Clinical responses observed with imatinib or sorafenib in melanoma patients expressing mutations in KIT - PubMed (original) (raw)
Case Reports
. 2010 Apr 13;102(8):1219-23.
doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6605635. Epub 2010 Apr 6.
Affiliations
- PMID: 20372153
- PMCID: PMC2856012
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6605635
Case Reports
Clinical responses observed with imatinib or sorafenib in melanoma patients expressing mutations in KIT
D Handolias et al. Br J Cancer. 2010.
Abstract
Background: Mutations in KIT are more frequent in specific melanoma subtypes, and response to KIT inhibition is likely to depend on the identified mutation.
Methods: A total of 32 patients with metastatic acral or mucosal melanoma were screened for mutations in KIT exons 11, 13 and 17.
Results: KIT mutations were found in 38% of mucosal and in 6% of acral melanomas. Three patients were treated with imatinib and one with sorafenib. All four patients responded to treatment, but three have since progressed within the brain.
Conclusion: The observed clinical responses support further investigation of KIT inhibitors in metastatic melanoma, selected according to KIT mutation status.
Figures
Figure 1
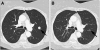
CT chest images of pulmonary metastasis arising from anal melanoma at baseline (A) and then at 3 months (B) showing reduction in the size of the lesion on imatinib (Case 1).
Figure 2
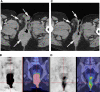
CT pelvis and FDG PET/CT images at baseline (A, B) and at 1 month (C, D) after treatment of a metastatic vulval melanoma with imatinib. Arrows indicate areas of response (Case 2).
Figure 3
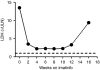
Marked LDH response within 2 weeks of commencing imatinib in a metastatic mucosal melanoma arising from the labia (Case 3). Dashed line indicates upper limit of the reference range.
Figure 4
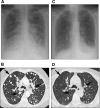
Chest X-ray and chest CT images at baseline (A, B) and then at 1 month (C, D) after treatment of a metastatic anal melanoma with sorafenib demonstrates significant reduction in the number and size of pulmonary metastases. Arrows indicate major sites of response (Case 4).
Similar articles
- KIT as a therapeutic target in metastatic melanoma.
Carvajal RD, Antonescu CR, Wolchok JD, Chapman PB, Roman RA, Teitcher J, Panageas KS, Busam KJ, Chmielowski B, Lutzky J, Pavlick AC, Fusco A, Cane L, Takebe N, Vemula S, Bouvier N, Bastian BC, Schwartz GK. Carvajal RD, et al. JAMA. 2011 Jun 8;305(22):2327-34. doi: 10.1001/jama.2011.746. JAMA. 2011. PMID: 21642685 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Imatinib for melanomas harboring mutationally activated or amplified KIT arising on mucosal, acral, and chronically sun-damaged skin.
Hodi FS, Corless CL, Giobbie-Hurder A, Fletcher JA, Zhu M, Marino-Enriquez A, Friedlander P, Gonzalez R, Weber JS, Gajewski TF, O'Day SJ, Kim KB, Lawrence D, Flaherty KT, Luke JJ, Collichio FA, Ernstoff MS, Heinrich MC, Beadling C, Zukotynski KA, Yap JT, Van den Abbeele AD, Demetri GD, Fisher DE. Hodi FS, et al. J Clin Oncol. 2013 Sep 10;31(26):3182-90. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2012.47.7836. Epub 2013 Jun 17. J Clin Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23775962 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Novel somatic KIT exon 8 mutation with dramatic response to imatinib in a patient with mucosal melanoma: a case report.
Rapisuwon S, Parks K, Al-Refaie W, Atkins MB. Rapisuwon S, et al. Melanoma Res. 2014 Oct;24(5):509-11. doi: 10.1097/CMR.0000000000000102. Melanoma Res. 2014. PMID: 25003536 - Anal mucosal melanoma with KIT-activating mutation and response to imatinib therapy--case report and review of the literature.
Satzger I, Küttler U, Völker B, Schenck F, Kapp A, Gutzmer R. Satzger I, et al. Dermatology. 2010;220(1):77-81. doi: 10.1159/000265558. Epub 2009 Dec 9. Dermatology. 2010. PMID: 19996579 Review. - A potential role for nilotinib in KIT-mutated melanoma.
Tran A, Tawbi HA. Tran A, et al. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2012 Jun;21(6):861-9. doi: 10.1517/13543784.2012.679341. Epub 2012 Apr 16. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2012. PMID: 22500535 Review.
Cited by
- Molecular-Targeted Therapy for Tumor-Agnostic Mutations in Acute Myeloid Leukemia.
Arai H, Minami Y, Chi S, Utsu Y, Masuda S, Aotsuka N. Arai H, et al. Biomedicines. 2022 Nov 22;10(12):3008. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10123008. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36551764 Free PMC article. Review. - Cancer genomics: from discovery science to personalized medicine.
Chin L, Andersen JN, Futreal PA. Chin L, et al. Nat Med. 2011 Mar;17(3):297-303. doi: 10.1038/nm.2323. Nat Med. 2011. PMID: 21383744 - Future of radiation therapy for malignant melanoma in an era of newer, more effective biological agents.
Khan MK, Khan N, Almasan A, Macklis R. Khan MK, et al. Onco Targets Ther. 2011;4:137-48. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S20257. Epub 2011 Aug 9. Onco Targets Ther. 2011. PMID: 21949607 Free PMC article. - Plasma Circulating Tumor DNA Levels for the Monitoring of Melanoma Patients: Landscape of Available Technologies and Clinical Applications.
Busser B, Lupo J, Sancey L, Mouret S, Faure P, Plumas J, Chaperot L, Leccia MT, Coll JL, Hurbin A, Hainaut P, Charles J. Busser B, et al. Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:5986129. doi: 10.1155/2017/5986129. Epub 2017 Apr 6. Biomed Res Int. 2017. PMID: 28484715 Free PMC article. Review. - Update on the targeted therapy of melanoma.
Johnson DB, Sosman JA. Johnson DB, et al. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2013 Jun;14(2):280-92. doi: 10.1007/s11864-013-0226-8. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23420410 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Altintas A, Cil T, Kilinc I, Kaplan MA, Ayyildiz O (2007) Central nervous system blastic crisis in chronic myeloid leukemia on imatinib mesylate therapy: a case report. J Neurooncol 84: 103–105 - PubMed
- Antonescu CR, Busam KJ, Francone TD, Wong GC, Guo T, Agaram NP, Besmer P, Jungbluth A, Gimbel M, Chen CT, Veach D, Clarkson BD, Paty PB, Weiser MR (2007) L576P KIT mutation in anal melanomas correlates with KIT protein expression and is sensitive to specific kinase inhibition. Int J Cancer 121: 257–264 - PubMed
- Beadling C, Jacobson-Dunlop E, Hodi FS, Le C, Warrick A, Patterson J, Town A, Harlow A, Cruz III F, Azar S, Rubin BP, Muller S, West R, Heinrich MC, Corless CL (2008) KIT gene mutations and copy number in melanoma subtypes. Clin Cancer Res 14: 6821–6828 - PubMed
- Breedveld P, Pluim D, Cipriani G, Wielinga P, van Tellingen O, Schinkel AH, Schellens JH (2005) The effect of Bcrp1 (Abcg2) on the in vivo pharmacokinetics and brain penetration of imatinib mesylate (Gleevec): implications for the use of breast cancer resistance protein and P-glycoprotein inhibitors to enable the brain penetration of imatinib in patients. Cancer Res 65: 2577–2582 - PubMed
- Curtin JA, Busam K, Pinkel D, Bastian BC (2006) Somatic activation of KIT in distinct subtypes of melanoma. J Clin Oncol 24: 4340–4346 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical