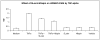Comparative efficacy and tolerability of 5-Loxin and AflapinAgainst osteoarthritis of the knee: a double blind, randomized, placebo controlled clinical study - PubMed (original) (raw)
Randomized Controlled Trial
. 2010 Nov 1;7(6):366-77.
doi: 10.7150/ijms.7.366.
Affiliations
- PMID: 21060724
- PMCID: PMC2974165
- DOI: 10.7150/ijms.7.366
Randomized Controlled Trial
Comparative efficacy and tolerability of 5-Loxin and AflapinAgainst osteoarthritis of the knee: a double blind, randomized, placebo controlled clinical study
Krishanu Sengupta et al. Int J Med Sci. 2010.
Abstract
Aflapin(®) is a novel synergistic composition derived from Boswellia serrata gum resin (Indian Patent Application No. 2229/CHE/2008). Aflapin is significantly better as an anti-inflammatory agent compared to the Boswellia extracts presently available in the market. A 90-day, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study was conducted to evaluate the comparative efficacy and tolerability of 5-Loxin(®) and Aflapin(®) in the treatment of osteoarthritis (OA) of the knee (Clinical trial registration number: ISRCTN80793440). Sixty OA subjects were included in the study. The subjects received either 100 mg (n=20) of 5-Loxin(®) or 100 mg (n=20) of Aflapin(®) or a placebo (n=20) daily for 90 days. Each patient was evaluated for pain and physical functions by using the standard tools (visual analog scale, Lequesne's Functional Index, and Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index) at the baseline (day 0), and at days 7, 30, 60 and 90. A battery of biochemical parameters in serum, urine and hematological parameters in citrated whole blood were performed to assess the safety of 5-Loxin(®) and Aflapin(®) in OA subjects. Fifty seven subjects completed the study. At the end of the study, both 5-Loxin(®) and Aflapin conferred clinically and statistically significant improvements in pain scores and physical function scores in OA subjects. Interestingly, significant improvements in pain score and functional ability were recorded as early as 7 days after initiation of the study in the treatment group supplemented with 100 mg Aflapin. Corroborating the improvements in pain scores in treatment groups, our in vitro studies provide evidences that Aflapin(®) is capable of inhibiting cartilage degrading enzyme MMP-3 and has the potential to regulate the inflammatory response by inhibiting ICAM-1. Aflapin(®) and 5-Loxin(®) reduce pain and improve physical functions significantly in OA subjects. Aflapin exhibited better efficacy compared to 5-Loxin(®). In comparison with placebo, the safety parameters were almost unchanged in the treatment groups. Hence both 5-Loxin(®) and Aflapin(®) are safe for human consumption.
Keywords: 5-Loxin®; Aflapin®; Boswellia serrata; anti-inflammation; osteoarthritis and clinical study..
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: The authors have declared that no conflict of interest exists.
Figures
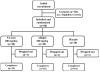
Figure 1
Flow chart of the subjects who participated in the clinical trial. Evaluations of physical activity and pain scores, serum biochemistry, hematology, and urine biochemistry were done at baseline (day 0) and on days 7, 30, 60 and 90 during follow up.
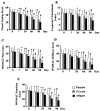
Figure 2
Bar diagrams represent the mean scores of (a) visual analog scale (VAS) (a); Lequesne's Functional Index (LFI) (b); Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC)-pain (c); WOMAC-stiffness (d); and WOMAC-function (e) in placebo, 100 mg/ day 5-Loxin® and 100 mg/day Aflapin® groups, respectively. 1 to 5, represent days of evaluations such as day 0, day 7, day 30, day 60 and day 90, respectively. Each bar represents mean ± standard deviation. In comparison with corresponding baseline data, the change in scores in the treatment groups was tested for significance using Tukey's multiple comparison test; * p<0.05; ** p<0.005.
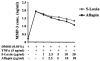
Figure 3
Aflapin and 5-Loxin inhibit matrix metalloproteinase-3 secretion from TNFα-induced human primary chondrocytes. Line diagram represents MMP-3 concentrations in the culture supernatants of chondrocytes treated with 5 ng/ml of human recombinant TNFα in presence or absence of different doses of either 5-Loxin or Aflapin as indicated. Vehicle control cultures received 0.01% DMSO. Each data point represents the mean of quadruplicate wells.
Figure 4
Aflapin and 5-Loxin inhibit TNFα-induced ICAM-1 expression on human dermal microvascular endothelial cells (HDMEC). Bar diagrams represent the ICAM-1 expression on HDMEC treated with 20ng/ml of human recombinant TNF-α in presence or absence of either 5-Loxin (4µg/ml) or Aflapin (4µg/ml) as indicated. Vehicle control cultures received 0.01% DMSO. Each experiment is done in quadruplicate wells. The results are expressed as the mean±SD of five experiments in quadruplicate wells. 5-Loxin and Aflapin significantly inhibits ICAM-1 expression induced by TNF-α (p<.01, student t-test).
Similar articles
- A double blind, randomized, placebo controlled study of the efficacy and safety of 5-Loxin for treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee.
Sengupta K, Alluri KV, Satish AR, Mishra S, Golakoti T, Sarma KV, Dey D, Raychaudhuri SP. Sengupta K, et al. Arthritis Res Ther. 2008;10(4):R85. doi: 10.1186/ar2461. Epub 2008 Jul 30. Arthritis Res Ther. 2008. PMID: 18667054 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - A double blind, randomized, placebo controlled clinical study evaluates the early efficacy of aflapin in subjects with osteoarthritis of knee.
Vishal AA, Mishra A, Raychaudhuri SP. Vishal AA, et al. Int J Med Sci. 2011;8(7):615-22. doi: 10.7150/ijms.8.615. Epub 2011 Oct 12. Int J Med Sci. 2011. PMID: 22022214 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Efficacy and Safety of Aflapin®, a Novel Boswellia Serrata Extract, in the Treatment of Osteoarthritis of the Knee: A Short-Term 30-Day Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Study.
Karlapudi V, Sunkara KB, Konda PR, Sarma KV, Rokkam MP. Karlapudi V, et al. J Am Nutr Assoc. 2023 Feb;42(2):159-168. doi: 10.1080/07315724.2021.2014370. Epub 2022 Feb 15. J Am Nutr Assoc. 2023. PMID: 35512759 Clinical Trial. - Efficacy evaluation of standardized Boswellia serrata extract (AflapinⓇ) in osteoarthritis: A systematic review and sub-group meta-analysis study.
Dubey V, Kheni D, Sureja V. Dubey V, et al. Explore (NY). 2024 Sep-Oct;20(5):102983. doi: 10.1016/j.explore.2024.02.001. Epub 2024 Feb 10. Explore (NY). 2024. PMID: 38365549 - Effectiveness of Boswellia and Boswellia extract for osteoarthritis patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Yu G, Xiang W, Zhang T, Zeng L, Yang K, Li J. Yu G, et al. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2020 Jul 17;20(1):225. doi: 10.1186/s12906-020-02985-6. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2020. PMID: 32680575 Free PMC article.
Cited by
- Nutraceutical Approach to Chronic Osteoarthritis: From Molecular Research to Clinical Evidence.
Colletti A, Cicero AFG. Colletti A, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 29;22(23):12920. doi: 10.3390/ijms222312920. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34884724 Free PMC article. Review. - Efficacy of Extracts of Oleogum Resin of Boswellia in the Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.
Dalmonte T, Andreani G, Rudelli C, Isani G. Dalmonte T, et al. Phytother Res. 2024 Dec;38(12):5672-5689. doi: 10.1002/ptr.8336. Epub 2024 Sep 23. Phytother Res. 2024. PMID: 39314013 Free PMC article. - Effect of a Herbal-Leucine mix on the IL-1β-induced cartilage degradation and inflammatory gene expression in human chondrocytes.
Akhtar N, Miller MJ, Haqqi TM. Akhtar N, et al. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2011 Aug 19;11:66. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-11-66. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2011. PMID: 21854562 Free PMC article. - Ayurvedic interventions for osteoarthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Kessler CS, Pinders L, Michalsen A, Cramer H. Kessler CS, et al. Rheumatol Int. 2015 Feb;35(2):211-32. doi: 10.1007/s00296-014-3095-y. Epub 2014 Jul 26. Rheumatol Int. 2015. PMID: 25062981 Review. - Methylsulfonylmethane and boswellic acids versus glucosamine sulfate in the treatment of knee arthritis: Randomized trial.
Notarnicola A, Maccagnano G, Moretti L, Pesce V, Tafuri S, Fiore A, Moretti B. Notarnicola A, et al. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2016 Mar;29(1):140-6. doi: 10.1177/0394632015622215. Epub 2015 Dec 18. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26684635 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
- Felson DT. An update on the pathogenesis and epidemiology of osteoarthritis. Radiol Clin. North. Am. 2004;42:1–9. - PubMed
- Felson DT, Lawrence RC, Dieppe PA, Hirsch R, Helmick CG, Jordan JM, Kington RS, Lane NE, Nevitt MC, Zhang Y, Sowers M, McAlindon T, Spector TD, Poole AR, Yanovski SZ, Ateshian G, Sharma L, Buckwalter JA, Brandt KD, Fries JF. Osteoarthritis: new insights. Part 1: the disease and its risk factors. Ann Intern Med. 2000;133:635–646. - PubMed
- Green GA. Understanding NSAIDs: from aspirin to COX-2. Clin Cornerstone. 2001;3:50–60. - PubMed
- Hochberg MC, Altman RD, Brandt KD, Clark BM, Dieppe PA, Griffin MR, Moskowitz RW, Schnitzer TJ. Guidelines for the medical management of osteoarthritis. Part II. Osteoarthritis of the knee. American College of Rheumatology. Arthritis Rheum. 1995;38:1541–1546. - PubMed
- American College of Rheumatology Subcommittee on Osteoarthritis Guidelines. Recommendations for the medical management of osteoarthritis of the hip and knee: 2000 update. Arthritis Rheum. 2000;43:1905–1915. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous