Informatics and data mining tools and strategies for the human connectome project - PubMed (original) (raw)
Informatics and data mining tools and strategies for the human connectome project
Daniel S Marcus et al. Front Neuroinform. 2011.
Abstract
The Human Connectome Project (HCP) is a major endeavor that will acquire and analyze connectivity data plus other neuroimaging, behavioral, and genetic data from 1,200 healthy adults. It will serve as a key resource for the neuroscience research community, enabling discoveries of how the brain is wired and how it functions in different individuals. To fulfill its potential, the HCP consortium is developing an informatics platform that will handle: (1) storage of primary and processed data, (2) systematic processing and analysis of the data, (3) open-access data-sharing, and (4) mining and exploration of the data. This informatics platform will include two primary components. ConnectomeDB will provide database services for storing and distributing the data, as well as data analysis pipelines. Connectome Workbench will provide visualization and exploration capabilities. The platform will be based on standard data formats and provide an open set of application programming interfaces (APIs) that will facilitate broad utilization of the data and integration of HCP services into a variety of external applications. Primary and processed data generated by the HCP will be openly shared with the scientific community, and the informatics platform will be available under an open source license. This paper describes the HCP informatics platform as currently envisioned and places it into the context of the overall HCP vision and agenda.
Keywords: Human Connectome Project; XNAT; brain parcellation; caret; connectomics; diffusion imaging; network analysis; resting state fMRI.
Figures
Figure 1
HCP subject workflow.
Figure 2
The Connectome UI. (Left) This mockup of the Visualization & Discovery track illustrates key concepts that are being implemented, including a faceted search interface to construct subject groups and an embedded version of Connectome Workbench. Both the search interface and Workbench view are fed by ConnectomeDB's open API. (Right) This mockup of the Download track illustrates the track's emphasis on guiding users quickly to standard download packages and navigation to specific data.
Figure 3
ConnectomeDB architecture, including data transfer components. ConnectomeDB will utilize the Tomcat servlet container as the application server and use the enterprise grade, open source PostgreSQL database for storage of non-imaging data, imaging session meta-data, and system data. Actual images and other binary content are stored on a file system rather than in the database, improving performance and making the data more easily consumable by external software packages.
Figure 4
HCP data distribution tiers.
Figure 5
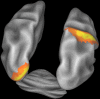
Connectome Workbench visualization of the inflated atlas surfaces for the left and right cerebral hemispheres plus the cerebellum. Probabilistic architectonic maps are shown of area 18 on the left hemisphere and area 2 on the right hemisphere.
Similar articles
- The Human Connectome Project: A retrospective.
Elam JS, Glasser MF, Harms MP, Sotiropoulos SN, Andersson JLR, Burgess GC, Curtiss SW, Oostenveld R, Larson-Prior LJ, Schoffelen JM, Hodge MR, Cler EA, Marcus DM, Barch DM, Yacoub E, Smith SM, Ugurbil K, Van Essen DC. Elam JS, et al. Neuroimage. 2021 Dec 1;244:118543. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2021.118543. Epub 2021 Sep 8. Neuroimage. 2021. PMID: 34508893 Free PMC article. Review. - ConnectomeDB--Sharing human brain connectivity data.
Hodge MR, Horton W, Brown T, Herrick R, Olsen T, Hileman ME, McKay M, Archie KA, Cler E, Harms MP, Burgess GC, Glasser MF, Elam JS, Curtiss SW, Barch DM, Oostenveld R, Larson-Prior LJ, Ugurbil K, Van Essen DC, Marcus DS. Hodge MR, et al. Neuroimage. 2016 Jan 1;124(Pt B):1102-1107. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.04.046. Epub 2015 Apr 29. Neuroimage. 2016. PMID: 25934470 Free PMC article. - Human Connectome Project informatics: quality control, database services, and data visualization.
Marcus DS, Harms MP, Snyder AZ, Jenkinson M, Wilson JA, Glasser MF, Barch DM, Archie KA, Burgess GC, Ramaratnam M, Hodge M, Horton W, Herrick R, Olsen T, McKay M, House M, Hileman M, Reid E, Harwell J, Coalson T, Schindler J, Elam JS, Curtiss SW, Van Essen DC; WU-Minn HCP Consortium. Marcus DS, et al. Neuroimage. 2013 Oct 15;80:202-19. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.05.077. Epub 2013 May 24. Neuroimage. 2013. PMID: 23707591 Free PMC article. - The Lifespan Human Connectome Project in Aging: An overview.
Bookheimer SY, Salat DH, Terpstra M, Ances BM, Barch DM, Buckner RL, Burgess GC, Curtiss SW, Diaz-Santos M, Elam JS, Fischl B, Greve DN, Hagy HA, Harms MP, Hatch OM, Hedden T, Hodge C, Japardi KC, Kuhn TP, Ly TK, Smith SM, Somerville LH, Uğurbil K, van der Kouwe A, Van Essen D, Woods RP, Yacoub E. Bookheimer SY, et al. Neuroimage. 2019 Jan 15;185:335-348. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2018.10.009. Epub 2018 Oct 15. Neuroimage. 2019. PMID: 30332613 Free PMC article. - The Human Connectome Project: a data acquisition perspective.
Van Essen DC, Ugurbil K, Auerbach E, Barch D, Behrens TE, Bucholz R, Chang A, Chen L, Corbetta M, Curtiss SW, Della Penna S, Feinberg D, Glasser MF, Harel N, Heath AC, Larson-Prior L, Marcus D, Michalareas G, Moeller S, Oostenveld R, Petersen SE, Prior F, Schlaggar BL, Smith SM, Snyder AZ, Xu J, Yacoub E; WU-Minn HCP Consortium. Van Essen DC, et al. Neuroimage. 2012 Oct 1;62(4):2222-31. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.02.018. Epub 2012 Feb 17. Neuroimage. 2012. PMID: 22366334 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Human Claustrum Connections: Robust In Vivo Detection by DWI-Based Tractography in Two Large Samples.
Wendt J, Neubauer A, Hedderich DM, Schmitz-Koep B, Ayyildiz S, Schinz D, Hippen R, Daamen M, Boecker H, Zimmer C, Wolke D, Bartmann P, Sorg C, Menegaux A. Wendt J, et al. Hum Brain Mapp. 2024 Oct;45(14):e70042. doi: 10.1002/hbm.70042. Hum Brain Mapp. 2024. PMID: 39397271 Free PMC article. - Individual variability in neural representations of mind-wandering.
Kucyi A, Anderson N, Bounyarith T, Braun D, Shareef-Trudeau L, Treves I, Braga RM, Hsieh PJ, Hung SM. Kucyi A, et al. Netw Neurosci. 2024 Oct 1;8(3):808-836. doi: 10.1162/netn_a_00387. eCollection 2024. Netw Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39355438 Free PMC article. - Heritability of movie-evoked brain activity and connectivity.
Gruskin DC, Vieira DJ, Lee JK, Patel GH. Gruskin DC, et al. bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Sep 16:2024.09.16.612469. doi: 10.1101/2024.09.16.612469. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39345386 Free PMC article. Preprint. - Children born very preterm experience altered cortical expansion over the first decade of life.
Gorham LS, Latham AR, Alexopoulos D, Kenley JK, Iannopollo E, Lean RE, Loseille D, Smyser TA, Neil JJ, Rogers CE, Smyser CD, Garcia K. Gorham LS, et al. Brain Commun. 2024 Sep 17;6(5):fcae318. doi: 10.1093/braincomms/fcae318. eCollection 2024. Brain Commun. 2024. PMID: 39329081 Free PMC article. - The degenerate coding of psychometric profiles through functional connectivity archetypes.
Di Plinio S, Northoff G, Ebisch S. Di Plinio S, et al. Front Hum Neurosci. 2024 Sep 10;18:1455776. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2024.1455776. eCollection 2024. Front Hum Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39318702 Free PMC article.
References
- de Pasquale F., Della Penna S., Snyder A. Z., Lewis C., Mantini D., Marzetti L., Belardinelli P., Ciancetta L., Pizzella V., Romani G. L., Corbetta M. (2010). Temporal dynamics of spontaneous MEG activity in brain networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 107, 6040–604510.1073/pnas.0913863107 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Fielding R. T. (2000). Architectural Styles and The Design of Network-Based Software Architectures. Doctoral dissertation, University of California, Irvine: Available at: http://www.ics.uci.edu/∼fielding/pubs/dissertation/top.htm
Grants and funding
- BB/C519938/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0700399/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- S10 RR022984/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB009352/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- U54 MH091657/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P30 NS048056/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous