T cell receptor (TCR)-induced tyrosine phosphorylation dynamics identifies THEMIS as a new TCR signalosome component - PubMed (original) (raw)
T cell receptor (TCR)-induced tyrosine phosphorylation dynamics identifies THEMIS as a new TCR signalosome component
Claudia Brockmeyer et al. J Biol Chem. 2011.
Abstract
Stimulation of the T cell antigen receptor (TCR) induces formation of a phosphorylation-dependent signaling network via multiprotein complexes, whose compositions and dynamics are incompletely understood. Using stable isotope labeling by amino acids in cell culture (SILAC)-based quantitative proteomics, we investigated the kinetics of signal propagation after TCR-induced protein tyrosine phosphorylation. We confidently assigned 77 proteins (of 758 identified) as a direct or indirect consequence of tyrosine phosphorylation that proceeds in successive "signaling waves" revealing the temporal pace at which tyrosine kinases activate cellular functions. The first wave includes thymocyte-expressed molecule involved in selection (THEMIS), a protein recently implicated in thymocyte development but whose signaling role is unclear. We found that tyrosine phosphorylation of THEMIS depends on the presence of the scaffold proteins Linker for activation of T cells (LAT) and SH2 domain-containing lymphocyte protein of 76 kDa (SLP-76). THEMIS associates with LAT, presumably via the adapter growth factor receptor-bound protein 2 (Grb2) and with phospholipase Cγ1 (PLC-γ1). RNAi-mediated THEMIS knock-down inhibited TCR-induced IL-2 gene expression due to reduced ERK and nuclear factor of activated T cells (NFAT)/activator protein 1 (AP-1) signaling, whereas JNK, p38, or nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) activation were unaffected. Our study reveals the dynamics of TCR-dependent signaling networks and suggests a specific role for THEMIS in early TCR signalosome function.
Figures
FIGURE 1.
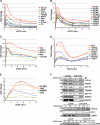
Quantitative analysis of TCR-dependent protein tyrosine phosphorylation. A, experimental workflow is shown. Jurkat cells were metabolically labeled with three combinations of arginine and lysine containing light (R0, K0) or heavy (R6, K4 or R10, K8) isotopes until complete incorporation (as described under “Experimental Procedures”). Equal numbers of cells for each labeling condition were divided into two series (1 and 2), activated with anti-CD3 Ab at 37 °C for the indicated times, and immediately lysed in ice-cold lysis buffer. Post-nuclear lysates of each activation series were mixed in a 1:1:1 ratio and subjected to Tyr(P) (pY) immunoprecipitation for 60–90 min at 4 °C using a mixture of three anti-Tyr(P) Abs coupled to beads (4G10, Tyr(P)-99, Tyr(P)-20). Beads were washed and eluted with phenyl phosphate, and eluates were separated by SDS-PAGE. 10 slices per gel lane were cut and digested with trypsin overnight, and the resulting tryptic peptides were analyzed by LC-MS/MS. After protein identification and quantitation, relative protein abundance in each activation series were bridged and normalized using quantitation of the common time point (0.5 min), thus, resulting in a continuous activation profile over 5 time points. B, 758 proteins were confidently identified from three independent SILAC experiments. 141 proteins that showed a significant increase (≥1.6-fold) above basal levels in anti-Tyr(P) immunoisolates after TCR stimulation were selected, of which 77 were retained after further manual validation. Numbers within bars indicate tyrosine-phosphorylated proteins identified in each set. C, over-represented domains within identified protein sequences from the three SILAC experiments; most domains are involved in signaling events. ArfGAP, GTPase activating proteins toward Arf; CH, calponin homology domain; RRM, RNA recognition motif; C2, calcium-dependent phospholipid binding domain; RhoGAP, Rho GTPase activating protein domain; RhoGEF, guanine nucleotide exchange factor for Rho GTPases domain; PH, Pleckstrin homology domain; SH2, Src homology domain 2; SH3, Src homology domain 3. D, analysis of activated signaling pathways by cross-correlation with the signaling pathways data base Kegg is shown.
FIGURE 2.
Kinetics of Tyr(P)-dependent signaling complexes after TCR stimulation. A, rapid, transient kinetics of known TCR-proximal signaling proteins involved in signal initiation are shown. The newly identified protein THEMIS falls in the same cluster. B, rapid, transient kinetics of nucleic acid-associated proteins (splicing factors (SF3Bs), transcription elongation factor (SUPT5H), cleavage and polyadenylation specificity factors (CPSFs)) are shown. C, rapid kinetics of CBL and components of the BRCA1 complex are shown. D, a representative group of proteins isolated at an intermediate stage after TCR activation is shown. Most proteins in this group are involved in cytoskeleton rearrangement and trafficking. E, a group of proteins isolated at the later stages after TCR activation, including proteins involved in endosomal sorting such as STAM1 and HGS is shown. F, validation of tyrosine phosphorylation by immunoblot (IB) is shown. Anti-Tyr(P) IPs of proteins isolated at early (_PLC-γ_1, ARAP1, SLP-76, THEMIS, ZAP-70, ABRO1, BRCC3), intermediate (COOL2, GIT1, ELMO-1), and later (HGS) time points after TCR activation are shown.
FIGURE 3.
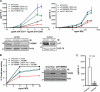
Dependence of global TCR signaling on the SLP-76·LAT signalosome. A, shown is the abundance of SLP-76-dependent and -independent proteins commonly identified from SILAC Tyr(P) IP in wild-type and SLP-76-deficient (J14) Jurkat cells at 30 s after TCR activation. B, complete anti-Tyr(P) isolation kinetics of SLP-76-dependent proteins from the same experiment as in A is shown. C, exemplary SLP-76-independent anti-Tyr(P) isolation kinetics of components of the BRCA1 complex from the same experiment as in A (note different Y axis scale) are shown. D, validation of SLP-76 dependence of Tyr(P) (pY) IPs in J14 and J14-SLP-76-FLAG cells by immunoblot probed with specific protein antibodies is shown.
FIGURE 4.
Themis is a new component of the SLP-76·LAT signalosome. A, shown is a THEMIS-One STrEP tag (OST) pulldown assay using Streptactin-Sepharose after anti-CD3 stimulation in Jurkat cells transfected with non-targeting control shRNA or a shRNA construct targeting LCK (70% knockdown efficiency). IB, immunoblot; pY, Tyr(P). B, THEMIS IP from anti-CD3 stimulated LAT-deficient (J.CaM2.5) and reconstituted cells is shown. C, THEMIS IP from anti-CD3 stimulated SLP-76-deficient (J14) and reconstituted cells is shown. D, THEMIS IPs from resting or anti-CD3-stimulated Jurkat cells is shown. Specific THEMIS antibody saturated with the peptide against which the antibody was raised served as a control. E, a THEMIS-OST pulldown assay from resting or CD3-stimulated Jurkat cells stably expressing THEMIS-OST using biotin-saturated Streptactin-Sepharose as control is shown. Both sets of blots were probed with antibodies against TCR-proximal signaling proteins.
FIGURE 5.
THEMIS is a positive regulator of TCR-induced signaling. A, IL-2 ELISAs of shControl, shTHEMIS1, shTHEMIS2, and shLAT Jurkat cells stimulated with plate-bound anti-CD3 and soluble anti-CD28 (left panel) or staphylococcal enterotoxin E-pulsed Raji B cells (right panel) for 24 h is shown. Immunoblot (IB) analysis of the cell lines used (lower panel, shTHEMIS1 (60% knockdown), shTHEMIS2 (90% knockdown), shLAT (60% knockdown), and the non-targeting shControl). B, IL-2-luciferase assay of shControl and shTHEMIS2 (90% knockdown) is shown. IL-2-luciferase cells were transduced with either empty vector or an shRNA-resistant mutant of THEMIS (right panel) and stimulated with staphylococcal enterotoxin E-pulsed Raji B cells (left panel). C, TCR stimulation-induced IL-2 secretion in peripheral CD4+CD25− T cells from wild-type and Themis knock-out mice is shown. Conventional CD4+ cells were purified by negative selection and stimulated with plate-bound anti-CD3 and soluble anti-CD28 Ab for 48 h. IL-2 concentrations in supernatants were measured by ELISA. Shown are data from three mice of each group, p = 0.03.
FIGURE 6.
THEMIS positively modulates NFAT/AP-1 and ERK activity. A, shown is an NFAT/AP-1-luciferase assay of shControl, shTHEMIS1 (60% knockdown), and shTHEMIS2 (90% knockdown) NFAT/AP-1-luciferase Jurkat cells after stimulation with plate-bound anti-CD3 and soluble anti-CD28 (left panel) and immunoblot (IB) analysis of THEMIS expression in the cell lines used (right panel). RLU, relative light units. B, an NF-κB-luciferase assay of shControl, shTHEMIS1, and shTHEMIS2 Jurkat cells stimulated as in A (for THEMIS expression levels in cell lines used see Fig. 5_A_, lower panel). C, immunoblots of ERK1/2 phosphorylation kinetics in shControl and shTHEMIS2 (90% knockdown) Jurkat cells in three independent experiments using decreasing anti-CD3 concentrations (total ERK1/2 and ZAP-70 blots are shown as loading controls) are shown.
FIGURE 7.
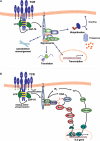
TCR-induced activation of signaling pathways observed in the present study. A, shown is a schematic representation of the cellular pathways observed in our SILAC analysis to be directly or indirectly affected by TCR stimulation-induced tyrosine phosphorylation in T cells. B, shown is a model of the possible role of THEMIS in the TCR signaling cascade. Upon TCR activation, THEMIS is phosphorylated on tyrosine and recruited to the plasma membrane where it interacts with PLC-γ1 and LAT, presumably via Grb2. THEMIS exerts a positive regulatory effect on ERK activation, presumably via a direct or indirect effect on Ras. IP3, inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate.
Similar articles
- A THEMIS:SHP1 complex promotes T-cell survival.
Paster W, Bruger AM, Katsch K, Grégoire C, Roncagalli R, Fu G, Gascoigne NR, Nika K, Cohnen A, Feller SM, Simister PC, Molder KC, Cordoba SP, Dushek O, Malissen B, Acuto O. Paster W, et al. EMBO J. 2015 Feb 3;34(3):393-409. doi: 10.15252/embj.201387725. Epub 2014 Dec 22. EMBO J. 2015. PMID: 25535246 Free PMC article. - Association of Grb2, Gads, and phospholipase C-gamma 1 with phosphorylated LAT tyrosine residues. Effect of LAT tyrosine mutations on T cell angigen receptor-mediated signaling.
Zhang W, Trible RP, Zhu M, Liu SK, McGlade CJ, Samelson LE. Zhang W, et al. J Biol Chem. 2000 Jul 28;275(30):23355-61. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M000404200. J Biol Chem. 2000. PMID: 10811803 - Pleiotropic contributions of phospholipase C-gamma1 (PLC-gamma1) to T-cell antigen receptor-mediated signaling: reconstitution studies of a PLC-gamma1-deficient Jurkat T-cell line.
Irvin BJ, Williams BL, Nilson AE, Maynor HO, Abraham RT. Irvin BJ, et al. Mol Cell Biol. 2000 Dec;20(24):9149-61. doi: 10.1128/MCB.20.24.9149-9161.2000. Mol Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 11094067 Free PMC article. - THEMIS: a critical TCR signal regulator for ligand discrimination.
Gascoigne NR, Acuto O. Gascoigne NR, et al. Curr Opin Immunol. 2015 Apr;33:86-92. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2015.01.020. Epub 2015 Feb 18. Curr Opin Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25700024 Review. - LAT, the linker for activation of T cells: a bridge between T cell-specific and general signaling pathways.
Wange RL. Wange RL. Sci STKE. 2000 Dec 19;2000(63):re1. doi: 10.1126/stke.2000.63.re1. Sci STKE. 2000. PMID: 11752630 Review.
Cited by
- THEMIS promotes T cell development and maintenance by rising the signaling threshold of the inhibitory receptor BTLA.
Mélique S, Vadel A, Rouquié N, Yang C, Bories C, Cotineau C, Saoudi A, Fazilleau N, Lesourne R. Mélique S, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 May 14;121(20):e2318773121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2318773121. Epub 2024 May 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 38713628 Free PMC article. - Positive regulation of Vav1 by Themis controls CD4 T cell pathogenicity in a mouse model of central nervous system inflammation.
Marrocco R, Bernard I, Joulia E, Barascud R, Dejean AS, Lesourne R, Saoudi A. Marrocco R, et al. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024 Apr 2;81(1):161. doi: 10.1007/s00018-024-05203-5. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 38565808 Free PMC article. - THEMIS is a substrate and allosteric activator of SHP1, playing dual roles during T cell development.
Zhang J, Jiang Z, Zhang X, Yang Z, Wang J, Chen J, Chen L, Song M, Zhang Y, Huang M, Chen S, Xiong X, Wang Y, Hao P, Horng T, Zhuang M, Zhang L, Zuo E, Bai F, Zheng J, Wang H, Fan G. Zhang J, et al. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2024 Jan;31(1):54-67. doi: 10.1038/s41594-023-01131-3. Epub 2024 Jan 4. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38177672 - Themis controls T cell activation, effector functions, and metabolism of peripheral CD8+ T cells.
Gautam N, Wojciech L, Yap J, Chua YL, Ding EM, Sim DC, Tan AS, Ahl PJ, Prasad M, Tung DW, Connolly JE, Adriani G, Brzostek J, Gascoigne NR. Gautam N, et al. Life Sci Alliance. 2023 Sep 22;6(12):e202302156. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202302156. Print 2023 Dec. Life Sci Alliance. 2023. PMID: 37739454 Free PMC article. - Negative times negative equals positive, THEMIS sets the rule on thymic selection and peripheral T cell responses.
Mélique S, Yang C, Lesourne R. Mélique S, et al. Biomed J. 2022 Apr;45(2):334-346. doi: 10.1016/j.bj.2022.03.008. Epub 2022 Mar 26. Biomed J. 2022. PMID: 35346866 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Acuto O., Di Bartolo V., Michel F. (2008) Nat. Rev. Immunol. 8, 699–712 - PubMed
- Olsen J. V., Blagoev B., Gnad F., Macek B., Kumar C., Mortensen P., Mann M. (2006) Cell 127, 635–648 - PubMed
- Hu Q., Noll R. J., Li H., Makarov A., Hardman M., Graham Cooks R. (2005) J. Mass Spectrom. 40, 430–443 - PubMed
- Makarov A. (2000) Anal. Chem. 72, 1156–1162 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous