sequencing data.
Nagarajan N, Guda C. Nagarajan N, et al. Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jul 25;15:1428158. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1428158. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39130636 Free PMC article.
References
- Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R, et al. Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:2129–39. - PubMed
- Paez JG, Janne PA, Lee JC, et al. EGFR mutations in lung cancer: correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy. Science. 2004;304:1497–500. - PubMed
- Riely GJ, Pao W, Pham D, et al. Clinical course of patients with non-small cell lung cancer and epidermal growth factor receptor exon 19 and exon 21 mutations treated with gefitinib or erlotinib. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12:839–44. - PubMed
- Jackman DM, Yeap BY, Sequist LV, et al. Exon 19 deletion mutations of epidermal growth factor receptor are associated with prolonged survival in non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with gefitinib or erlotinib. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12:3908–14. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P01 CA129243-020003/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 CA097980/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K08-CA097980/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-CA121210/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA121210-02/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA121210/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 CA097980-04/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA129243/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous