Differential phosphoproteomics of fibroblast growth factor signaling: identification of Src family kinase-mediated phosphorylation events - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2010 May 7;9(5):2317-28.
doi: 10.1021/pr9010475.
Affiliations
- PMID: 20225815
- PMCID: PMC2950672
- DOI: 10.1021/pr9010475
Free PMC article
Differential phosphoproteomics of fibroblast growth factor signaling: identification of Src family kinase-mediated phosphorylation events
Debbie L Cunningham et al. J Proteome Res. 2010.
Free PMC article
Abstract
Activation of signal transduction by the receptor tyrosine kinase, fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR), results in a cascade of protein-protein interactions that rely on the occurrence of specific tyrosine phosphorylation events. One such protein recruited to the activated receptor complex is the nonreceptor tyrosine kinase, Src, which is involved in both initiation and termination of further signaling events. To gain a further understanding of the tyrosine phosphorylation events that occur during FGF signaling, with a specific focus on those that are dependent on Src family kinase (SFK) activity, we have applied SILAC combined with chemical inhibition of SFK activity to search for phosphorylation events that are dependent on SFK activity in FGF stimulated cells. In addition, we used a more targeted approach to carry out high coverage phosphopeptide mapping of one Src substrate protein, the multifunctional adaptor Dok1, and to identify SFK-dependent Dok1 binding partners. From these analyses we identify 80 SFK-dependent phosphorylation events on 40 proteins. We further identify 18 SFK-dependent Dok1 interactions and 9 SFK-dependent Dok1 phosphorylation sites, 6 of which had not previously been known to be SFK-dependent.
Figures
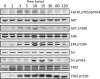
Figure 1
Profiles of phosphorylation events in the presence of FGF2. NIH 3T3s were stimulated with 20 ng/mL FGF2 for varying lengths of time. Western blot analysis was carried out on whole cell lysates using antibodies against indicated proteins and phospho-proteins.
Figure 2
Representative mass spectra for identification and site localization of tyrosine phosphorylation. (a) Afadin is phosphorylated at pY203. (b) Catenin delta-1 is phosphorylated at pY865. Peptides are labeled with 13C(6),15N(4) Arg and 13C(6) Lys. pY indicates phosphotyrosine.
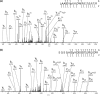
Figure 3
Partial co-elution of isobaric phosphopeptides. The Dok1 peptide LPSPPGPQELLDSPPALYAEPLDSLR is present in three different singly phosphorylated forms, with phosphorylation occurring at Ser281, Ser291, and Tyr296. The selected-ion chromatogram for the [M + 3H]3+ light precursor is shown. Comparison of the heavy/light ratios for the three versions indicates that only Tyr296 is Src-dependent.
Similar articles
- Phosphoproteomics Analysis Identifies Novel Candidate Substrates of the Nonreceptor Tyrosine Kinase, _S_rc-_r_elated Kinase Lacking C-terminal Regulatory Tyrosine and N-terminal _M_yristoylation _S_ites (SRMS).
Goel RK, Paczkowska M, Reimand J, Napper S, Lukong KE. Goel RK, et al. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2018 May;17(5):925-947. doi: 10.1074/mcp.RA118.000643. Epub 2018 Mar 1. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2018. PMID: 29496907 Free PMC article. - A nuclear export signal and phosphorylation regulate Dok1 subcellular localization and functions.
Niu Y, Roy F, Saltel F, Andrieu-Soler C, Dong W, Chantegrel AL, Accardi R, Thépot A, Foiselle N, Tommasino M, Jurdic P, Sylla BS. Niu Y, et al. Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Jun;26(11):4288-301. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01817-05. Mol Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16705178 Free PMC article. - Identification of targets of c-Src tyrosine kinase by chemical complementation and phosphoproteomics.
Ferrando IM, Chaerkady R, Zhong J, Molina H, Jacob HK, Herbst-Robinson K, Dancy BM, Katju V, Bose R, Zhang J, Pandey A, Cole PA. Ferrando IM, et al. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2012 Aug;11(8):355-69. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M111.015750. Epub 2012 Apr 12. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2012. PMID: 22499769 Free PMC article. - Src family kinases: regulation of their activities, levels and identification of new pathways.
Ingley E. Ingley E. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008 Jan;1784(1):56-65. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2007.08.012. Epub 2007 Aug 22. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008. PMID: 17905674 Review. - New Structural Perspectives in G Protein-Coupled Receptor-Mediated Src Family Kinase Activation.
Berndt S, Liebscher I. Berndt S, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 17;22(12):6489. doi: 10.3390/ijms22126489. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34204297 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Role of bFGF in Acquired Resistance upon Anti-VEGF Therapy in Cancer.
Zahra FT, Sajib MS, Mikelis CM. Zahra FT, et al. Cancers (Basel). 2021 Mar 20;13(6):1422. doi: 10.3390/cancers13061422. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33804681 Free PMC article. Review. - Regulation of fibroblast growth factor receptor signalling and trafficking by Src and Eps8.
Auciello G, Cunningham DL, Tatar T, Heath JK, Rappoport JZ. Auciello G, et al. J Cell Sci. 2013 Jan 15;126(Pt 2):613-24. doi: 10.1242/jcs.116228. Epub 2012 Nov 30. J Cell Sci. 2013. PMID: 23203811 Free PMC article. - P2X(7) receptor antagonists display agonist-like effects on cell signaling proteins.
Hedden L, Benes CH, Soltoff SP. Hedden L, et al. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011 May;1810(5):532-42. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2011.03.009. Epub 2011 Mar 21. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011. PMID: 21397667 Free PMC article. - Structural insights into FRS2α PTB domain recognition by neurotrophin receptor TrkB.
Zeng L, Kuti M, Mujtaba S, Zhou MM. Zeng L, et al. Proteins. 2014 Jul;82(7):1534-41. doi: 10.1002/prot.24523. Proteins. 2014. PMID: 24470253 Free PMC article. - Pharmacological targeting of phosphoinositide lipid kinases and phosphatases in the immune system: success, disappointment, and new opportunities.
Blunt MD, Ward SG. Blunt MD, et al. Front Immunol. 2012 Aug 2;3:226. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2012.00226. eCollection 2012. Front Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22876243 Free PMC article.
References
- Itoh N.; Ornitz D. M. Functional evolutionary history of the mouse Fgf gene family. Dev. Dyn. 2008, 237 (1), 18–27. - PubMed
- Grose R.; Dickson C. Fibroblast growth factor signaling in tumorigenesis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2005, 16 (2), 179–86. - PubMed
- Katoh M. Cancer genomics and genetics of FGFR2 (Review). Int. J. Oncol. 2008, 33 (2), 233–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous