Randomized phase II study of erlotinib in combination with placebo or R1507, a monoclonal antibody to insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor, for advanced-stage non-small-cell lung cancer - PubMed (original) (raw)
Clinical Trial
. 2011 Dec 1;29(34):4574-80.
doi: 10.1200/JCO.2011.36.6799. Epub 2011 Oct 24.
David R Spigel, David Chen, Martin B Steins, Jeffrey A Engelman, Claus-Peter Schneider, Silvia Novello, Wilfried E E Eberhardt, Lucio Crino, Kai Habben, Lian Liu, Pasi A Jänne, Carrie M Brownstein, Martin Reck
Affiliations
- PMID: 22025157
- PMCID: PMC5320944
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2011.36.6799
Clinical Trial
Randomized phase II study of erlotinib in combination with placebo or R1507, a monoclonal antibody to insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor, for advanced-stage non-small-cell lung cancer
Suresh S Ramalingam et al. J Clin Oncol. 2011.
Abstract
Purpose: R1507 is a selective, fully human, recombinant monoclonal antibody (immunoglobulin G1 subclass) against insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF-1R). The strong preclinical evidence supporting coinhibition of IGF-1R and epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) as anticancer therapy prompted this study.
Patients and methods: Patients with advanced-stage non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with progression following one or two prior regimens, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status 0 to 2, and measurable disease were eligible. Patients were randomly assigned to receive erlotinib (150 mg orally once a day) in combination with either placebo, R1507 9 mg/kg weekly, or R1507 16 mg/kg intravenously once every 3 weeks. Treatment cycles were repeated every 3 weeks. The primary end point was comparison of the 12-week progression-free survival (PFS) rate.
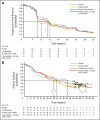
Results: In all, 172 patients were enrolled: median age, 61 years; female, 33%; never-smokers, 12%; and performance status 0 or 1, 88%. The median number of R1507 doses was six for the weekly arm and 3.5 for the every-3-weeks arm. Grades 3 to 4 adverse events occurred in 37%, 44%, and 48% of patients with placebo, R1507 weekly, and R1507 every 3 weeks, respectively. The 12-week PFS rates were 39%, 37%, and 44%, and the median overall survival was 8.1, 8.1, and 12.1 months for the three groups, respectively, with statistically nonsignificant hazard ratios. The 12-week PFS rate in patients with KRAS mutation was 36% with R1507 compared with 0% with placebo.
Conclusion: The combination of R1507 with erlotinib did not provide PFS or survival advantage over erlotinib alone in an unselected group of patients with advanced NSCLC. Predictive biomarkers are essential for further development of combined inhibition of IGF-1R and EGFR.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00760929.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors' disclosures of potential conflicts of interest and author contributions are found at the end of this article.
Figures
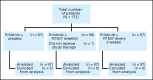
Fig 1.
CONSORT diagram for treatment assignment. R1507, selective, fully human, recombinant monoclonal antibody against insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor.
Fig 2.
Kaplan-Meier curve for (A) progression-free survival and (B) overall survival.
Similar articles
- Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase II trial of sorafenib and erlotinib or erlotinib alone in previously treated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer.
Spigel DR, Burris HA 3rd, Greco FA, Shipley DL, Friedman EK, Waterhouse DM, Whorf RC, Mitchell RB, Daniel DB, Zangmeister J, Bass JD, Hainsworth JD. Spigel DR, et al. J Clin Oncol. 2011 Jun 20;29(18):2582-9. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2010.30.7678. Epub 2011 May 16. J Clin Oncol. 2011. PMID: 21576636 Clinical Trial. - Intercalated combination of chemotherapy and erlotinib for patients with advanced stage non-small-cell lung cancer (FASTACT-2): a randomised, double-blind trial.
Wu YL, Lee JS, Thongprasert S, Yu CJ, Zhang L, Ladrera G, Srimuninnimit V, Sriuranpong V, Sandoval-Tan J, Zhu Y, Liao M, Zhou C, Pan H, Lee V, Chen YM, Sun Y, Margono B, Fuerte F, Chang GC, Seetalarom K, Wang J, Cheng A, Syahruddin E, Qian X, Ho J, Kurnianda J, Liu HE, Jin K, Truman M, Bara I, Mok T. Wu YL, et al. Lancet Oncol. 2013 Jul;14(8):777-86. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(13)70254-7. Epub 2013 Jun 17. Lancet Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23782814 Clinical Trial. - Erlotinib alone or with bevacizumab as first-line therapy in patients with advanced non-squamous non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring EGFR mutations (JO25567): an open-label, randomised, multicentre, phase 2 study.
Seto T, Kato T, Nishio M, Goto K, Atagi S, Hosomi Y, Yamamoto N, Hida T, Maemondo M, Nakagawa K, Nagase S, Okamoto I, Yamanaka T, Tajima K, Harada R, Fukuoka M, Yamamoto N. Seto T, et al. Lancet Oncol. 2014 Oct;15(11):1236-44. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(14)70381-X. Epub 2014 Aug 27. Lancet Oncol. 2014. PMID: 25175099 Clinical Trial. - First-line treatment of advanced epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation positive non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer.
Greenhalgh J, Dwan K, Boland A, Bates V, Vecchio F, Dundar Y, Jain P, Green JA. Greenhalgh J, et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 May 25;(5):CD010383. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010383.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27223332 Updated. Review. - Combining targeted agents: blocking the epidermal growth factor and vascular endothelial growth factor pathways.
Sandler A, Herbst R. Sandler A, et al. Clin Cancer Res. 2006 Jul 15;12(14 Pt 2):4421s-4425s. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-0796. Clin Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 16857821 Review.
Cited by
- Novel small molecule EGFR inhibitors as candidate drugs in non-small cell lung cancer.
Berardi R, Santoni M, Morgese F, Ballatore Z, Savini A, Onofri A, Mazzanti P, Pistelli M, Pierantoni C, De Lisa M, Caramanti M, Pagliaretta S, Pellei C, Cascinu S. Berardi R, et al. Onco Targets Ther. 2013 May 21;6:563-76. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S28155. Print 2013. Onco Targets Ther. 2013. PMID: 23723712 Free PMC article. - Targeting the insulin-like growth factor receptor and Src signaling network for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer.
Min HY, Yun HJ, Lee JS, Lee HJ, Cho J, Jang HJ, Park SH, Liu D, Oh SH, Lee JJ, Wistuba II, Lee HY. Min HY, et al. Mol Cancer. 2015 Jun 4;14:113. doi: 10.1186/s12943-015-0392-3. Mol Cancer. 2015. PMID: 26041671 Free PMC article. - Inhibition of IGF1R signaling abrogates resistance to afatinib (BIBW2992) in EGFR T790M mutant lung cancer cells.
Lee Y, Wang Y, James M, Jeong JH, You M. Lee Y, et al. Mol Carcinog. 2016 May;55(5):991-1001. doi: 10.1002/mc.22342. Epub 2015 Jun 4. Mol Carcinog. 2016. PMID: 26052929 Free PMC article. - Phase 2 Study of Erlotinib in Combination With Linsitinib (OSI-906) or Placebo in Chemotherapy-Naive Patients With Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer and Activating Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Mutations.
Leighl NB, Rizvi NA, de Lima LG Jr, Arpornwirat W, Rudin CM, Chiappori AA, Ahn MJ, Chow LQ, Bazhenova L, Dechaphunkul A, Sunpaweravong P, Eaton K, Chen J, Medley S, Poondru S, Singh M, Steinberg J, Juergens RA, Gadgeel SM. Leighl NB, et al. Clin Lung Cancer. 2017 Jan;18(1):34-42.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.cllc.2016.07.007. Epub 2016 Aug 8. Clin Lung Cancer. 2017. PMID: 27686971 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - The links between insulin resistance, diabetes, and cancer.
Orgel E, Mittelman SD. Orgel E, et al. Curr Diab Rep. 2013 Apr;13(2):213-22. doi: 10.1007/s11892-012-0356-6. Curr Diab Rep. 2013. PMID: 23271574 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Shepherd FA, Rodrigues Pereira J, Ciuleanu T, et al. Erlotinib in previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:123–132. - PubMed
- Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R, et al. Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:2129–2139. - PubMed
- Desbois-Mouthon C, Cacheux W, Blivet-Van Eggelpoël MJ, et al. Impact of IGF-1R/EGFR cross-talks on hepatoma cell sensitivity to gefitinib. Int J Cancer. 2006;119:2557–2566. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous