Impact of epidermal growth factor receptor and KRAS mutations on clinical outcomes in previously untreated non-small cell lung cancer patients: results of an online tumor registry of clinical trials - PubMed (original) (raw)
Impact of epidermal growth factor receptor and KRAS mutations on clinical outcomes in previously untreated non-small cell lung cancer patients: results of an online tumor registry of clinical trials
David M Jackman et al. Clin Cancer Res. 2009.
Abstract
Purpose: The impact of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and KRAS genotypes on outcomes with erlotinib or gefitinib therapy continues to be debated. This study combines patient data from five trials in predominantly Western populations to assess the impact of EGFR and KRAS mutations on first-line therapy with an EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) and compare clinical versus molecular predictors of sensitivity.
Experimental design: Chemotherapy-naïve patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer and known EGFR mutation status treated with erlotinib or gefitinib monotherapy as part of a clinical trial were eligible for inclusion. Patients received daily erlotinib (150 mg) or gefitinib (250 mg) until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. Data were collected in a password-protected web database. Clinical outcomes were analyzed to look for differences based on EGFR and KRAS genotypes, as well as clinical characteristics.
Results: Patients (223) from five clinical trials were included. Sensitizing EGFR mutations were associated with a 67% response rate, time to progression (TTP) of 11.8 months, and overall survival of 23.9 months. Exon 19 deletions were associated with longer median TTP and overall survival compared with L858R mutations. Wild-type EGFR was associated with poorer outcomes (response rate, 3%; TTP, 3.2 months) irrespective of KRAS status. No difference in outcome was seen between patients harboring KRAS transition versus transversion mutations. EGFR genotype was more effective than clinical characteristics at selecting appropriate patients for consideration of first-line therapy with an EGFR-TKI.
Conclusion: EGFR mutation status is associated with sensitivity to treatment with an EGFR-TKI in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Patients harboring sensitizing EGFR mutations should be considered for first-line erlotinib or gefitinib.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest
D.M. Jackman, consultant, Genentech; honoraria, Roche. V.A. Miller, consultant, Genentech. P.A. Janne, consultant, AVEO Pharmaceuticals, Boehringer Ingelheim, Roche; research funding, Pfizer, Genentech; patent holder, Genzyme. G.J. Riely, consultant, Astra Zeneca, Roche. M.I. Gallegos Ruiz, employment, Roche. B.E. Johnson, consultant, patent holder, Genzyme. The other authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures
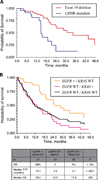
Fig. 1
A, OS in patients with exon 19 deletions versus L858R point mutations. B, OS based on EGFR and KRAS status.
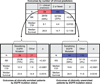
Fig. 2
Comparison of outcomes by clinical enrichment and EGFR mutation analysis.
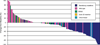
Fig. 3
Maximal reduction for indicator lesions (Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors classification) by EGFR and KRAS genotype.
Similar articles
- Distinct clinical course of EGFR-mutant resected lung cancers: results of testing of 1118 surgical specimens and effects of adjuvant gefitinib and erlotinib.
D'Angelo SP, Janjigian YY, Ahye N, Riely GJ, Chaft JE, Sima CS, Shen R, Zheng J, Dycoco J, Kris MG, Zakowski MF, Ladanyi M, Rusch V, Azzoli CG. D'Angelo SP, et al. J Thorac Oncol. 2012 Dec;7(12):1815-1822. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e31826bb7b2. J Thorac Oncol. 2012. PMID: 23154553 - A multicenter blinded study evaluating EGFR and KRAS mutation testing methods in the clinical non-small cell lung cancer setting--IFCT/ERMETIC2 Project Part 1: Comparison of testing methods in 20 French molecular genetic National Cancer Institute platforms.
Beau-Faller M, Blons H, Domerg C, Gajda D, Richard N, Escande F, Solassol J, Denis MG, Cayre A, Nanni-Metellus I, Olschwang S, Lizard S, Piard F, Pretet JL, de Fraipont F, Bièche I, de Cremoux P, Rouquette I, Bringuier PP, Mosser J, Legrain M, Voegeli AC, Saulnier P, Morin F, Pignon JP, Zalcman G, Cadranel J. Beau-Faller M, et al. J Mol Diagn. 2014 Jan;16(1):45-55. doi: 10.1016/j.jmoldx.2013.07.009. Epub 2013 Oct 30. J Mol Diagn. 2014. PMID: 24183959 - A phase II study of erlotinib monotherapy in pre-treated non-small cell lung cancer without EGFR gene mutation who have never/light smoking history: re-evaluation of EGFR gene status (NEJ006/TCOG0903).
Matsumoto Y, Maemondo M, Ishii Y, Okudera K, Demura Y, Takamura K, Kobayashi K, Morikawa N, Gemma A, Ishimoto O, Usui K, Harada M, Miura S, Fujita Y, Sato I, Saijo Y; North-East Japan Study Group. Matsumoto Y, et al. Lung Cancer. 2014 Nov;86(2):195-200. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2014.08.019. Epub 2014 Sep 16. Lung Cancer. 2014. PMID: 25249428 Clinical Trial. - Personalized medicine in non-small-cell lung cancer: is KRAS a useful marker in selecting patients for epidermal growth factor receptor-targeted therapy?
Roberts PJ, Stinchcombe TE, Der CJ, Socinski MA. Roberts PJ, et al. J Clin Oncol. 2010 Nov 1;28(31):4769-77. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2009.27.4365. Epub 2010 Oct 4. J Clin Oncol. 2010. PMID: 20921461 Review. - First-line treatment of advanced epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation positive non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer.
Greenhalgh J, Dwan K, Boland A, Bates V, Vecchio F, Dundar Y, Jain P, Green JA. Greenhalgh J, et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 May 25;(5):CD010383. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010383.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27223332 Updated. Review.
Cited by
- KRAS-mutation status dependent effect of zoledronic acid in human non-small cell cancer preclinical models.
Kenessey I, Kói K, Horváth O, Cserepes M, Molnár D, Izsák V, Dobos J, Hegedűs B, Tóvári J, Tímár J. Kenessey I, et al. Oncotarget. 2016 Nov 29;7(48):79503-79514. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12806. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27780929 Free PMC article. - Aberrant signaling pathways in squamous cell lung carcinoma.
Shi I, Hashemi Sadraei N, Duan ZH, Shi T. Shi I, et al. Cancer Inform. 2011;10:273-85. doi: 10.4137/CIN.S8283. Epub 2011 Nov 21. Cancer Inform. 2011. PMID: 22174565 Free PMC article. - Molecular profiling of non-small cell lung cancer.
Forsythe ML, Alwithenani A, Bethune D, Castonguay M, Drucker A, Flowerdew G, French D, Fris J, Greer W, Henteleff H, MacNeil M, Marignani P, Morzycki W, Plourde M, Snow S, Xu Z. Forsythe ML, et al. PLoS One. 2020 Aug 5;15(8):e0236580. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0236580. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32756609 Free PMC article. - The emerging role of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) inhibitors in first-line treatment for patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer positive for EGFR mutations.
Okamoto I, Mitsudomi T, Nakagawa K, Fukuoka M. Okamoto I, et al. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2010 Sep;2(5):301-7. doi: 10.1177/1758834010370698. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2010. PMID: 21789142 Free PMC article. - Tumor epidermal growth factor receptor genotype and depression in stage IV non-small cell lung cancer.
Pirl WF, Traeger L, Greer JA, Bemis H, Gallagher E, Lennes I, Sequist L, Heist R, Temel JS. Pirl WF, et al. Oncologist. 2011;16(9):1299-306. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2011-0116. Epub 2011 Aug 1. Oncologist. 2011. PMID: 21807767 Free PMC article.
References
- Fukuoka M, Yano S, Giaccone G, et al. Multiinstitutional randomized phase II trial of gefitinib for previously treated patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (The IDEAL 1 trial) [corrected] J Clin Oncol. 2003;21:2237–2246. - PubMed
- Kris MG, Natale RB, Herbst RS, et al. Efficacy of gefitinib, an inhibitor of the epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase, in symptomatic patients with non-small cell lung cancer: a randomized trial. JAMA. 2003;290:2149–2158. - PubMed
- Perez-Soler R, Chachoua A, Hammond LA, et al. Determinants of tumor response and survival with erlotinib in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22:3238–3247. - PubMed
- Shepherd FA, Rodrigues Pereira J, Ciuleanu T, et al. Erlotinib in previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:123–132. - PubMed
- Cappuzzo F, Hirsch FR, Rossi E, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor gene and protein and gefitinib sensitivity in non-small-cell lung cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2005;97:643–655. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous