RNA-directed DNA methylation requires an AGO4-interacting member of the SPT5 elongation factor family - PubMed (original) (raw)
RNA-directed DNA methylation requires an AGO4-interacting member of the SPT5 elongation factor family
Natacha Bies-Etheve et al. EMBO Rep. 2009 Jun.
Abstract
Recent studies have identified a conserved WG/GW-containing motif, known as the Argonaute (AGO) hook, which is involved in the recruitment of AGOs to distinct components of the eukaryotic RNA silencing pathways. By using this motif as a model to detect new components in plant RNA silencing pathways, we identified SPT5-like, a plant-specific AGO4-interacting member of the nuclear SPT5 (Suppressor of Ty insertion 5) RNA polymerase (RNAP) elongation factor family that is characterized by the presence of a carboxy-terminal extension with more than 40 WG/GW motifs. Knockout SPT5-like mutants show a decrease in the accumulation of several 24-nt RNAs and hypomethylation at different loci revealing an implication in RNA-directed DNA methylation (RdDM). Here, we propose that SPT5-like emerged in plants as a facultative RNAP elongation factor. Its plant-specific origin and role in RdDM might reflect functional interactions with plant-specific RNA Pols required for RdDM.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Figure 1
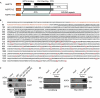
SPT5-like proteins are plant-specific members of the SPT5 family. (A) Structures of human SPT5, its Arabidopsis homologues and the SPT5-like protein. Conserved acidic, SPT4-binding, RNAPII-binding and carboxy-terminal repeats (CTRs) are indicated as the conservation percentages. (B) Primary sequence of the Arabidopsis SPT5-like sequence. The amino-terminal acidic domain is shown in orange and the conserved binding region is underlined. The GW/WG residues in the SPT5-like amino-terminal repeats are shown in orange and underlined. (C) Preferential binding of AGO4 on the SPT5-like WG repeats. Myc-AGO4 or Flag-AGO1 extracts were applied to equimolar amounts of GST and GST-based fusion protein beads, and the bound proteins were detected by immunoblotting with Myc or M2 antibodies. The GST protein was used as a control. (D) Physical interaction between AGO4 and SPT5-like was detected by coimmunoprecipitation. Proteins from both control and Myc-AGO4 transgenic lines were immunoprecipitated using cMyc antibodies, and analysed to detect the Myc epitope (AGO4) and SPT5-like (SPT5l). AGO, Argonaute; GST, glutathione _S_-transferase; RNAP, RNA polymerase; SPT5, Suppressor of Ty insertion 5.
Figure 2
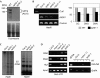
DNA methylation defects in spt5-like knockout mutants. (A) Western blot and Coomassie blue staining on wild-type (WT) and mutant flower protein extracts (∼20 μg) using an SPT5-like specific antibody. (B) DNA methylation at the AtSN1 locus in spt5-like and control genotypes Col-0 and nrpe1-11 (polV). Left panel, _Hae_III-digested DNA was used as a template for PCR reactions using AtSN1 primers (412 and 413) and control primers. Cut 1 primers (400 and 402) should not allow DNA amplification if the digestion is complete. Control primers (410 and 411) allow equilibration of DNA quantities used as templates. Right panel, DNA methylation was analysed by bisulphite sequencing. Histograms represent the percentage of CG, CNG and CNN methylation in the indicated genotypes. (C) DNA methylation at the 5S ribosomal RNA locus in spt5-like and Col-0. Genomic DNA was digested with _Hpa_II or _Hae_III and blots were hybridized with a 5S ribosomal RNA repeat probe. (D) DNA methylation at the solo LTR locus and IG/LINE expression in spt5-like and control genotypes Col-0, nrpd1-4 (polIV) nrpe1-11. Left panel, genomic DNA was digested by various methylation-sensitive enzymes before being used for PCR amplification using _solo LTR_-specific primers (769 and 770). Input indicates amplification from equal quantities of undigested DNA. Right panel, RT-PCR performed on Col-0, nrpe1-11 and spt5-like-1 messenger RNA. gDNA correspond to amplification from genomic Col-0 DNA. +/− RT indicates whether or not transcriptase treatment was carried out. _GAPA_s (glyceraldehyde 3-dehydrogenase A) have been used to check equilibration. All primers are described in supplementary Table 1 online. Ab, antibody; AtSN1, Arabidopsis thaliana short interspersed element 1; IG/LINE, intergenic/long interspersed element; LTR, long terminal repeat; RT–PCR, reverse transcription–PCR; SPT5, Suppressor of Ty insertion 5; Und., undigested DNA.
Figure 3
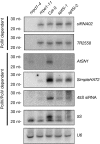
Short interfering RNA accumulation defect in spt5-like mutants. Small RNA blot assays for U6 and various endogenous siRNAs in spt5-like, nrpd1-4 and nrpe1-11 mutants. Blots were stripped and reprobed multiple times with probes indicated on the right. siRNA accumulation dependency on polIV or polV is indicated on the left. U6 was used as an equilibration control. AtSN1, Arabidopsis thaliana short interspersed element 1; nrpd1, nuclear RNA polymerase IV largest subunit; nrpe1, nuclear RNA polymerase V largest subunit; siRNA, short interfering RNA; SPT5, Suppressor of Ty insertion 5.
Figure 4
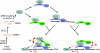
Hypothetical model for the action of SPT5-like in RNA-directed DNA methylation. Two possible mechanisms for the mode of action of SPT5-like in RdDM are presented. Both involve the recruitment of AGO4 to PolV and SPT5-like (SPT5l) but differ in the subsequent role of the latter. (A) Recycling of AGO4 through SPT5-like. (B) Recruitment of SPT5l through the AGO hook domain. AGO, Argonaute; DCL3, dicer-like 3; DRM2, domain rearranged methylase 2; dsRNA, double-stranded RNA; meC, methylated cytosine; RdDM, RNA-directed DNA methylation; RDR2, RNA dependent RNA polymerase 2; siRNA, short interfering RNA; SPT5, Suppressor of Ty insertion 5; Spt5l, SPT5 like.
Similar articles
- An effector of RNA-directed DNA methylation in arabidopsis is an ARGONAUTE 4- and RNA-binding protein.
He XJ, Hsu YF, Zhu S, Wierzbicki AT, Pontes O, Pikaard CS, Liu HL, Wang CS, Jin H, Zhu JK. He XJ, et al. Cell. 2009 May 1;137(3):498-508. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.04.028. Cell. 2009. PMID: 19410546 Free PMC article. - NRPD4, a protein related to the RPB4 subunit of RNA polymerase II, is a component of RNA polymerases IV and V and is required for RNA-directed DNA methylation.
He XJ, Hsu YF, Pontes O, Zhu J, Lu J, Bressan RA, Pikaard C, Wang CS, Zhu JK. He XJ, et al. Genes Dev. 2009 Feb 1;23(3):318-30. doi: 10.1101/gad.1765209. Genes Dev. 2009. PMID: 19204117 Free PMC article. - Evidence for ARGONAUTE4-DNA interactions in RNA-directed DNA methylation in plants.
Lahmy S, Pontier D, Bies-Etheve N, Laudié M, Feng S, Jobet E, Hale CJ, Cooke R, Hakimi MA, Angelov D, Jacobsen SE, Lagrange T. Lahmy S, et al. Genes Dev. 2016 Dec 1;30(23):2565-2570. doi: 10.1101/gad.289553.116. Epub 2016 Dec 16. Genes Dev. 2016. PMID: 27986858 Free PMC article. - Biochemical Analysis of Yeast Suppressor of Ty 4/5 (Spt4/5) Reveals the Importance of Nucleic Acid Interactions in the Prevention of RNA Polymerase II Arrest.
Crickard JB, Fu J, Reese JC. Crickard JB, et al. J Biol Chem. 2016 May 6;291(19):9853-70. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.716001. Epub 2016 Mar 4. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 26945063 Free PMC article. - A nexus for gene expression-molecular mechanisms of Spt5 and NusG in the three domains of life.
Werner F. Werner F. J Mol Biol. 2012 Mar 16;417(1-2):13-27. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2012.01.031. Epub 2012 Jan 27. J Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22306403 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Metamorphic proteins under a computational microscope: Lessons from a fold-switching RfaH protein.
Artsimovitch I, Ramírez-Sarmiento CA. Artsimovitch I, et al. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022 Oct 21;20:5824-5837. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2022.10.024. eCollection 2022. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022. PMID: 36382197 Free PMC article. Review. - Enzymatic reactions of AGO4 in RNA-directed DNA methylation: siRNA duplex loading, passenger strand elimination, target RNA slicing, and sliced target retention.
Wang F, Huang HY, Huang J, Singh J, Pikaard CS. Wang F, et al. Genes Dev. 2023 Feb 1;37(3-4):103-118. doi: 10.1101/gad.350240.122. Epub 2023 Feb 6. Genes Dev. 2023. PMID: 36746605 Free PMC article. - SPT5-like, a new component in plant RdDM.
Wang MB, Dennis ES. Wang MB, et al. EMBO Rep. 2009 Jun;10(6):573-5. doi: 10.1038/embor.2009.101. Epub 2009 May 15. EMBO Rep. 2009. PMID: 19444314 Free PMC article. No abstract available. - RNA-directed DNA methylation and plant development require an IWR1-type transcription factor.
Kanno T, Bucher E, Daxinger L, Huettel B, Kreil DP, Breinig F, Lind M, Schmitt MJ, Simon SA, Gurazada SG, Meyers BC, Lorkovic ZJ, Matzke AJ, Matzke M. Kanno T, et al. EMBO Rep. 2010 Jan;11(1):65-71. doi: 10.1038/embor.2009.246. Epub 2009 Dec 11. EMBO Rep. 2010. PMID: 20010803 Free PMC article. - Tracing the origin and evolution history of methylation-related genes in plants.
Pei L, Zhang L, Li J, Shen C, Qiu P, Tu L, Zhang X, Wang M. Pei L, et al. BMC Plant Biol. 2019 Jul 12;19(1):307. doi: 10.1186/s12870-019-1923-7. BMC Plant Biol. 2019. PMID: 31299897 Free PMC article.
References
- Alonso JM et al. (2003) Genome-wide insertional mutagenesis of Arabidopsis thaliana. Science 301: 653–657 - PubMed
- Fraga MF et al. (2008) Epigenetic inactivation of the Groucho homologue gene TLE1 in hematologic malignancies. Cancer Res 68: 4116–4122 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials