Foodborne outbreak and nonmotile Salmonella enterica variant, France - PubMed (original) (raw)
Foodborne outbreak and nonmotile Salmonella enterica variant, France
Simon Le Hello et al. Emerg Infect Dis. 2012 Jan.
Abstract
We report a food-related outbreak of salmonellosis in humans caused by a nonmotile variant of Salmonella enterica serotype Typhimurium in France in 2009. This nonmotile variant had been circulating in laying hens but was not considered as Typhimurium and consequently escaped European poultry flock regulations.
Figures
Figure A1
Phylogenetic analysis of _Xba_I–pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) profiles obtained among a subset of 40 selected nonmotile Salmonella enterica serotype
1
,4,[5],12:–:– strains isolated from humans and nonhumans during 2001–2009, France. Multilocus variable number tandem repeat analysis (MLVA), strain code, antimicrobial susceptibility testing (AST), PFGE profile found in our PFGE Typhimurium database, antigenic formula (serotype), and source and year of isolation are indicated to the right of the PFGE profiles. The MLVA groups indicated in the rectangles are the strains with the MLVA type found in our food poisoning investigation with its single- and double-locus variant with 1 repetition difference. P1 indicates the egg producer implicated in the tiramisu food poisoning. A, amoxicillin; S, streptomycin; Sp, spectinomycin; C, chloramphenicol; Su, sulfonamide; Te, tetracycline; Tmp, trimethoprim; Na, nalidixic acid. *Auto sampling; †authority sampling I; ‡tiramisu consumption; §authority sampling II.
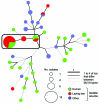
Figure
Minimum-spanning tree of multilocus variable number tandem repeat analysis (MLVA) of Salmonella enterica serotype
1
,4,[5],12:–:– strains isolated from humans and nonhumans during 2001–2009, France. Each MLVA type is indicated by 1 node or branch tip, displayed as circles that are connected by branches of minimum-spanning tree. The length and the color of the branches represent genetic distances (changes in loci) between 2 neighboring types. The sizes of the different color circles depend on their population size. Wedges in circles indicate the proportion of isolates from respective sources with a particular MLVA type. A complex is shown in the black rectangle, based on maximum neighbor distance of changes at 2 loci and minimum size of 2 types. This specific complex linked the tiramisu food poisoning strains and other loci-derived strains for 2005–2009.
Similar articles
- Whole-Genome Sequencing and Bioinformatic Analysis of Isolates from Foodborne Illness Outbreaks of Campylobacter jejuni and Salmonella enterica.
Oakeson KF, Wagner JM, Rohrwasser A, Atkinson-Dunn R. Oakeson KF, et al. J Clin Microbiol. 2018 Oct 25;56(11):e00161-18. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00161-18. Print 2018 Nov. J Clin Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30158193 Free PMC article. - Detection of Salmonella in spent hens and eggs associated with foodborne infections.
Otomo Y, Abe K, Odagiri K, Shiroto A, Takatori K, Hara-Kudo Y. Otomo Y, et al. Avian Dis. 2007 Jun;51(2):578-83. doi: 10.1637/0005-2086(2007)51[578:DOSISH]2.0.CO;2. Avian Dis. 2007. PMID: 17626487 - Salmonellosis outbreak due to chicken contact leading to a foodborne outbreak associated with infected delicatessen workers.
Hedican E, Miller B, Ziemer B, LeMaster P, Jawahir S, Leano F, Smith K. Hedican E, et al. Foodborne Pathog Dis. 2010 Aug;7(8):995-7. doi: 10.1089/fpd.2009.0495. Foodborne Pathog Dis. 2010. PMID: 20470192 - Salmonella Enteritidis Outbreaks Associated with Egg-Producing Farms Not Regulated by Food and Drug Administration's Egg Safety Rule.
Stilz CR, Cavallo S, Garman K, Dunn JR. Stilz CR, et al. Foodborne Pathog Dis. 2022 Aug;19(8):529-534. doi: 10.1089/fpd.2022.0025. Epub 2022 Jun 7. Foodborne Pathog Dis. 2022. PMID: 35671524 Review. - Review of egg-related salmonellosis and reduction strategies in United States, Australia, United Kingdom and New Zealand.
Chousalkar K, Gast R, Martelli F, Pande V. Chousalkar K, et al. Crit Rev Microbiol. 2018 May;44(3):290-303. doi: 10.1080/1040841X.2017.1368998. Epub 2017 Sep 14. Crit Rev Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 28903617 Review.
Cited by
- Nationwide trends and features of human salmonellosis outbreaks in China.
Wang Z, Zhou H, Liu Y, Huang C, Chen J, Siddique A, Yin R, Jia C, Li Y, Zhao G, Yue M. Wang Z, et al. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2024 Dec;13(1):2372364. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2024.2372364. Epub 2024 Jul 18. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2024. PMID: 38923510 Free PMC article. - Salmonellosis outbreak archive in China: data collection and assembly.
Wang Z, Huang C, Liu Y, Chen J, Yin R, Jia C, Kang X, Zhou X, Liao S, Jin X, Feng M, Jiang Z, Song Y, Zhou H, Yao Y, Teng L, Wang B, Li Y, Yue M. Wang Z, et al. Sci Data. 2024 Feb 27;11(1):244. doi: 10.1038/s41597-024-03085-7. Sci Data. 2024. PMID: 38413596 Free PMC article. - Detection of Atypical Salmonella Infantis Phenotypes in Broiler Environmental Samples.
Hess C, Drauch V, Spergser J, Kornschober C, Hess M. Hess C, et al. Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Jun 15;11(3):e0010623. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00106-23. Epub 2023 May 11. Microbiol Spectr. 2023. PMID: 37166309 Free PMC article. - Salmonella enterica serotype enteritidis in French Polynesia, South Pacific, 2008-2013.
Le Hello S, Maillard F, Mallet HP, Daudens E, Levy M, Roy V, Branaa P, Bertrand S, Fabre L, Weill FX. Le Hello S, et al. Emerg Infect Dis. 2015 Jun;21(6):1045-8. doi: 10.3201/eid2106.141103. Emerg Infect Dis. 2015. PMID: 25988406 Free PMC article. - Association between indoor environmental contamination by Salmonella enterica and contamination of eggs on layer farms.
Gole VC, Torok V, Sexton M, Caraguel CG, Chousalkar KK. Gole VC, et al. J Clin Microbiol. 2014 Sep;52(9):3250-8. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00816-14. Epub 2014 Jun 25. J Clin Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24966362 Free PMC article.
References
- Grimont PAD, Weill FX. Antigenic formulae of the Salmonella serovars, 9th ed. Paris: World Health Organization Collaborating Center for Reference and Research on Salmonella, Institut Pasteur; 2007.
- Barbour EK, Nabbut NH, Al-Nakhli HM. A non-motile Salmonella mutant (6,7:–:–) and two serological variants encountered in Saudi Arabia. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg [A]. 1984;256:548–52. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical