Molecular characterization and antimicrobial susceptibility of Salmonella isolates from infections in humans in Henan Province, China - PubMed (original) (raw)
Molecular characterization and antimicrobial susceptibility of Salmonella isolates from infections in humans in Henan Province, China
Shengli Xia et al. J Clin Microbiol. 2009 Feb.
Abstract
We characterized 208 human Salmonella isolates from 2006 to 2007 and 27 human Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium isolates from 1987 to 1993 from Henan Province, China, by serotyping, by antimicrobial susceptibility testing, and, for the most common serovars, by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE). The most common serovars among the 2006-2007 isolates were S. enterica serovar Typhimurium (27%), S. enterica serovar Enteritidis (17%), S. enterica serovar Derby (10%), S. enterica serovar Indiana (6%), and S. enterica serovar Litchfield (6%). A high percentage of the isolates were multiple-drug resistant, and 54% were resistant to both nalidixic acid and ciprofloxacin. Of these, 42% were resistant to a high level of ciprofloxacin (MIC > 4 microg/ml), whereas for the remaining isolates, the MICs ranged from 0.125 to 2 microg/ml. Five isolates (2%) were ceftiofur resistant and harbored bla(CTX-M14) or bla(CTX-M15). With the possible exception of the quinolones and cephalosporins, the 1987-1993 S. enterica serovar Typhimurium isolates were almost as resistant as the recent isolates. PFGE typing of S. enterica serovar Typhimurium showed that the most common cluster predominated over time. Two other clusters have emerged, and another cluster has disappeared.
Figures
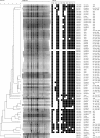
FIG. 1.
Phylogeny of PFGE patterns of 83 Salmonella serovar Typhimurium isolates from humans with infections during the periods 1987 to 1993 and 2006 to 2007 in Henan Province, China. N2, panel used for susceptibility testing; AMP, ampicillin; APR, apramycin; XNL, ceftiofur; CHL, chloramphenicol; CIP, ciprofloxacin; FFN, florfenicol; GEN, gentamicin; NAL, nalidixic acid; NEO, neomycin; SPE, spectinomycin; STR, streptomycin; SMX, sulfamethoxazole; TET, tetracycline; TMP, trimethoprim. Isolate numbers are noted to the right of the PFGE patterns.
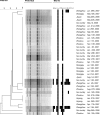
FIG. 2.
Phylogeny of PFGE patterns of 35 Salmonella serovar Enteritidis isolates from humans with infections during the period 2006 to 2007 in Henan Province, China. N2, panel used for susceptibility testing; AMP, ampicillin; APR, apramycin; XNL, ceftiofur; CHL, chloramphenicol; CIP, ciprofloxacin; COL, colistin, FFN, florfenicol; GEN, gentamicin; NAL, nalidixic acid; NEO, neomycin; SPE, spectinomycin; STR, streptomycin; SMX, sulfamethoxazole; TET, tetracycline; TMP, trimethoprim; AUG2, amoxicillin plus clavulanic acid; CEP, cephalosporin; POD, cefpodoxime.
FIG. 3.
Phylogeny of PFGE patterns of 20 Salmonella serovar Derby isolates from humans with infections during the period 2006 to 2007 in Henan Province, China. N2, panel used for susceptibility testing; AMP, ampicillin; APR, apramycin; XNL, ceftiofur; CHL, chloramphenicol; CIP, ciprofloxacin; COL, colistin, FFN, florfenicol; GEN, gentamicin; NAL, nalidixic acid; NEO, neomycin; SPE, spectinomycin; STR, streptomycin; SMX, sulfamethoxazole; TET, tetracycline; TMP, trimethoprim; AUG2, amoxicillin plus clavulanic acid; CEP, cephalosporin; POD, cefpodoxime.
Similar articles
- Serovar distribution, antimicrobial resistance profiles, and PFGE typing of Salmonella enterica strains isolated from 2007-2012 in Guangdong, China.
Ke B, Sun J, He D, Li X, Liang Z, Ke CW. Ke B, et al. BMC Infect Dis. 2014 Jun 17;14:338. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-14-338. BMC Infect Dis. 2014. PMID: 24939394 Free PMC article. - The phenotypic and molecular characteristics of antimicrobial resistance of Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Typhimurium in Henan Province, China.
Dong N, Li Y, Zhao J, Ma H, Wang J, Liang B, Du X, Wu F, Xia S, Yang X, Liu H, Yang C, Qiu S, Song H, Jia L, Li Y, Sun Y. Dong N, et al. BMC Infect Dis. 2020 Jul 15;20(1):511. doi: 10.1186/s12879-020-05203-3. BMC Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32669095 Free PMC article. - Characterization of Salmonella enterica isolates from infants and toddlers in Wuhan, China.
Cui S, Li J, Sun Z, Hu C, Jin S, Li F, Guo Y, Ran L, Ma Y. Cui S, et al. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2009 Jan;63(1):87-94. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkn452. Epub 2008 Nov 4. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2009. PMID: 18984647 - Salmonella serovars from foodborne and waterborne diseases in Korea, 1998-2007: total isolates decreasing versus rare serovars emerging.
Kim S. Kim S. J Korean Med Sci. 2010 Dec;25(12):1693-9. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2010.25.12.1693. Epub 2010 Nov 24. J Korean Med Sci. 2010. PMID: 21165281 Free PMC article. Review. - Epidemiology, Clinical Presentation, Laboratory Diagnosis, Antimicrobial Resistance, and Antimicrobial Management of Invasive Salmonella Infections.
Crump JA, Sjölund-Karlsson M, Gordon MA, Parry CM. Crump JA, et al. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2015 Oct;28(4):901-37. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00002-15. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2015. PMID: 26180063 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- The characteristics of _mcr_-bearing plasmids in clinical Salmonella enterica in Sichuan, China, 2014 to 2017.
Sun X, Zhang L, Meng J, Peng K, Huang W, Lei G, Wang Z, Li R, Yang X. Sun X, et al. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023 Aug 29;13:1240580. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1240580. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37705933 Free PMC article. - Genomic Investigation of Antimicrobial-Resistant Salmonella enterica Isolates From Dead Chick Embryos in China.
Elbediwi M, Tang Y, Shi D, Ramadan H, Xu Y, Xu S, Li Y, Yue M. Elbediwi M, et al. Front Microbiol. 2021 Aug 23;12:684400. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.684400. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34497590 Free PMC article. - Prevalence of Salmonella enterica in poultry and eggs in Uruguay during an epidemic due to Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis.
Betancor L, Pereira M, Martinez A, Giossa G, Fookes M, Flores K, Barrios P, Repiso V, Vignoli R, Cordeiro N, Algorta G, Thomson N, Maskell D, Schelotto F, Chabalgoity JA. Betancor L, et al. J Clin Microbiol. 2010 Jul;48(7):2413-23. doi: 10.1128/JCM.02137-09. Epub 2010 May 19. J Clin Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20484605 Free PMC article. - Epidemiological and Molecular Investigations on Salmonella Responsible for Gastrointestinal Infections in the Southwest of Shanghai From 1998 to 2017.
Qi X, Li P, Xu X, Yuan Y, Bu S, Lin D. Qi X, et al. Front Microbiol. 2019 Sep 18;10:2025. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02025. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31620098 Free PMC article. - Whole-genome sequencing of multidrug resistance Salmonella Typhi clinical strains isolated from Balochistan, Pakistan.
Fatima S, Ishaq Z, Irfan M, AlAsmari AF, Achakzai JK, Zaheer T, Ali A, Akbar A. Fatima S, et al. Front Public Health. 2023 May 16;11:1151805. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1151805. eCollection 2023. Front Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37261234 Free PMC article.
References
- Cavaco, L. M., N. Frimodt-Møller, H. Hasman, L. Guardabassi, L. Nielsen, and F. M. Aarestrup. 2008. Prevalence of quinolone resistance mechanisms and associations to minimum inhibitory concentrations in quinolone-resistant Escherichia coli isolated from humans and swine in Denmark. Microb. Drug Resist. 14163-169. - PubMed
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. 2007. National Antimicrobial Resistance Monitoring System for Enteric Bacteria (NARMS): human isolates final report, 2004. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Atlanta, Georgia. http://www.cdc.gov/narms/.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical