Functional variation of the dopamine D2 receptor gene is associated with emotional control as well as brain activity and connectivity during emotion processing in humans - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2009 Nov 25;29(47):14812-9.
doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3609-09.2009.
Luciana Lo Bianco, Paolo Taurisano, Barbara Gelao, Raffaella Romano, Leonardo Fazio, Apostolos Papazacharias, Annabella Di Giorgio, Grazia Caforio, Antonio Rampino, Rita Masellis, Audrey Papp, Gianluca Ursini, Lorenzo Sinibaldi, Teresa Popolizio, Wolfgang Sadee, Alessandro Bertolino
Affiliations
- PMID: 19940176
- PMCID: PMC2834475
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3609-09.2009
Functional variation of the dopamine D2 receptor gene is associated with emotional control as well as brain activity and connectivity during emotion processing in humans
Giuseppe Blasi et al. J Neurosci. 2009.
Abstract
Personality traits related to emotion processing are, at least in part, heritable and genetically determined. Dopamine D(2) receptor signaling is involved in modulation of emotional behavior and activity of associated brain regions such as the amygdala and the prefrontal cortex. An intronic single nucleotide polymorphism within the D(2) receptor gene (DRD2) (rs1076560, guanine > thymine or G > T) shifts splicing of the two protein isoforms (D(2) short, mainly presynaptic, and D(2) long) and has been associated with modulation of memory performance and brain activity. Here, our aim was to investigate the association of DRD2 rs1076560 genotype with personality traits of emotional stability and with brain physiology during processing of emotionally relevant stimuli. DRD2 genotype and Big Five Questionnaire scores were evaluated in 134 healthy subjects demonstrating that GG subjects have reduced "emotion control" compared with GT subjects. Functional magnetic resonance imaging in a sample of 24 individuals indicated greater amygdala activity during implicit processing and greater dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC) response during explicit processing of facial emotional stimuli in GG subjects compared with GT. Other results also demonstrate an interaction between DRD2 genotype and facial emotional expression on functional connectivity of both amygdala and dorsolateral prefrontal regions with overlapping medial prefrontal areas. Moreover, rs1076560 genotype is associated with differential relationships between amygdala/DLPFC functional connectivity and emotion control scores. These results suggest that genetically determined D(2) signaling may explain part of personality traits related to emotion processing and individual variability in specific brain responses to emotionally relevant inputs.
Figures
Figure 1.
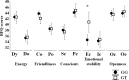
Plots showing the association of DRD2 rs1076560 with BFQ scores. Only the emotion control facet was significantly different between the two genotype groups. *p < 0.05. For statistics, see Results. Dy, Dynamism; DO, dominance; Co, cooperativeness; Po, politeness; Sc, scrupulousness; Pe, perseverance; Ec, emotion control; Ic, impulse control; Oc, openness to culture; Oe, openness to experience; Conscient, conscientiousness.
Figure 2.
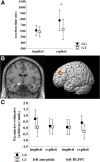
A, Plot showing reaction time data during implicit and explicit processing of faces stimuli. For statistics, see Results. *p < 0.05. B, Coronal section and rendered image showing brain regions in which a DRD2 rs1076560 genotype × task interaction was present, i.e., left amygdala and left lateral prefrontal cortex. C, For illustrative purposes, parameter estimates extracted from clusters shown in A displaying BOLD response in left amygdala and left lateral prefrontal cortex during the implicit and the explicit part of the task as a function of DRD2 rs1076560 genotype.
Figure 3.
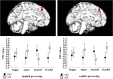
Rendered images of sagittal sections of the brain showing medial prefrontal clusters in which significant interaction between DRD2 rs1076560 and facial expressions was present on functional connectivity with left amygdala during implicit processing (left) and with left DLPFC during explicit processing (right). Mean ± SE. PPI values are shown in the plots.
Figure 4.
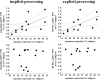
Scatter plots showing relationships between mean PPI values of emotionally charged faces (angry, fearful, and happy) extracted from clusters displayed in Figure 3 during implicit (x, y, z: −15, 38, 49) (left scatter plots) and explicit (x, y, z: −15, 41, 45) (right scatter plots) processing and emotion control scores as measured with the BFQ. In GT individuals, positive relationships are present during both implicit and explicit processing, whereas in GG subjects, no such relationships have been found. For statistics, see Results. mPFC, Medial prefrontal cortex.
Similar articles
- DRD2 genotype-based variation of default mode network activity and of its relationship with striatal DAT binding.
Sambataro F, Fazio L, Taurisano P, Gelao B, Porcelli A, Mancini M, Sinibaldi L, Ursini G, Masellis R, Caforio G, Di Giorgio A, Niccoli-Asabella A, Popolizio T, Blasi G, Bertolino A. Sambataro F, et al. Schizophr Bull. 2013 Jan;39(1):206-16. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbr128. Epub 2011 Oct 5. Schizophr Bull. 2013. PMID: 21976709 Free PMC article. - DRD2 polymorphisms modulate reward and emotion processing, dopamine neurotransmission and openness to experience.
Peciña M, Mickey BJ, Love T, Wang H, Langenecker SA, Hodgkinson C, Shen PH, Villafuerte S, Hsu D, Weisenbach SL, Stohler CS, Goldman D, Zubieta JK. Peciña M, et al. Cortex. 2013 Mar;49(3):877-90. doi: 10.1016/j.cortex.2012.01.010. Epub 2012 Feb 14. Cortex. 2013. PMID: 22424959 Free PMC article. - Genetically determined measures of striatal D2 signaling predict prefrontal activity during working memory performance.
Bertolino A, Taurisano P, Pisciotta NM, Blasi G, Fazio L, Romano R, Gelao B, Lo Bianco L, Lozupone M, Di Giorgio A, Caforio G, Sambataro F, Niccoli-Asabella A, Papp A, Ursini G, Sinibaldi L, Popolizio T, Sadee W, Rubini G. Bertolino A, et al. PLoS One. 2010 Feb 22;5(2):e9348. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0009348. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20179754 Free PMC article. - Anatomical insights into the interaction of emotion and cognition in the prefrontal cortex.
Ray RD, Zald DH. Ray RD, et al. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2012 Jan;36(1):479-501. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2011.08.005. Epub 2011 Aug 25. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2012. PMID: 21889953 Free PMC article. Review. - Emotion, cognition, and mental state representation in amygdala and prefrontal cortex.
Salzman CD, Fusi S. Salzman CD, et al. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2010;33:173-202. doi: 10.1146/annurev.neuro.051508.135256. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20331363 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- mRNA transcript diversity creates new opportunities for pharmacological intervention.
Barrie ES, Smith RM, Sanford JC, Sadee W. Barrie ES, et al. Mol Pharmacol. 2012 May;81(5):620-30. doi: 10.1124/mol.111.076604. Epub 2012 Feb 7. Mol Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22319206 Free PMC article. Review. - Association between Ability Emotional Intelligence and Left Insula during Social Judgment of Facial Emotions.
Quarto T, Blasi G, Maddalena C, Viscanti G, Lanciano T, Soleti E, Mangiulli I, Taurisano P, Fazio L, Bertolino A, Curci A. Quarto T, et al. PLoS One. 2016 Feb 9;11(2):e0148621. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0148621. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26859495 Free PMC article. - BDNF rs6265 methylation and genotype interact on risk for schizophrenia.
Ursini G, Cavalleri T, Fazio L, Angrisano T, Iacovelli L, Porcelli A, Maddalena G, Punzi G, Mancini M, Gelao B, Romano R, Masellis R, Calabrese F, Rampino A, Taurisano P, Di Giorgio A, Keller S, Tarantini L, Sinibaldi L, Quarto T, Popolizio T, Caforio G, Blasi G, Riva MA, De Blasi A, Chiariotti L, Bollati V, Bertolino A. Ursini G, et al. Epigenetics. 2016;11(1):11-23. doi: 10.1080/15592294.2015.1117736. Epub 2016 Feb 18. Epigenetics. 2016. PMID: 26889735 Free PMC article. - A splicing-regulatory polymorphism in DRD2 disrupts ZRANB2 binding, impairs cognitive functioning and increases risk for schizophrenia in six Han Chinese samples.
Cohen OS, Weickert TW, Hess JL, Paish LM, McCoy SY, Rothmond DA, Galletly C, Liu D, Weinberg DD, Huang XF, Xu Q, Shen Y, Zhang D, Yue W, Yan J, Wang L, Lu T, He L, Shi Y, Xu M, Che R, Tang W, Chen CH, Chang WH, Hwu HG, Liu CM, Liu YL, Wen CC, Fann CS, Chang CC, Kanazawa T, Middleton FA, Duncan TM, Faraone SV, Weickert CS, Tsuang MT, Glatt SJ. Cohen OS, et al. Mol Psychiatry. 2016 Jul;21(7):975-82. doi: 10.1038/mp.2015.137. Epub 2015 Sep 8. Mol Psychiatry. 2016. PMID: 26347318 - Replication in Imaging Genetics: The Case of Threat-Related Amygdala Reactivity.
Avinun R, Nevo A, Knodt AR, Elliott ML, Hariri AR. Avinun R, et al. Biol Psychiatry. 2018 Jul 15;84(2):148-159. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2017.11.010. Epub 2017 Nov 16. Biol Psychiatry. 2018. PMID: 29279201 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Arnsten AF, Li BM. Neurobiology of executive functions: catecholamine influences on prefrontal cortical functions. Biol Psychiatry. 2005;57:1377–1384. - PubMed
- Bertolino A, Caforio G, Blasi G, De Candia M, Latorre V, Petruzzella V, Altamura M, Nappi G, Papa S, Callicott JH, Mattay VS, Bellomo A, Scarabino T, Weinberger DR, Nardini M. Interaction of COMT Val108/158 Met genotype and olanzapine treatment on prefrontal cortical function in patients with schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry. 2004;161:1798–1805. - PubMed
- Bertolino A, Arciero G, Rubino V, Latorre V, De Candia M, Mazzola V, Blasi G, Caforio G, Hariri A, Kolachana B, Nardini M, Weinberger DR, Scarabino T. Variation of human amygdala response during threatening stimuli as a function of 5′HTTLPR genotype and personality style. Biol Psychiatry. 2005;57:1517–1525. - PubMed
- Bertolino A, Fazio L, Caforio G, Blasi G, Rampino A, Romano R, Di Giorgio A, Taurisano P, Papp A, Pinsonneault J, Wang D, Nardini M, Popolizio T, Sadee W. Functional variants of the dopamine receptor D2 gene modulate prefronto-striatal phenotypes in schizophrenia. Brain. 2009a;132:417–425. - PMC - PubMed
- Bertolino A, Fazio L, Di Giorgio A, Blasi G, Romano R, Taurisano P, Caforio G, Sinibaldi L, Ursini G, Popolizio T, Tirotta E, Papp A, Dallapiccola B, Borrelli E, Sadee W. Genetically determined interaction between the dopamine transporter and the D2 receptor on prefronto-striatal activity and volume in humans. J Neurosci. 2009b;29:1224–1234. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous