IDN1 and IDN2 are required for de novo DNA methylation in Arabidopsis thaliana - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2009 Dec;16(12):1325-7.
doi: 10.1038/nsmb.1690. Epub 2009 Nov 15.
Affiliations
- PMID: 19915591
- PMCID: PMC2842998
- DOI: 10.1038/nsmb.1690
IDN1 and IDN2 are required for de novo DNA methylation in Arabidopsis thaliana
Israel Ausin et al. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2009 Dec.
Abstract
DNA methylation is an epigenetic mark affecting genes and transposons. Screening for mutants that fail to establish DNA methylation yielded two we termed "involved in de novo" (idn) 1 and 2. IDN1 encodes DMS3, an SMC-related protein, and IDN2 encodes a previously unknown double-stranded RNA-binding protein with homology to SGS3. IDN1 and IDN2 control de novo methylation and small interfering RNA (siRNA)-mediated maintenance methylation and are components of the RNA-directed DNA methylation pathway.
Figures
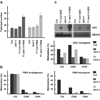
Figure 1. De novo methylation phenotype of idn mutants
a) Flowering time measured as total number of leaves produced by wild type, idn mutants and FWA transformed T1 plants under long day conditions. Error bars depict standard deviation. b) Methylation status of wild type and idn mutants at endogenous and transgenic FWA. c) SDC expression levels in idn mutants before and after SDC transformation. Hybridization with a UBQ10 probe is shown as loading control. Panel below shows methylation status of wild type and idn mutants at transgenic SDC.
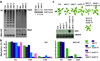
Figure 2. Maintenance methylation phenotype of idn mutants
a) Methylation sensitive enzyme Southern hybridization assay at 5S and MEA-ISR loci, and HaeIII cutting assay at AtSN1. HaeIII, is blocked by C methylation in GGCC context, HpaII is blocked by C methylation in CCGG context and MspI is blocked by methylation of the external C in CCGG context. b) Methylation status of wild type, idn and idn cmt3–11 double mutants at endogenous SDC and methylation status of wild type and idn mutants at MEA-ISR. c) Morphological and molecular phenotype of idn cmt3–11 double mutants.
Similar articles
- A subgroup of SGS3-like proteins act redundantly in RNA-directed DNA methylation.
Xie M, Ren G, Costa-Nunes P, Pontes O, Yu B. Xie M, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 May;40(10):4422-31. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks034. Epub 2012 Feb 1. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22302148 Free PMC article. - INVOLVED IN DE NOVO 2-containing complex involved in RNA-directed DNA methylation in Arabidopsis.
Ausin I, Greenberg MV, Simanshu DK, Hale CJ, Vashisht AA, Simon SA, Lee TF, Feng S, Española SD, Meyers BC, Wohlschlegel JA, Patel DJ, Jacobsen SE. Ausin I, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 May 29;109(22):8374-81. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1206638109. Epub 2012 May 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22592791 Free PMC article. - IDN2 has a role downstream of siRNA formation in RNA-directed DNA methylation.
Finke A, Kuhlmann M, Mette MF. Finke A, et al. Epigenetics. 2012 Aug;7(8):950-60. doi: 10.4161/epi.21237. Epub 2012 Jul 19. Epigenetics. 2012. PMID: 22810086 Free PMC article. - Mechanisms underlying epigenetic regulation in Arabidopsis thaliana.
Jones AL, Sung S. Jones AL, et al. Integr Comp Biol. 2014 Jul;54(1):61-7. doi: 10.1093/icb/icu030. Epub 2014 May 7. Integr Comp Biol. 2014. PMID: 24808013 Free PMC article. Review. - Advances of RNA polymerase IV in controlling DNA methylation and development in plants.
Xu MX, Zhou M. Xu MX, et al. Yi Chuan. 2022 Jul 20;44(7):567-580. doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.22-063. Yi Chuan. 2022. PMID: 35858769 Review.
Cited by
- Regulation and function of DNA methylation in plants and animals.
He XJ, Chen T, Zhu JK. He XJ, et al. Cell Res. 2011 Mar;21(3):442-65. doi: 10.1038/cr.2011.23. Epub 2011 Feb 15. Cell Res. 2011. PMID: 21321601 Free PMC article. Review. - Long non-coding RNA and chromatin remodeling.
Han P, Chang CP. Han P, et al. RNA Biol. 2015;12(10):1094-8. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2015.1063770. Epub 2015 Jul 15. RNA Biol. 2015. PMID: 26177256 Free PMC article. Review. - Multisubunit RNA polymerases IV and V: purveyors of non-coding RNA for plant gene silencing.
Haag JR, Pikaard CS. Haag JR, et al. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2011 Jul 22;12(8):483-92. doi: 10.1038/nrm3152. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21779025 Review. - Identification of genes required for de novo DNA methylation in Arabidopsis.
Greenberg MV, Ausin I, Chan SW, Cokus SJ, Cuperus JT, Feng S, Law JA, Chu C, Pellegrini M, Carrington JC, Jacobsen SE. Greenberg MV, et al. Epigenetics. 2011 Mar;6(3):344-54. doi: 10.4161/epi.6.3.14242. Epub 2011 Mar 1. Epigenetics. 2011. PMID: 21150311 Free PMC article. - RNA-directed DNA methylation: an epigenetic pathway of increasing complexity.
Matzke MA, Mosher RA. Matzke MA, et al. Nat Rev Genet. 2014 Jun;15(6):394-408. doi: 10.1038/nrg3683. Epub 2014 May 8. Nat Rev Genet. 2014. PMID: 24805120 Review.
References
- Chan SW, et al. Science. 2004;303:1336. - PubMed
- Cao X, Jacobsen SE. Curr Biol. 2002;12:1138–1144. - PubMed
- Henderson IR, Jacobsen SE. Nature. 2007;447:418–424. - PubMed
- Li CF, et al. Cell. 2006;126:93–106. - PubMed
- Pontes O, et al. Cell. 2006;126:79–92. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- R01 GM060398/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 GM060398/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM60398/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases