The exocyst complex in polarized exocytosis - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
The exocyst complex in polarized exocytosis
Bing He et al. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2009 Aug.
Abstract
The exocyst is an octameric protein complex, which mediates the tethering of post-Golgi secretory vesicles to the plasma membrane before exocytic fusion. The exocyst assembles by side-by-side packing of rod-shaped subunits composed of helical bundles. The targeting of secretory vesicles to the plasma membrane involves direct interactions of the exocyst with PI(4,5)P(2). In addition, a number of small GTP-binding proteins interact with components of the exocyst and regulate the assembly, localization, and function of this complex. Here we review the recent advances in the field, focusing on the function of the exocyst in polarized exocytosis.
Figures
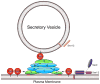
Figure 1. A model for the function of the exocyst complex in tethering the secretory vesicles to the plasma membrane in yeast
Sec3 and Exo70 directly associate with PI(4,5)P2 (shown in red) in the plasma membrane via their positively charged residues (“+++”). Exo70 and Sec3 interact with the rest of the exocyst subunits riding on the arriving secretory vesicles. Another exocyst subunit Sec15 directly binds to the GTP-bound form of Rab GTPase Sec4, which is peripherally associated with the secretory vesicle and regulates the assembly of the exocyst complex. The assembly of the exocyst serves to tether the vesicles to the plasma membrane site specified by Sec3 and Exo70. The exocyst may also regulate the assembly of the SNARE complex through direct or indirect interactions. The exocyst is also regulated by the Rho GTPases Cdc42, Rho1, and Rho3. Cdc42 and Rho1 interact with Sec3 and control the polarized localization of the exocyst. Rho3 interacts with Exo70; however, the functional implication of this interaction is not clear. “3”: Sec3; “5”: Sec5; “6”: Sec6; “8”: Sec8; “10”: Sec10; “15”: Sec15; “70”: Exo70; “84”: Exo84. Sso1/2 and Sec9 are the t-SNAREs and Snc1/2 are the v-SNAREs for exocytosis at the plasma membrane in yeast.
Similar articles
- Interactions between Rabs, tethers, SNAREs and their regulators in exocytosis.
Novick P, Medkova M, Dong G, Hutagalung A, Reinisch K, Grosshans B. Novick P, et al. Biochem Soc Trans. 2006 Nov;34(Pt 5):683-6. doi: 10.1042/BST0340683. Biochem Soc Trans. 2006. PMID: 17052174 - The role of Sec3p in secretory vesicle targeting and exocyst complex assembly.
Luo G, Zhang J, Guo W. Luo G, et al. Mol Biol Cell. 2014 Nov 15;25(23):3813-22. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E14-04-0907. Epub 2014 Sep 17. Mol Biol Cell. 2014. PMID: 25232005 Free PMC article. - Cyclical regulation of the exocyst and cell polarity determinants for polarized cell growth.
Zajac A, Sun X, Zhang J, Guo W. Zajac A, et al. Mol Biol Cell. 2005 Mar;16(3):1500-12. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e04-10-0896. Epub 2005 Jan 12. Mol Biol Cell. 2005. PMID: 15647373 Free PMC article. - Dissecting the plant exocyst.
Saeed B, Brillada C, Trujillo M. Saeed B, et al. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2019 Dec;52:69-76. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2019.08.004. Epub 2019 Sep 8. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2019. PMID: 31509792 Review. - The exocyst complex in polarized exocytosis.
Hsu SC, TerBush D, Abraham M, Guo W. Hsu SC, et al. Int Rev Cytol. 2004;233:243-65. doi: 10.1016/S0074-7696(04)33006-8. Int Rev Cytol. 2004. PMID: 15037366 Review.
Cited by
- Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease and intracellular traffic.
Bucci C, Bakke O, Progida C. Bucci C, et al. Prog Neurobiol. 2012 Dec;99(3):191-225. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2012.03.003. Epub 2012 Mar 22. Prog Neurobiol. 2012. PMID: 22465036 Free PMC article. Review. - Ubiquitination of Innate Immune Regulator TRAF3 Orchestrates Expulsion of Intracellular Bacteria by Exocyst Complex.
Miao Y, Wu J, Abraham SN. Miao Y, et al. Immunity. 2016 Jul 19;45(1):94-105. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2016.06.023. Immunity. 2016. PMID: 27438768 Free PMC article. - The Functions, Methods, and Mobility of Mitochondrial Transfer Between Cells.
Qin Y, Jiang X, Yang Q, Zhao J, Zhou Q, Zhou Y. Qin Y, et al. Front Oncol. 2021 May 10;11:672781. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.672781. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34041035 Free PMC article. Review. - Phosphatidylserine Synthase Controls Cell Elongation Especially in the Uppermost Internode in Rice by Regulation of Exocytosis.
Ma J, Cheng Z, Chen J, Shen J, Zhang B, Ren Y, Ding Y, Zhou Y, Zhang H, Zhou K, Wang JL, Lei C, Zhang X, Guo X, Gao H, Bao Y, Wan JM. Ma J, et al. PLoS One. 2016 Apr 7;11(4):e0153119. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0153119. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27055010 Free PMC article. - Fission yeast sec3 bridges the exocyst complex to the actin cytoskeleton.
Jourdain I, Dooley HC, Toda T. Jourdain I, et al. Traffic. 2012 Nov;13(11):1481-95. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2012.01408.x. Epub 2012 Sep 7. Traffic. 2012. PMID: 22891673 Free PMC article.
References
- Hsu SC, Ting AE, Hazuka CD, Davanger S, Kenny JW, Kee Y, Scheller RH. The mammalian brain rsec6/8 complex. Neuron. 1996;17(6):1209–19. First purification of mammalian exocyst complex from rat brain extract by chromatography. - PubMed
- Munson M, Novick P. The exocyst defrocked, a framework of rods revealed. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2006;13(7):577–81. Review. - PubMed
- Dong G, Hutagalung AH, Fu C, Novick P, Reinisch KM. The structures of exocyst subunit Exo70p and the Exo84p C-terminal domains reveal a common motif. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2005;12(12):1094–100. This paper demonstrates the crystal structure of near full length of yeast Exo70 and the C-terminal domain of yeast Exo84. Exo70 and Exo84CT are principally composed of α-helices that fold into four and two helical bundles, respectively. These helical bundles pack against each other and form rod-shape structures. The authors also show that the C-terminus of Exo70 contains a number of basic residues that cluster into an electropositive surface patch. - PubMed
- Hamburger ZA, Hamburger AE, West AP, Jr, Weis WI. Crystal structure of the S. cerevisiae exocyst component Exo70p. J Mol Biol. 2006;356(1):9–21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous