The adaptor protein of the anaphase promoting complex Cdh1 is essential in maintaining replicative lifespan and in learning and memory - PubMed (original) (raw)
The adaptor protein of the anaphase promoting complex Cdh1 is essential in maintaining replicative lifespan and in learning and memory
Min Li et al. Nat Cell Biol. 2008 Sep.
Abstract
The anaphase promoting complex (APC) or cyclosome is a multisubunit E3 ubiquitin ligase. Cdc20 (fizzy (fzy)) or p55CDC, and Cdh1 (Hct1, srw1 or fizzy-related 1 (fzr1)) encode two adaptor proteins that bring substrates to the APC. Both APC-Cdc20 and APC-Cdh1 have been implicated in the control of mitosis through mediating ubiquitination of mitotic regulators, such as cyclin B1 and securin. However, the importance of Cdh1 function in vivo and whether its function is redundant with that of Cdc20 are unclear. Here we have analysed mice lacking Cdh1. We show that Cdh1 is essential for placental development and that its deficiency causes early lethality. Cdhl-deficient mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) entered replicative senescence prematurely because of stabilization of Ets2 and subsequent activation of p6(Ink4a) expression. These results have uncovered an unexpected role of the APC in maintaining replicative lifespan of MEFs. Further, Cdh1 heterozygous mice show defects in late-phase long-term potentiation (L-LTP) in the hippocampus and are deficient in contextual fear-conditioning, suggesting that Cdh1 has a role in learning and memory.
Figures
Figure 1
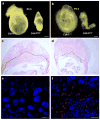
Absence of Cdh1 causes early lethality in mice. a and b. Retarded development of Cdh1gt/gt embryos at E8.5 and E9.5 c and d. H&E stained sections of wildtype ( c) and mutant (d) E9.5 whole deciduas. The black outline delineates the boundary between deciduous and placental tissues. e and f. Immunostaining of cyclin B1 on wildtype ( e) and mutant (f) E9.5 placentas. Scale bars in a and b, 40 μm; in c and d, 20 μm; in e and f, 10 μm.
Figure 2
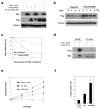
Analyses of Cdh1gt/gt MEFs. a. Growth curve analysis of MEFs at passage 3 (MTT assay). b. BrdU incorporation assays of passage 3 MEFs. c. Immunoblotting of phospho-histone H3 in passage 3 MEFs. d. Growth curve analysis of MEFs at passage 6. e and f. Immunoblotting analysis of various cell cycle regulators in MEFs (e) and E9.0 embryos (f). Results in a, b, and d were from three independent experiments. Error bars are standard deviations.
Figure 3
Cdh1 regulates the expression of p16 through modulating the stability of Ets2. a. Western blot analysis of p16, p53 and Ets2 in MEFs. b. Quantitation of Ets2 levels in a. c. RT-PCR analysis of gene expression in MEFs. d. Quantitation of p16 levels in c. e. Analysis of Ets2 stability in wildtype and Cdh1 mutant MEFs treated with cyclohexamide (CHX). f. Quantitation of Ets2 levels in e. g. The effect of Cdh1 overexpression on the stability of Ets2 in wildtype MEFs. Full scans of the gels in a, e, and g are presented in supplemental figure 5.
Figure 4
Ets2 is potential substrate of APC-Cdh1. a. Immunoblotting analysis of ETS2 (wildtype and destruction box mutated) in 293T cells transfected with control or _Cdh1_-expressiong plasmids. b. Analysis of wildtype and destruction box-mutated Ets2 expressed in HeLa cells treated with cyclohexamide (CHX). c. Quantitation of the results in b. c. Ets2 interacts with Cdh1. Myc-Cdh1 and Flag-Ets2 were transiently expressed in 293T cells. Flag-Ets2 was immunoprecipitated and blotted for the presence of Myc-Cdh1. e. Analysis of the effect of Est2 expression on the proliferative potential of wildtype MEFs. f. Quantitation of cells positive for senescence-associated β-galactosidase. Results in e and f were from three independent experiments. Error bars indicate standard deviation. Full scans of the gels in a, b, and d are presented in supplemental figure 5.
Figure 5
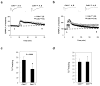
Learning and memory defects in Cdh1 heterozygous mice. a. Early-phase LTP induced by a single 100 Hz stimulus (1s). 5 slices per mouse from a total of 5 mice of each genotype were used. Representative fEPSP recordings from time points A and B are shown for each condition. Calibration: 1 mV, 5 ms. b. Late-phase LTP elicited by four 100 Hz trains (1s) with 5 min intertrain interval. 10 slices per mouse from a total of 8 mice of each genotype were used. Representative fEPSP recordings from time points A and B are shown for each condition. Calibration: 1 mV, 5 ms. c. Analysis of contextual fear conditioning. d. Analysis of cued fear conditioning. 10 measurements were made in c and d and error bars indicate standard deviation.
Comment in
- A tal(in) of cell spreading.
Frame M, Norman J. Frame M, et al. Nat Cell Biol. 2008 Sep;10(9):1017-9. doi: 10.1038/ncb0908-1017. Nat Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18758489
Similar articles
- TPR subunits of the anaphase-promoting complex mediate binding to the activator protein CDH1.
Vodermaier HC, Gieffers C, Maurer-Stroh S, Eisenhaber F, Peters JM. Vodermaier HC, et al. Curr Biol. 2003 Sep 2;13(17):1459-68. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(03)00581-5. Curr Biol. 2003. PMID: 12956947 - The regulation of Cdc20 proteolysis reveals a role for APC components Cdc23 and Cdc27 during S phase and early mitosis.
Prinz S, Hwang ES, Visintin R, Amon A. Prinz S, et al. Curr Biol. 1998 Jun 18;8(13):750-60. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(98)70298-2. Curr Biol. 1998. PMID: 9651679 - The E3 ligase APC/C-Cdh1 is required for associative fear memory and long-term potentiation in the amygdala of adult mice.
Pick JE, Malumbres M, Klann E. Pick JE, et al. Learn Mem. 2012 Dec 14;20(1):11-20. doi: 10.1101/lm.027383.112. Learn Mem. 2012. PMID: 23242419 Free PMC article. - Mitotic regulation of the anaphase-promoting complex.
Baker DJ, Dawlaty MM, Galardy P, van Deursen JM. Baker DJ, et al. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2007 Mar;64(5):589-600. doi: 10.1007/s00018-007-6443-1. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2007. PMID: 17334950 Free PMC article. Review. - Non-mitotic functions of the Anaphase-Promoting Complex.
Eguren M, Manchado E, Malumbres M. Eguren M, et al. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2011 Aug;22(6):572-8. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2011.03.010. Epub 2011 Mar 23. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2011. PMID: 21439391 Review.
Cited by
- The anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome activator Cdh1 modulates Rho GTPase by targeting p190 RhoGAP for degradation.
Naoe H, Araki K, Nagano O, Kobayashi Y, Ishizawa J, Chiyoda T, Shimizu T, Yamamura K, Sasaki Y, Saya H, Kuninaka S. Naoe H, et al. Mol Cell Biol. 2010 Aug;30(16):3994-4005. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01358-09. Epub 2010 Jun 7. Mol Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20530197 Free PMC article. - Cdc20 is critical for meiosis I and fertility of female mice.
Jin F, Hamada M, Malureanu L, Jeganathan KB, Zhou W, Morbeck DE, van Deursen JM. Jin F, et al. PLoS Genet. 2010 Sep 30;6(9):e1001147. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1001147. PLoS Genet. 2010. PMID: 20941357 Free PMC article. - Cdc20 hypomorphic mice fail to counteract de novo synthesis of cyclin B1 in mitosis.
Malureanu L, Jeganathan KB, Jin F, Baker DJ, van Ree JH, Gullon O, Chen Z, Henley JR, van Deursen JM. Malureanu L, et al. J Cell Biol. 2010 Oct 18;191(2):313-29. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201003090. J Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20956380 Free PMC article. - APC/C ubiquitin ligase: Functions and mechanisms in tumorigenesis.
Schrock MS, Stromberg BR, Scarberry L, Summers MK. Schrock MS, et al. Semin Cancer Biol. 2020 Dec;67(Pt 2):80-91. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2020.03.001. Epub 2020 Mar 9. Semin Cancer Biol. 2020. PMID: 32165320 Free PMC article. Review. - Cell cycle, CDKs and cancer: a changing paradigm.
Malumbres M, Barbacid M. Malumbres M, et al. Nat Rev Cancer. 2009 Mar;9(3):153-66. doi: 10.1038/nrc2602. Nat Rev Cancer. 2009. PMID: 19238148 Review.
References
- Edgar BA, Orr-Weaver TL. Endoreplication cell cycles: more for less. Cell. 2001;105:297–306. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 CA122623/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- NS047384/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 NS034007/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R29 NS034007/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- CA116097/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- NS034007/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA116097/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS034007/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA116097-02/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS047384/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous