The Polycomb complex PRC2 and its mark in life - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
The Polycomb complex PRC2 and its mark in life
Raphaël Margueron et al. Nature. 2011.
Abstract
Polycomb group proteins maintain the gene-expression pattern of different cells that is set during early development by regulating chromatin structure. In mammals, two main Polycomb group complexes exist - Polycomb repressive complex 1 (PRC1) and 2 (PRC2). PRC1 compacts chromatin and catalyses the monoubiquitylation of histone H2A. PRC2 also contributes to chromatin compaction, and catalyses the methylation of histone H3 at lysine 27. PRC2 is involved in various biological processes, including differentiation, maintaining cell identity and proliferation, and stem-cell plasticity. Recent studies of PRC2 have expanded our perspectives on its function and regulation, and uncovered a role for non-coding RNA in the recruitment of PRC2 to target genes.
Figures
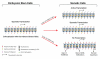
Figure 1
Schematic representation of Polycomb complex PRC1/2. Left) Diagrams representing the composition of PRC2 and PRC1 are shown. In the case of PRC1, the left diagrams correspond to the classical PRC1 complexes, while the right one corresponds to the so-called PRC1-like complexes. Due to their homology with Drosophila Psc protein, we assumed that Bmi-1-, Mel18- and NSPC1-containing PRC1 complex could compact chromatin. The CBXs “pocket” shape represent the chromodomain that specifically recognized H3K9/27me3. HPH1/2/3 are the abbreviation for Human Polyhomeotic Homolog 1/2/3. X, Y and Z represent various proteins such as SCMH1/2, FBXL10, E2F6, JARID1d that could contribute to the formation of PRC1-like complexes whose exact composition is still enigmatic. B) Characterized domains with potential functions are indicated for each PRC2 component. Note that domains based on evolutionary conservation are underscored below. For Ezh2, the numbers indicate the percent homology between mouse and Drosophila homologs.
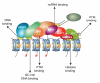
Figure 2
Chromatin properties at PRC2 target genes in ES cells and differentiated cells. Schematic representation of chromatin at PcG target genes as a function of ES cell differentiation. In ES cells, most PcG targets are methylated on both H3K4 and H3K27 and colocalize with the histone variant H2Az. During differentiation, H2Az is removed, and some bivalent domains are resolved. For example, genes that are actively transcribed lose H3K27me3. A significant proportion of PcG targets that retain H3K27me3 but lose H3K4me3 are targeted by other silencing pathways such as DNA methylation or H3K9 trimethylation.
Figure 3
Multiple interactions of PRC2 with chromatin. Schematic representation of PRC2 holoenzyme at chromatin. Putative interactions with either DNA or histones that could explain PRC2 recruitment are highlighted.
Figure 4
PRC2 mediated regulation of pluripotency and differentiation. A) Comparison of expression levels of pluripotency factors and factors that induce cell commitment during ES cell differentiation in wild type and PRC2 impaired ES cells. B) Consequences to the outcome of cell differentiation upon PRC2 inactivation.
Similar articles
- Interdependence of PRC1 and PRC2 for recruitment to Polycomb Response Elements.
Kahn TG, Dorafshan E, Schultheis D, Zare A, Stenberg P, Reim I, Pirrotta V, Schwartz YB. Kahn TG, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Dec 1;44(21):10132-10149. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw701. Epub 2016 Aug 23. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. PMID: 27557709 Free PMC article. - Histone methylation by PRC2 is inhibited by active chromatin marks.
Schmitges FW, Prusty AB, Faty M, Stützer A, Lingaraju GM, Aiwazian J, Sack R, Hess D, Li L, Zhou S, Bunker RD, Wirth U, Bouwmeester T, Bauer A, Ly-Hartig N, Zhao K, Chan H, Gu J, Gut H, Fischle W, Müller J, Thomä NH. Schmitges FW, et al. Mol Cell. 2011 May 6;42(3):330-41. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2011.03.025. Mol Cell. 2011. PMID: 21549310 - Dense chromatin activates Polycomb repressive complex 2 to regulate H3 lysine 27 methylation.
Yuan W, Wu T, Fu H, Dai C, Wu H, Liu N, Li X, Xu M, Zhang Z, Niu T, Han Z, Chai J, Zhou XJ, Gao S, Zhu B. Yuan W, et al. Science. 2012 Aug 24;337(6097):971-5. doi: 10.1126/science.1225237. Science. 2012. PMID: 22923582 - Polycomb-mediated histone modifications and gene regulation.
Ito S, Umehara T, Koseki H. Ito S, et al. Biochem Soc Trans. 2024 Feb 28;52(1):151-161. doi: 10.1042/BST20230336. Biochem Soc Trans. 2024. PMID: 38288743 Review. - Inner workings and regulatory inputs that control Polycomb repressive complex 2.
O'Meara MM, Simon JA. O'Meara MM, et al. Chromosoma. 2012 Jun;121(3):221-34. doi: 10.1007/s00412-012-0361-1. Epub 2012 Feb 19. Chromosoma. 2012. PMID: 22349693 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Deregulation of epigenetic mechanisms by the hepatitis B virus X protein in hepatocarcinogenesis.
Andrisani OM. Andrisani OM. Viruses. 2013 Mar 18;5(3):858-72. doi: 10.3390/v5030858. Viruses. 2013. PMID: 23507839 Free PMC article. Review. - Subgenual cingulate resting regional cerebral blood flow in premenstrual dysphoric disorder: differential regulation by ovarian steroids and preliminary evidence for an association with expression of ESC/E(Z) complex genes.
Wei SM, Baller EB, Martinez PE, Goff AC, Li HJ, Kohn PD, Kippenhan JS, Soldin SJ, Rubinow DR, Goldman D, Schmidt PJ, Berman KF. Wei SM, et al. Transl Psychiatry. 2021 Apr 8;11(1):206. doi: 10.1038/s41398-021-01328-4. Transl Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 33833224 Free PMC article. - EZH2: Its regulation and roles in immune disturbance of SLE.
Yang Y, Liu K, Liu M, Zhang H, Guo M. Yang Y, et al. Front Pharmacol. 2022 Oct 13;13:1002741. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1002741. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36313363 Free PMC article. Review. - BRCA1 is a negative modulator of the PRC2 complex.
Wang L, Zeng X, Chen S, Ding L, Zhong J, Zhao JC, Wang L, Sarver A, Koller A, Zhi J, Ma Y, Yu J, Chen J, Huang H. Wang L, et al. EMBO J. 2013 May 29;32(11):1584-97. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2013.95. Epub 2013 Apr 26. EMBO J. 2013. PMID: 23624935 Free PMC article. - MicroRNA-128 coordinately targets Polycomb Repressor Complexes in glioma stem cells.
Peruzzi P, Bronisz A, Nowicki MO, Wang Y, Ogawa D, Price R, Nakano I, Kwon CH, Hayes J, Lawler SE, Ostrowski MC, Chiocca EA, Godlewski J. Peruzzi P, et al. Neuro Oncol. 2013 Sep;15(9):1212-24. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/not055. Epub 2013 Jun 3. Neuro Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23733246 Free PMC article.
References
- Lewis P. Pc: Polycomb. Drosophila Information Service. 1949;21:69.
- Lewis EB. A gene complex controlling segmentation in Drosophila. Nature. 1978;276:565–570. - PubMed
- Schuettengruber B, Cavalli G. Recruitment of polycomb group complexes and their role in the dynamic regulation of cell fate choice. Development (Cambridge, England) 2009;136:3531–3542. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01GM064844/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- 4R37GM037120/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM064844/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- R37 GM037120/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases