Whole exome capture in solution with 3 Gbp of data - PubMed (original) (raw)
doi: 10.1186/gb-2010-11-6-r62. Epub 2010 Jun 17.
Min Wang, Daniel L Burgess, Christie Kovar, Matthew J Rodesch, Mark D'Ascenzo, Jacob Kitzman, Yuan-Qing Wu, Irene Newsham, Todd A Richmond, Jeffrey A Jeddeloh, Donna Muzny, Thomas J Albert, Richard A Gibbs
Affiliations
- PMID: 20565776
- PMCID: PMC2911110
- DOI: 10.1186/gb-2010-11-6-r62
Whole exome capture in solution with 3 Gbp of data
Matthew N Bainbridge et al. Genome Biol. 2010.
Abstract
We have developed a solution-based method for targeted DNA capture-sequencing that is directed to the complete human exome. Using this approach allows the discovery of greater than 95% of all expected heterozygous singe base variants, requires as little as 3 Gbp of raw sequence data and constitutes an effective tool for identifying rare coding alleles in large scale genomic studies.
Figures
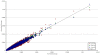
Figure 1
Normalized coverage of replicate SOLiD libraries 2 to 4 versus normalized coverage of replicate library 1. Average coverage for each target region in library 1 is plotted against library 2 (blue), library 3 (green) and library 4 (red). Coverage for each target is represented as a proportion of the total sequence generated. The line X = Y indicates approximately equal levels of coverage in both libraries.
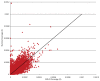
Figure 2
Average coverage for each target region as sequenced by Illumina 75-bp frag reads plotted against SOLiD library 1. Coverage for each target is normalized for the total sequence aligned to target. The line X = Y indicates approximately equal levels of coverage in both libraries.
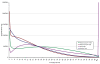
Figure 3
Coverage distribution across target regions of SOLiD libraries 1 (10 Gbp) and 2 (3 Gbp) and Illumina PE and frag libraries. The number of bases at each level of coverage for each library type is shown for approximately 10 Gbp of SOLiD data (green), approximately 3 Gbp of SOLiD data (red), approximately 3 Gbp of Illumina PE data (yellow) and approximately 3 Gbp of Illumian frag data (blue) after duplicate removal.
Similar articles
- Targeted enrichment beyond the consensus coding DNA sequence exome reveals exons with higher variant densities.
Bainbridge MN, Wang M, Wu Y, Newsham I, Muzny DM, Jefferies JL, Albert TJ, Burgess DL, Gibbs RA. Bainbridge MN, et al. Genome Biol. 2011 Jul 25;12(7):R68. doi: 10.1186/gb-2011-12-7-r68. Genome Biol. 2011. PMID: 21787409 Free PMC article. - Screening the human exome: a comparison of whole genome and whole transcriptome sequencing.
Cirulli ET, Singh A, Shianna KV, Ge D, Smith JP, Maia JM, Heinzen EL, Goedert JJ, Goldstein DB; Center for HIV/AIDS Vaccine Immunology (CHAVI). Cirulli ET, et al. Genome Biol. 2010;11(5):R57. doi: 10.1186/gb-2010-11-5-r57. Epub 2010 May 28. Genome Biol. 2010. PMID: 20598109 Free PMC article. - Targeted capture and massively parallel sequencing of 12 human exomes.
Ng SB, Turner EH, Robertson PD, Flygare SD, Bigham AW, Lee C, Shaffer T, Wong M, Bhattacharjee A, Eichler EE, Bamshad M, Nickerson DA, Shendure J. Ng SB, et al. Nature. 2009 Sep 10;461(7261):272-6. doi: 10.1038/nature08250. Epub 2009 Aug 16. Nature. 2009. PMID: 19684571 Free PMC article. - Multiplex amplification of large sets of human exons.
Porreca GJ, Zhang K, Li JB, Xie B, Austin D, Vassallo SL, LeProust EM, Peck BJ, Emig CJ, Dahl F, Gao Y, Church GM, Shendure J. Porreca GJ, et al. Nat Methods. 2007 Nov;4(11):931-6. doi: 10.1038/nmeth1110. Epub 2007 Oct 14. Nat Methods. 2007. PMID: 17934468 - Targeted high throughput sequencing of a cancer-related exome subset by specific sequence capture with a fully automated microarray platform.
Summerer D, Schracke N, Wu H, Cheng Y, Bau S, Stähler CF, Stähler PF, Beier M. Summerer D, et al. Genomics. 2010 Apr;95(4):241-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2010.01.006. Epub 2010 Feb 6. Genomics. 2010. PMID: 20138981
Cited by
- Oligonucleotide capture sequencing of the SARS-CoV-2 genome and subgenomic fragments from COVID-19 individuals.
Doddapaneni H, Cregeen SJ, Sucgang R, Meng Q, Qin X, Avadhanula V, Chao H, Menon V, Nicholson E, Henke D, Piedra FA, Rajan A, Momin Z, Kottapalli K, Hoffman KL, Sedlazeck FJ, Metcalf G, Piedra PA, Muzny DM, Petrosino JF, Gibbs RA. Doddapaneni H, et al. bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2020 Jul 27:2020.07.27.223495. doi: 10.1101/2020.07.27.223495. bioRxiv. 2020. PMID: 32766579 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint. - Whole genome sequencing analysis of Plasmodium vivax using whole genome capture.
Bright AT, Tewhey R, Abeles S, Chuquiyauri R, Llanos-Cuentas A, Ferreira MU, Schork NJ, Vinetz JM, Winzeler EA. Bright AT, et al. BMC Genomics. 2012 Jun 21;13:262. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-262. BMC Genomics. 2012. PMID: 22721170 Free PMC article. - Multiplex Chromosomal Exome Sequencing Accelerates Identification of ENU-Induced Mutations in the Mouse.
Sun M, Mondal K, Patel V, Horner VL, Long AB, Cutler DJ, Caspary T, Zwick ME. Sun M, et al. G3 (Bethesda). 2012 Jan;2(1):143-50. doi: 10.1534/g3.111.001669. Epub 2012 Jan 1. G3 (Bethesda). 2012. PMID: 22384391 Free PMC article. - Analysis of archived residual newborn screening blood spots after whole genome amplification.
Cantarel BL, Lei Y, Weaver D, Zhu H, Farrell A, Benstead-Hume G, Reese J, Finnell RH. Cantarel BL, et al. BMC Genomics. 2015 Aug 13;16(1):602. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-1747-2. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 26268606 Free PMC article. - Targeted enrichment beyond the consensus coding DNA sequence exome reveals exons with higher variant densities.
Bainbridge MN, Wang M, Wu Y, Newsham I, Muzny DM, Jefferies JL, Albert TJ, Burgess DL, Gibbs RA. Bainbridge MN, et al. Genome Biol. 2011 Jul 25;12(7):R68. doi: 10.1186/gb-2011-12-7-r68. Genome Biol. 2011. PMID: 21787409 Free PMC article.
References
- Gnirke A, Melnikov A, Maguire J, Rogov P, LeProust EM, Brockman W, Fennell T, Giannoukos G, Fisher S, Russ C, Gabriel S, Jaffe DB, Lander ES, Nusbaum C. Solution hybrid selection with ultra-long oligonucleotides for massively parallel targeted sequencing. Nat Biotechnol. 2009;27:182–189. doi: 10.1038/nbt.1523. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials