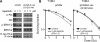Radiosensitization of epidermal growth factor receptor/HER2-positive pancreatic cancer is mediated by inhibition of Akt independent of ras mutational status - PubMed (original) (raw)
Radiosensitization of epidermal growth factor receptor/HER2-positive pancreatic cancer is mediated by inhibition of Akt independent of ras mutational status
Randall J Kimple et al. Clin Cancer Res. 2010.
Abstract
Purpose: Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) family members (e.g., EGFR, HER2, HER3, and HER4) are commonly overexpressed in pancreatic cancer. We investigated the effects of inhibition of EGFR/HER2 signaling on pancreatic cancer to elucidate the role(s) of EGFR/HER2 in radiosensitization and to provide evidence in support of further clinical investigations.
Experimental design: Expression of EGFR family members in pancreatic cancer lines was assessed by quantitative reverse transcription-PCR. Cell growth inhibition was determined by MTS assay. The effects of inhibition of EGFR family receptors and downstream signaling pathways on in vitro radiosensitivity were evaluated using clonogenic assays. Growth delay was used to evaluate the effects of nelfinavir on in vivo tumor radiosensitivity.
Results: Lapatinib inhibited cell growth in four pancreatic cancer cell lines, but radiosensitized only wild-type K-ras-expressing T3M4 cells. Akt activation was blocked in a wild-type K-ras cell line, whereas constitutive phosphorylation of Akt and extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) was seen in lines expressing mutant K-ras. Overexpression of constitutively active K-ras (G12V) abrogated lapatinib-mediated inhibition of both Akt phosphorylation and radiosensitization. Inhibition of MAP/ERK kinase/ERK signaling with U0126 had no effect on radiosensitization, whereas inhibition of activated Akt with LY294002 (enhancement ratio, 1.2-1.8) or nelfinavir (enhancement ratio, 1.2-1.4) radiosensitized cells regardless of K-ras mutation status. Oral nelfinavir administration to mice bearing mutant K-ras-containing Capan-2 xenografts resulted in a greater than additive increase in radiation-mediated tumor growth delay (synergy assessment ratio of 1.5).
Conclusions: Inhibition of EGFR/HER2 enhances radiosensitivity in wild-type K-ras pancreatic cancer. Nelfinavir, and other phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt inhibitors, are effective pancreatic radiosensitizers regardless of K-ras mutation status.
Figures
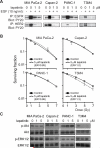
FIGURE 1. Lapatinib inhibits EGFR and HER2 but does not radiosensitize pancreatic cancer cells
A, Lapatinib inhibits EGF-induced activation of EGFR and HER2 in all four cell lines. Cells were serum-starved and treated with lapatinib and/or EGF. Lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-EGFR or anti-HER2 antibodies and then immunoblotted with an anti-phosphotyrosine antibody. B, T3M4 cells harvoring wild-type K-ras were radiosensitized by lapatinib treatment (p<0.0001) whereas lines harboring mutant K-ras (MIA PaCa-2, Capan-2, and PANC-1) were not radiosensitized by lapatinib. Plating efficiency of unirradiated cells in the presence or absence of lapatinib was not significantly different for any cell line. C, Lapatinib strongly inhibits constitutive phosphorylation of Akt in T3M4 cells harboring wild-type K-ras whereas cells harboring K-ras mutations (Capan-2, MIA PaCa-2 and PANC-1) show little/no inhibition of Akt phosphorylation. Cells were treated with lapatinib at the indicated doses for 2 hours and protein lysates collected and analyzed by western blot analysis with indicated antibodies.
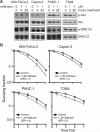
FIGURE 2. Ectopic expression of mutant K-ras abrogates lapatinib-mediated radiosensitization of T3M4 cells
A, T3M4 cells were transfected with either empty vector (pCGN) or pCGN-K-ras(G12V)-HA, subjected to treatment with lapatinib (5 μM) or DMSO vehicle for 2 hours and protein lysates harvested and analyzed by western blot analysis with antibodies against p-ERK1/2, ERK1/2, p-Akt or Akt. Expression of K-ras(G12V) blocked lapatinib-mediated Akt inhibition in T3M4 cells. B, Clonogenic survival assays of T3M4 cells transfected with pCGN vector control showed radiosensitization by lapatinib (p<0.0001) whereas cells expressing pCGN-K-ras(G12V)-HA were completely resistant to the radiosensitizing effect of lapatinib treatment. Plating efficiency of unirradiated cells in the presence or absence of lapatinib was not significantly different for any cell line.
FIGURE 3. Pancreatic cancer cells are radiosensitized by inhibition of PI3K/Akt
A, Akt phosphorylation is inhibited by treatment with LY294002 (5, 10, or 20 μM) but not DMSO control for 2 hours prior to collection of protein lysates and analysis by western blot. B, In clonogenic survival assays, LY294002 (10 μM) radiosensitized all pancreatic cancer cell lines tested, regardless of K-ras mutation status (p ≤ 0.002 for each). Plating efficiency of unirradiated cells in the presence or absence of LY294002 was not significantly different for any cell line.
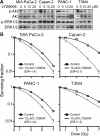
FIGURE 4. Nelfinavir inhibits Akt phosphorylation and radiosensitizes both wild-type and mutant K-ras pancreatic cell lines
A, Cells were treated with nelfinavir (1 μM) for 4 or 28 h, and levels of p-ERK1/2 and p-Akt assessed by western blotting as above. After 28 hours, phosphorylation of Akt, but not ERK1/2, was decreased. B, All cell lines tested were radiosensitized following pretreatment with nelfinavir (1 μM) for 26 hours prior to and 2 hours after radiation.
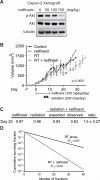
FIGURE 5. Nelfinavir inhibits Akt phosphorylation and radiosensitizes Capan-2 xenografts
A, Capan-2 cells (5 × 106) were injected into the flank of nude mice and allowed to grow until palpable, prior to initiating treatment with indicated doses of nelfinavir administered via gastric gavage once daily. Mice were sacrificed on the 5th day of therapy and cellular lysates analyzed by western blot for total-Akt, phospho-Akt, and α-tubulin. B, Mean tumor volumes (n=6 per group). C, Fractional product values showing synergy for nelfinavir plus radiation treatment with an observed:expected ratio of 1.5 ± 0.27 at day 25. D, Cumulative surviving fraction (CSF) following multiple small doses of radiation alone (solid line) and radiation + nelfinavir (dotted line). Based on the surviving fraction after 2 Gy (SF2Gy) for Capan-2 cells (Fig. 4B) treated with radiation alone (SF2Gy = 0.85) or radiation + nelfinavir (SF2Gy = 0.68), where CSF = SF2Gy^(# of 2 Gy fractions) and using the assumptions of no repopulation, reoxygenation, or redistribution and a constant SF2Gy over time.
Similar articles
- In pancreatic carcinoma, dual EGFR/HER2 targeting with cetuximab/trastuzumab is more effective than treatment with trastuzumab/erlotinib or lapatinib alone: implication of receptors' down-regulation and dimers' disruption.
Larbouret C, Gaborit N, Chardès T, Coelho M, Campigna E, Bascoul-Mollevi C, Mach JP, Azria D, Robert B, Pèlegrin A. Larbouret C, et al. Neoplasia. 2012 Feb;14(2):121-30. doi: 10.1593/neo.111602. Neoplasia. 2012. PMID: 22431920 Free PMC article. - Effects of the EGFR/HER2 kinase inhibitor GW572016 on EGFR- and HER2-overexpressing breast cancer cell line proliferation, radiosensitization, and resistance.
Zhou H, Kim YS, Peletier A, McCall W, Earp HS, Sartor CI. Zhou H, et al. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2004 Feb 1;58(2):344-52. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2003.09.046. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2004. PMID: 14751502 - Targeting epidermal growth factor receptor-associated signaling pathways in non-small cell lung cancer cells: implication in radiation response.
Choi EJ, Ryu YK, Kim SY, Wu HG, Kim JS, Kim IH, Kim IA. Choi EJ, et al. Mol Cancer Res. 2010 Jul;8(7):1027-36. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-09-0507. Epub 2010 Jun 29. Mol Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20587532 - Signaling inhibition with radiation in colorectal cancer: clinical trials.
McKenna WG, Muschel RJ, Gupta A, Hahn S, Bernhard EJ. McKenna WG, et al. Semin Oncol. 2003 Jun;30(3 Suppl 6):56-67. doi: 10.1016/s0093-7754(03)00126-x. Semin Oncol. 2003. PMID: 12802796 Review. - Modulating the tumor microenvironment to increase radiation responsiveness.
Karar J, Maity A. Karar J, et al. Cancer Biol Ther. 2009 Nov;8(21):1994-2001. doi: 10.4161/cbt.8.21.9988. Epub 2009 Nov 3. Cancer Biol Ther. 2009. PMID: 19823031 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- EGFR signaling promotes resistance to CHK1 inhibitor prexasertib in triple negative breast cancer.
Lee KJ, Wright G, Bryant H, Wiggins LA, Schuler M, Gassman NR. Lee KJ, et al. Cancer Drug Resist. 2020 Dec 5;3(4):980-991. doi: 10.20517/cdr.2020.73. eCollection 2020. Cancer Drug Resist. 2020. PMID: 35582228 Free PMC article. - Molecular pathways associated with oxidative stress and their potential applications in radiotherapy (Review).
Liu R, Bian Y, Liu L, Liu L, Liu X, Ma S. Liu R, et al. Int J Mol Med. 2022 May;49(5):65. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2022.5121. Epub 2022 Mar 16. Int J Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 35293589 Free PMC article. Review. - The Cellular Origins of Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts and Their Opposing Contributions to Pancreatic Cancer Growth.
Manoukian P, Bijlsma M, van Laarhoven H. Manoukian P, et al. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Sep 27;9:743907. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.743907. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34646829 Free PMC article. Review. - Drug Repurposing, an Attractive Strategy in Pancreatic Cancer Treatment: Preclinical and Clinical Updates.
De Lellis L, Veschi S, Tinari N, Mokini Z, Carradori S, Brocco D, Florio R, Grassadonia A, Cama A. De Lellis L, et al. Cancers (Basel). 2021 Aug 5;13(16):3946. doi: 10.3390/cancers13163946. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34439102 Free PMC article. Review. - The Anti-Cancer Properties of the HIV Protease Inhibitor Nelfinavir.
Subeha MR, Telleria CM. Subeha MR, et al. Cancers (Basel). 2020 Nov 19;12(11):3437. doi: 10.3390/cancers12113437. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33228205 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- American Cancer Society . Cancer Facts and Figures 2007. American Cancer Society; Atlanta: 2007.
- Harari PM, Huang SM. Radiation response modification following molecular inhibition of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling. Semin Radiat Oncol. 2001;11:281–9. - PubMed
- Moore MJ, Goldstein D, Hamm J, et al. Erlotinib plus gemcitabine compared with gemcitabine alone in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer: a phase III trial of the National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:1960–6. - PubMed
- Yamanaka Y, Friess H, Kobrin MS, Buchler M, Beger HG, Korc M. Coexpression of epidermal growth factor receptor and ligands in human pancreatic cancer is associated with enhanced tumor aggressiveness. Anticancer Res. 1993;13:565–9. - PubMed
- Dong M, Nio Y, Guo KJ, Tamura K, Tian YL, Dong YT. Epidermal growth factor and its receptor as prognostic indicators in Chinese patients with pancreatic cancer. Anticancer Res. 1998;18:4613–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 1-P50-CA106991-01/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA009688/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- L30 CA130159-01/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 2-T32-CA009688/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA115888/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA115888-03/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA106991-04/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA115888-02/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA106991/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA115888-04/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- L30 CA130159/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous