Chromosome 9p21 in sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in the UK and seven other countries: a genome-wide association study - PubMed (original) (raw)
Comparative Study
doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(10)70197-6.
Kin Mok, Stephen Newhouse, Michael E Weale, Bradley Smith, Caroline Vance, Lauren Johnson, Jan H Veldink, Michael A van Es, Leonard H van den Berg, Wim Robberecht, Philip Van Damme, Orla Hardiman, Anne E Farmer, Cathryn M Lewis, Amy W Butler, Olubunmi Abel, Peter M Andersen, Isabella Fogh, Vincenzo Silani, Adriano Chiò, Bryan J Traynor, Judith Melki, Vincent Meininger, John E Landers, Peter McGuffin, Jonathan D Glass, Hardev Pall, P Nigel Leigh, John Hardy, Robert H Brown Jr, John F Powell, Richard W Orrell, Karen E Morrison, Pamela J Shaw, Christopher E Shaw, Ammar Al-Chalabi
Affiliations
- PMID: 20801717
- PMCID: PMC3257853
- DOI: 10.1016/S1474-4422(10)70197-6
Comparative Study
Chromosome 9p21 in sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in the UK and seven other countries: a genome-wide association study
Aleksey Shatunov et al. Lancet Neurol. 2010 Oct.
Erratum in
- Lancet Neurol. 2011 Mar;10(3):205
Abstract
Background: Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a neurodegenerative disease of motor neurons that results in progressive weakness and death from respiratory failure, commonly within about 3 years. Previous studies have shown association of a locus on chromosome 9p with ALS and linkage with ALS-frontotemporal dementia. We aimed to test whether this genomic region is also associated with ALS in an independent set of UK samples, and to identify risk factors associated with ALS in a further genome-wide association study that combined data from the independent analysis with those from other countries.
Methods: We collected samples from patients with sporadic ALS from 20 UK hospitals and obtained UK control samples from the control groups of the Depression Case Control study, the Bipolar Affective Case Control Study, and the British 1958 birth cohort DNA collection. Genotyping of DNA in this independent analysis was done with Illumina HumanHap550 BeadChips. We then undertook a joint genome-wide analysis that combined data from the independent set with published data from the UK, USA, Netherlands, Ireland, Italy, France, Sweden, and Belgium. The threshold for significance was p=0·05 in the independent analysis, because we were interested in replicating a small number of previously reported associations, whereas the Bonferroni-corrected threshold for significance in the joint analysis was p=2·20×10(-7)
Findings: After quality control, samples were available from 599 patients and 4144 control individuals in the independent set. In this analysis, two single nucleotide polymorphisms in a locus on chromosome 9p21.2 were associated with ALS: rs3849942 (p=2·22×10(-6); odds ratio [OR] 1·39, 95% CI 1·21-1·59) and rs2814707 (p=3·32×10(-6); 1·38, 1·20-1·58). In the joint analysis, which included samples from 4312 patients with ALS and 8425 control individuals, rs3849942 (p=4·64×10(-10); OR 1·22, 95% CI 1·15-1·30) and rs2814707 (p=4·72×10(-10); 1·22, 1·15-1·30) were associated with ALS.
Interpretation: We have found strong evidence of a genetic association of two single nucleotide polymorphisms on chromosome 9 with sporadic ALS, in line with findings from previous independent GWAS of ALS and linkage studies of ALS-frontotemporal dementia. Our findings together with these earlier findings suggest that genetic variation at this locus on chromosome 9 causes sporadic ALS and familial ALS-frontotemporal dementia. Resequencing studies and then functional analysis should be done to identify the defective gene.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
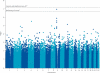
Figure 1
p values for association in the independent genome-wide association study
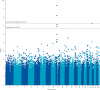
Figure 2
p values for association in the joint analysis
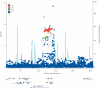
Figure 3
Genetic architecture of the associated region Circles=−log10 of the p value of association with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis for typed and imputed single nucleotide polymorphisms in the joint analysis, coloured according to linkage disequilibrium with rs3849942 (shown as a purple diamond) as measured by r. Blue lines=recombination rate across the locus based on the 1000 genomes project. Genes in the region are displayed below the graph. Arrows indicate the direction of transcription.
Comment in
- Chromosome 9p21 in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: the plot thickens.
Daoud H, Belzil V, Dion PA, Rouleau GA. Daoud H, et al. Lancet Neurol. 2010 Oct;9(10):945-7. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(10)70211-8. Lancet Neurol. 2010. PMID: 20801719 No abstract available.
Similar articles
- Chromosome 9p21 in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in Finland: a genome-wide association study.
Laaksovirta H, Peuralinna T, Schymick JC, Scholz SW, Lai SL, Myllykangas L, Sulkava R, Jansson L, Hernandez DG, Gibbs JR, Nalls MA, Heckerman D, Tienari PJ, Traynor BJ. Laaksovirta H, et al. Lancet Neurol. 2010 Oct;9(10):978-85. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(10)70184-8. Lancet Neurol. 2010. PMID: 20801718 Free PMC article. - C9orf72 and UNC13A are shared risk loci for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal dementia: a genome-wide meta-analysis.
Diekstra FP, Van Deerlin VM, van Swieten JC, Al-Chalabi A, Ludolph AC, Weishaupt JH, Hardiman O, Landers JE, Brown RH Jr, van Es MA, Pasterkamp RJ, Koppers M, Andersen PM, Estrada K, Rivadeneira F, Hofman A, Uitterlinden AG, van Damme P, Melki J, Meininger V, Shatunov A, Shaw CE, Leigh PN, Shaw PJ, Morrison KE, Fogh I, Chiò A, Traynor BJ, Czell D, Weber M, Heutink P, de Bakker PI, Silani V, Robberecht W, van den Berg LH, Veldink JH. Diekstra FP, et al. Ann Neurol. 2014 Jul;76(1):120-33. doi: 10.1002/ana.24198. Epub 2014 Jun 27. Ann Neurol. 2014. PMID: 24931836 Free PMC article. - Genome-wide association study identifies 19p13.3 (UNC13A) and 9p21.2 as susceptibility loci for sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.
van Es MA, Veldink JH, Saris CG, Blauw HM, van Vught PW, Birve A, Lemmens R, Schelhaas HJ, Groen EJ, Huisman MH, van der Kooi AJ, de Visser M, Dahlberg C, Estrada K, Rivadeneira F, Hofman A, Zwarts MJ, van Doormaal PT, Rujescu D, Strengman E, Giegling I, Muglia P, Tomik B, Slowik A, Uitterlinden AG, Hendrich C, Waibel S, Meyer T, Ludolph AC, Glass JD, Purcell S, Cichon S, Nöthen MM, Wichmann HE, Schreiber S, Vermeulen SH, Kiemeney LA, Wokke JH, Cronin S, McLaughlin RL, Hardiman O, Fumoto K, Pasterkamp RJ, Meininger V, Melki J, Leigh PN, Shaw CE, Landers JE, Al-Chalabi A, Brown RH Jr, Robberecht W, Andersen PM, Ophoff RA, van den Berg LH. van Es MA, et al. Nat Genet. 2009 Oct;41(10):1083-7. doi: 10.1038/ng.442. Epub 2009 Sep 6. Nat Genet. 2009. PMID: 19734901 - [Genetic coherence between hereditary amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal dementia].
Gjerde KV, Tysnes OB. Gjerde KV, et al. Tidsskr Nor Laegeforen. 2014 Feb 11;134(3):302-6. doi: 10.4045/tidsskr.13.0049. Tidsskr Nor Laegeforen. 2014. PMID: 24518478 Review. Norwegian. - Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a clinical review.
Masrori P, Van Damme P. Masrori P, et al. Eur J Neurol. 2020 Oct;27(10):1918-1929. doi: 10.1111/ene.14393. Epub 2020 Jul 7. Eur J Neurol. 2020. PMID: 32526057 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Mapping of gene expression reveals CYP27A1 as a susceptibility gene for sporadic ALS.
Diekstra FP, Saris CG, van Rheenen W, Franke L, Jansen RC, van Es MA, van Vught PW, Blauw HM, Groen EJ, Horvath S, Estrada K, Rivadeneira F, Hofman A, Uitterlinden AG, Robberecht W, Andersen PM, Melki J, Meininger V, Hardiman O, Landers JE, Brown RH Jr, Shatunov A, Shaw CE, Leigh PN, Al-Chalabi A, Ophoff RA, van den Berg LH, Veldink JH. Diekstra FP, et al. PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e35333. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0035333. Epub 2012 Apr 11. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22509407 Free PMC article. - Road to the chromosome 9p-linked ALS/FTD locus.
Traynor BJ. Traynor BJ. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2012 Apr;83(4):356-7. doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2012-302429. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2012. PMID: 22399792 Free PMC article. No abstract available. - UNC13A in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: from genetic association to therapeutic target.
Willemse SW, Harley P, van Eijk RPA, Demaegd KC, Zelina P, Pasterkamp RJ, van Damme P, Ingre C, van Rheenen W, Veldink JH, Kiernan MC, Al-Chalabi A, van den Berg LH, Fratta P, van Es MA. Willemse SW, et al. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2023 Aug;94(8):649-656. doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2022-330504. Epub 2023 Feb 3. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 36737245 Free PMC article. Review. - Global variation in prevalence and incidence of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Xu L, Liu T, Liu L, Yao X, Chen L, Fan D, Zhan S, Wang S. Xu L, et al. J Neurol. 2020 Apr;267(4):944-953. doi: 10.1007/s00415-019-09652-y. Epub 2019 Dec 3. J Neurol. 2020. PMID: 31797084 - Converging mechanisms in ALS and FTD: disrupted RNA and protein homeostasis.
Ling SC, Polymenidou M, Cleveland DW. Ling SC, et al. Neuron. 2013 Aug 7;79(3):416-38. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2013.07.033. Neuron. 2013. PMID: 23931993 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Johnston CA, Stanton BR, Turner MR. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in an urban setting: a population based study of inner city London. J Neurol. 2006;253:1642–1643. - PubMed
- Morita M, Al-Chalabi A, Andersen PM. A locus on chromosome 9p confers susceptibility to amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal dementia. Neurology. 2006;66:839–844. - PubMed
- Vance C, Al-Chalabi A, Ruddy D. Familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis with frontotemporal dementia is linked to a locus on chromosome 9p13.2-21.3. Brain. 2006;129:868–876. - PubMed
- Valdmanis PN, Dupre N, Bouchard JP. Three families with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal dementia with evidence of linkage to chromosome 9p. Arch Neurol. 2007;64:240–245. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 089701/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 068545/Z/02/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- G0000934/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 070122/A/02/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- Z01 AG000949/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- G0900688/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0701420/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0600974/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- Z01-AG000949-02/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- G0601943/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0701075/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous