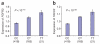A sequence variant at 4p16.3 confers susceptibility to urinary bladder cancer - PubMed (original) (raw)
doi: 10.1038/ng.558. Epub 2010 Mar 28.
Patrick Sulem, Soren Besenbacher, Sita H Vermeulen, Asgeir Sigurdsson, Gudmar Thorleifsson, Daniel F Gudbjartsson, Simon N Stacey, Julius Gudmundsson, Carlo Zanon, Jelena Kostic, Gisli Masson, Hjordis Bjarnason, Stefan T Palsson, Oskar B Skarphedinsson, Sigurjon A Gudjonsson, J Alfred Witjes, Anne J Grotenhuis, Gerald W Verhaegh, D Timothy Bishop, Sei Chung Sak, Ananya Choudhury, Faye Elliott, Jennifer H Barrett, Carolyn D Hurst, Petra J de Verdier, Charlotta Ryk, Peter Rudnai, Eugene Gurzau, Kvetoslava Koppova, Paolo Vineis, Silvia Polidoro, Simonetta Guarrera, Carlotta Sacerdote, Marcello Campagna, Donatella Placidi, Cecilia Arici, Maurice P Zeegers, Eliane Kellen, Berta Saez Gutierrez, José I Sanz-Velez, Manuel Sanchez-Zalabardo, Gabriel Valdivia, Maria D Garcia-Prats, Jan G Hengstler, Meinolf Blaszkewicz, Holger Dietrich, Roel A Ophoff, Leonard H van den Berg, Kristin Alexiusdottir, Kristleifur Kristjansson, Gudmundur Geirsson, Sigfus Nikulasson, Vigdis Petursdottir, Augustine Kong, Thorgeir Thorgeirsson, N Aydin Mungan, Annika Lindblom, Michael A van Es, Stefano Porru, Frank Buntinx, Klaus Golka, José I Mayordomo, Rajiv Kumar, Giuseppe Matullo, Gunnar Steineck, Anne E Kiltie, Katja K H Aben, Eirikur Jonsson, Unnur Thorsteinsdottir, Margaret A Knowles, Thorunn Rafnar, Kari Stefansson
Affiliations
- PMID: 20348956
- PMCID: PMC2923020
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.558
A sequence variant at 4p16.3 confers susceptibility to urinary bladder cancer
Lambertus A Kiemeney et al. Nat Genet. 2010 May.
Abstract
Previously, we reported germline DNA variants associated with risk of urinary bladder cancer (UBC) in Dutch and Icelandic subjects. Here we expanded the Icelandic sample set and tested the top 20 markers from the combined analysis in several European case-control sample sets, with a total of 4,739 cases and 45,549 controls. The T allele of rs798766 on 4p16.3 was found to associate with UBC (odds ratio = 1.24, P = 9.9 x 10(-12)). rs798766 is located in an intron of TACC3, 70 kb from FGFR3, which often harbors activating somatic mutations in low-grade, noninvasive UBC. Notably, rs798766[T] shows stronger association with low-grade and low-stage UBC than with more aggressive forms of the disease and is associated with higher risk of recurrence in low-grade stage Ta tumors. The frequency of rs798766[T] is higher in Ta tumors that carry an activating mutation in FGFR3 than in Ta tumors with wild-type FGFR3. Our results show a link between germline variants, somatic mutations of FGFR3 and risk of UBC.
Figures
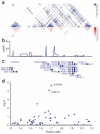
Figure 1
Schematic view of the structure and association results in the UBC-associated region on chromosome 4p16.3. (a) Pairwise correlation structure in an 800-kb interval (1.3–2.1 Mb, NCBI B35) on chromosome 4p16.3. The upper plot shows pairwise _D_’ for 292 common SNPs (with minor allele frequency > 5%) from the HapMap (v21) CEU dataset. The lower plot shows the corresponding _r_2 values. (b) Estimated recombination rates (saRR) in cM per Mb from the HapMap (v21) Phase II data. (c) Location of known genes in the region. (d) Schematic view of the association with bladder cancer for all SNPs tested in the region for the initial scan (Iceland and The Netherlands). The y axis shows the −log10 P value.
Figure 2
Correlation between genotypes of rs798766 and the expression of FGFR3 and TACC3 in adipose tissue from 604 individuals. (a) Expression of FGFR3. (b) Expression of TACC3. Expression is shown as 10(average MLR), where MLR is the mean log10 expression ratio and the average is taken over individuals with a particular genotype. Regression of the MLR values on the number of copies of the UBC risk variant rs798766[T] shows that the expression of FGFR3 is increased by an estimated 22.4% with each T allele carried, whereas the expression of TACC3 is increased by an estimated 9.1% with each allele. The effect of age and sex is taken into account in the regression by including the variables age, sex and the interaction of age × sex among the explanatory variables.
Comment in
- Word of wisdom. Re: a sequence variant at 4p16.3 confers susceptibility to urinary bladder cancer.
Zlotta AR. Zlotta AR. Eur Urol. 2010 Dec;58(6):943-4. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2010.09.022. Eur Urol. 2010. PMID: 21414868 No abstract available.
Similar articles
- Genetic polymorphisms on 8q24.1 and 4p16.3 are not linked with urothelial carcinoma of the bladder in contrast to their association with aggressive upper urinary tract tumours.
Yates DR, Rouprêt M, Drouin SJ, Audouin M, Cancel-Tassin G, Comperat E, Bitker MO, Cussenot O. Yates DR, et al. World J Urol. 2013 Feb;31(1):53-9. doi: 10.1007/s00345-012-0954-6. Epub 2012 Sep 28. World J Urol. 2013. PMID: 23053209 - Chromosome 4p16.3 variant modify bladder cancer risk in a Chinese population.
Wang M, Chu H, Yan F, Qin C, Li P, Yuan L, Yin C, Xu J, Zhang Z. Wang M, et al. Carcinogenesis. 2011 Jun;32(6):872-5. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgr060. Epub 2011 Mar 31. Carcinogenesis. 2011. PMID: 21459758 Free PMC article. - Plasma 25-hydroxyvitamin D(3) and bladder cancer risk according to tumor stage and FGFR3 status: a mechanism-based epidemiological study.
Amaral AF, Méndez-Pertuz M, Muñoz A, Silverman DT, Allory Y, Kogevinas M, Lloreta J, Rothman N, Carrato A, Rivas del Fresno M, Real FX, Malats N; Spanish Bladder Cancer/EPICURO Study investigators. Amaral AF, et al. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2012 Dec 19;104(24):1897-904. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djs444. Epub 2012 Oct 29. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2012. PMID: 23108201 Free PMC article. - Clinical significance of fibroblast growth factor receptor-3 mutations in bladder cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Liu X, Zhang W, Geng D, He J, Zhao Y, Yu L. Liu X, et al. Genet Mol Res. 2014 Feb 20;13(1):1109-20. doi: 10.4238/2014.February.20.12. Genet Mol Res. 2014. PMID: 24634132 Review. - Association between the TACC3 rs798766 Polymorphism and Risk of Urinary Bladder Cancer: A Synthesis Based on Current Evidence.
Meng XY, Shi MJ, Chen JF, Liao Y, Hu BW, Hireche A. Meng XY, et al. Dis Markers. 2017;2017:7850708. doi: 10.1155/2017/7850708. Epub 2017 Jun 5. Dis Markers. 2017. PMID: 28655970 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- TERT Polymorphism rs2736100-C Is Associated with EGFR Mutation-Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.
Wei R, Cao L, Pu H, Wang H, Zheng Y, Niu X, Weng X, Zhang H, Favus M, Zhang L, Jia W, Zeng Y, Amos CI, Lu S, Wang HY, Liu Y, Liu W. Wei R, et al. Clin Cancer Res. 2015 Nov 15;21(22):5173-5180. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-0009. Epub 2015 Jul 6. Clin Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 26149460 Free PMC article. - Genetic polymorphisms on 8q24.1 and 4p16.3 are not linked with urothelial carcinoma of the bladder in contrast to their association with aggressive upper urinary tract tumours.
Yates DR, Rouprêt M, Drouin SJ, Audouin M, Cancel-Tassin G, Comperat E, Bitker MO, Cussenot O. Yates DR, et al. World J Urol. 2013 Feb;31(1):53-9. doi: 10.1007/s00345-012-0954-6. Epub 2012 Sep 28. World J Urol. 2013. PMID: 23053209 - Genome-Wide Association Study Adjusted for Occupational and Environmental Factors for Bladder Cancer Susceptibility.
Takeuchi T, Hattori-Kato M, Okuno Y, Zaitsu M, Azuma T. Takeuchi T, et al. Genes (Basel). 2022 Feb 28;13(3):448. doi: 10.3390/genes13030448. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35328002 Free PMC article. - TP53 codon 72 polymorphism is associated with FGFR3 and RAS mutation in non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer.
Kawahara T, Kojima T, Kandori S, Kurobe M, Yoshino T, Kimura T, Nagumo Y, Ishituka R, Mitsuzuka K, Narita S, Kobayashi T, Matsui Y, Ogawa O, Sugimoto M, Miyazaki J, Nishiyama H. Kawahara T, et al. PLoS One. 2019 Aug 1;14(8):e0220173. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0220173. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31369573 Free PMC article. - TACC3 is essential for EGF-mediated EMT in cervical cancer.
Ha GH, Kim JL, Breuer EK. Ha GH, et al. PLoS One. 2013 Aug 1;8(8):e70353. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0070353. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23936413 Free PMC article.
References
- Parkin DM. The global burden of urinary bladder cancer. Scand. J. Urol. Nephrol. Suppl. 2008:12–20. - PubMed
- Knowles MA. Molecular subtypes of bladder cancer: Jekyll and Hyde or chalk and cheese? Carcinogenesis. 2006;27:361–373. - PubMed
- Murta-Nascimento C, et al. Risk of bladder cancer associated with family history of cancer: do low-penetrance polymorphisms account for the increase in risk? Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2007;16:1595–1600. - PubMed
- Aben KK, et al. Familial aggregation of urothelial cell carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer. 2002;98:274–278. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 10589/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- 12933/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- A11505/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- A7298/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical