The val158met polymorphism of human catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) affects anterior cingulate cortex activation in response to painful laser stimulation - PubMed (original) (raw)
The val158met polymorphism of human catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) affects anterior cingulate cortex activation in response to painful laser stimulation
Arian Mobascher et al. Mol Pain. 2010.
Abstract
Background: Pain is a complex experience with sensory, emotional and cognitive aspects. Genetic and environmental factors contribute to pain-related phenotypes such as chronic pain states. Genetic variations in the gene coding for catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) have been suggested to affect clinical and experimental pain-related phenotypes including regional mu-opioid system responses to painful stimulation as measured by ligand-PET (positron emission tomography). The functional val158met single nucleotide polymorphism has been most widely studied. However, apart from its impact on pain-induced opioid release the effect of this genetic variation on cerebral pain processing has not been studied with activation measures such as functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), PET or electroencephalography. In the present fMRI study we therefore sought to investigate the impact of the COMT val158met polymorphism on the blood oxygen level-dependent (BOLD) response to painful laser stimulation.
Results: 57 subjects were studied. We found that subjects homozygous for the met158 allele exhibit a higher BOLD response in the anterior cingulate cortex (ACC), foremost in the mid-cingulate cortex, than carriers of the val158 allele.
Conclusion: This result is in line with previous studies that reported higher pain sensitivity in homozygous met carriers. It adds to the current literature in suggesting that this behavioral phenotype may be mediated by, or is at least associated with, increased ACC activity. More generally, apart from one report that focused on pain-induced opioid release, this is the first functional neuroimaging study showing an effect of the COMT val158met polymorphism on cerebral pain processing.
Figures
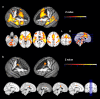
Figure 1
BOLD response to laser stimulation. a) Group average. N = 57 subjects. GLM whole-brain analysis. Second-level mixed-effects FLAME. Cluster-corrected threshold Z = 3.5, p = 0.05. Upper row: 3 D surface projection. Lower row: axial slices. R = right. L = left. b) Two-group t-test. _COMT_met/met (N = 19) vs. _COMT_val carriers (N = 38). Voxel-by-voxel analysis restricted to the anterior cingulate cortex (according to the Harvard Oxford atlas). Second-level mixed-effects FLAME. Cluster-corrected threshold Z = 2.3, p = 0.05. Upper row: 3 D surface projection. Lower row: sagittal slices.
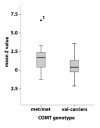
Figure 2
Boxplot of COMT genotype effect on fMRI BOLD activation in the anterior cingulate cortex (ACC). Median, 25th percentile, 75th percentile, minimum value, maximum value and outliers are shown. 1 The high BOLD activation in response to laser stimulation in this subject was reproduced in a second experiment that was performed two month later (mean Z value in the ACC = 5.3), suggesting that this 'outlier' is reflecting biological variance in the sample and not a measurement error. Furthermore, the genotype effect on ACC activation remained significant, (F = 7.06; p = 0.01; F = 4.92; p = 0.031 age-corrected) even when this subject was excluded from the analysis.
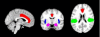
Figure 3
Regions of interests. Red - anterior cingulate cortex, blue - insula, green - parietal opercular cortex, purple = amygdalae.
Similar articles
- Effects of functional polymorphisms of opioid receptor mu 1 and catechol-O-methyltransferase on the neural processing of pain.
Cheong Y, Lee S, Okazawa H, Kosaka H, Jung M. Cheong Y, et al. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2024 May;78(5):300-308. doi: 10.1111/pcn.13648. Epub 2024 Feb 25. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38403942 Free PMC article. - Opposite effects of catechol-O-methyltransferase Val158Met on cortical function in healthy subjects and patients with schizophrenia.
Prata DP, Mechelli A, Fu CH, Picchioni M, Kane F, Kalidindi S, McDonald C, Howes O, Kravariti E, Demjaha A, Toulopoulou T, Diforti M, Murray RM, Collier DA, McGuire PK. Prata DP, et al. Biol Psychiatry. 2009 Mar 15;65(6):473-80. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2008.09.027. Epub 2008 Dec 3. Biol Psychiatry. 2009. PMID: 19054502 - The association between the Val158Met polymorphism of the catechol-O-methyl transferase gene and morphological abnormalities of the brain in chronic schizophrenia.
Ohnishi T, Hashimoto R, Mori T, Nemoto K, Moriguchi Y, Iida H, Noguchi H, Nakabayashi T, Hori H, Ohmori M, Tsukue R, Anami K, Hirabayashi N, Harada S, Arima K, Saitoh O, Kunugi H. Ohnishi T, et al. Brain. 2006 Feb;129(Pt 2):399-410. doi: 10.1093/brain/awh702. Epub 2005 Dec 5. Brain. 2006. PMID: 16330500 - The effects of catechol O-methyltransferase genotype on brain activation elicited by affective stimuli and cognitive tasks.
Heinz A, Smolka MN. Heinz A, et al. Rev Neurosci. 2006;17(3):359-67. doi: 10.1515/revneuro.2006.17.3.359. Rev Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16878403 Review. - Catechol-O-methyltransferase gene polymorphism and chronic human pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Tammimäki A, Männistö PT. Tammimäki A, et al. Pharmacogenet Genomics. 2012 Sep;22(9):673-91. doi: 10.1097/FPC.0b013e3283560c46. Pharmacogenet Genomics. 2012. PMID: 22722321 Review.
Cited by
- The polymorphism Val158Met in the COMT gene: disrupted dopamine system in fibromyalgia patients?
Gerra MC, Dallabona C, Manfredini M, Giordano R, Capriotti C, González-Villar A, Triñanes Y, Arendt-Nielsen L, Carrillo-de-la-Peña MT. Gerra MC, et al. Pain. 2024 Dec 1;165(12):e184-e189. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000003313. Epub 2024 Jun 25. Pain. 2024. PMID: 38916531 Free PMC article. - Persistent Catechol-O-methyltransferase-dependent Pain Is Initiated by Peripheral β-Adrenergic Receptors.
Ciszek BP, O'Buckley SC, Nackley AG. Ciszek BP, et al. Anesthesiology. 2016 May;124(5):1122-35. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000001070. Anesthesiology. 2016. PMID: 26950706 Free PMC article. - Alcohol dependence as a chronic pain disorder.
Egli M, Koob GF, Edwards S. Egli M, et al. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2012 Nov;36(10):2179-92. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2012.07.010. Epub 2012 Sep 11. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2012. PMID: 22975446 Free PMC article. Review. - Janus molecule I: dichotomous effects of COMT in neuropathic vs nociceptive pain modalities.
Segall SK, Maixner W, Belfer I, Wiltshire T, Seltzer Z, Diatchenko L. Segall SK, et al. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2012 May;11(3):222-35. doi: 10.2174/187152712800672490. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2012. PMID: 22483297 Free PMC article. Review. - Genetic contribution of catechol-O-methyltransferase in hippocampal structural and functional changes of female migraine sufferers.
Liu J, Lan L, Mu J, Zhao L, Yuan K, Zhang Y, Huang L, Liang F, Tian J. Liu J, et al. Hum Brain Mapp. 2015 May;36(5):1782-95. doi: 10.1002/hbm.22737. Epub 2015 Jan 19. Hum Brain Mapp. 2015. PMID: 25598522 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous