Using formaldehyde-assisted isolation of regulatory elements (FAIRE) to isolate active regulatory DNA - PubMed (original) (raw)
Using formaldehyde-assisted isolation of regulatory elements (FAIRE) to isolate active regulatory DNA
Jeremy M Simon et al. Nat Protoc. 2012.
Erratum in
- Nat Protoc. 2014 Feb;9(2):501-3
Abstract
Eviction or destabilization of nucleosomes from chromatin is a hallmark of functional regulatory elements in eukaryotic genomes. Historically identified by nuclease hypersensitivity, these regulatory elements are typically bound by transcription factors or other regulatory proteins. FAIRE (formaldehyde-assisted isolation of regulatory elements) is an alternative approach to identify these genomic regions and has proven successful in a multitude of eukaryotic cell and tissue types. Cells or dissociated tissues are cross-linked briefly with formaldehyde, lysed and sonicated. Sheared chromatin is subjected to phenol/chloroform extraction and the isolated DNA, typically encompassing 1-3% of the human genome, is purified. We provide guidelines for quantitative analysis by PCR, microarrays or next-generation sequencing. Regulatory elements enriched by FAIRE have high concordance with those identified by nuclease hypersensitivity or chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP), and the entire procedure can be completed in 3 d. FAIRE has low technical variability, which allows its usage in large-scale studies of chromatin from normal or diseased tissues.
Figures
Figure 1
Example timeline for FAIRE protocol. Steps are grouped by day for the typical timeline, but utilizing Pause Points will extend the duration.
Figure 2
Representative gel image showing varying degrees of sonication. NIH3T3 cells were fixed and lysed as described above. Chromatin was then sheared by sonication for 0, 2, 4, 6, 8, and 10 cycles using the parameters outlined in step 2A. After clearing cell debris, crosslinks were reversed, and purified DNA was run on a 1% agarose gel. A 100 bp ladder (lane marked M) is included for reference. The target range for fragment sizes is shown. Six cycles yields an ideal distribution of fragment lengths; fewer than six cycles of sonication is insufficient for solubilization and shearing of chromatin, whereas sonication beyond six cycles leads to oversonication. A high molecular weight band is slightly visible and marked with an asterisk.
Figure 3
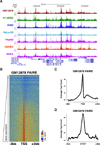
Expected results from FAIRE-seq experiments. A. Genomic locus residing on chromosome 19 as visualized with the UCSC Genome Browser shows consistent FAIRE enrichment at transcriptional start sites (TSS) across seven ENCODE cell lines. Data are presented as number of aligned, in silico extended reads per base, on a scale of 0 to 50 reads. Pink coloring atop tall peaks of enrichment represent where signal exceeded this range. B. Heatmap of normalized GM12878 FAIRE signal ±3kb around TSS ranked by gene expression in GM12878 cells. Color was assigned on a log2 scale of −6 (background) to −2 (enriched). C. Average GM12878 FAIRE signal ±3kb around TSS across all genes. Enrichment peaks around −125bp. D. Average GM12878 FAIRE signal ±3kb around GM12878 CTCF sites, representing a class of distal regulatory elements.
Similar articles
- FAIRE (Formaldehyde-Assisted Isolation of Regulatory Elements) isolates active regulatory elements from human chromatin.
Giresi PG, Kim J, McDaniell RM, Iyer VR, Lieb JD. Giresi PG, et al. Genome Res. 2007 Jun;17(6):877-85. doi: 10.1101/gr.5533506. Epub 2006 Dec 19. Genome Res. 2007. PMID: 17179217 Free PMC article. - Isolation of active regulatory elements from eukaryotic chromatin using FAIRE (Formaldehyde Assisted Isolation of Regulatory Elements).
Giresi PG, Lieb JD. Giresi PG, et al. Methods. 2009 Jul;48(3):233-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2009.03.003. Epub 2009 Mar 18. Methods. 2009. PMID: 19303047 Free PMC article. - A detailed protocol for formaldehyde-assisted isolation of regulatory elements (FAIRE).
Simon JM, Giresi PG, Davis IJ, Lieb JD. Simon JM, et al. Curr Protoc Mol Biol. 2013;Chapter 21:Unit21.26. doi: 10.1002/0471142727.mb2126s102. Curr Protoc Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23547014 - Formaldehyde-assisted isolation of regulatory elements.
Nagy PL, Price DH. Nagy PL, et al. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. 2009 Nov-Dec;1(3):400-406. doi: 10.1002/wsbm.36. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. 2009. PMID: 20046543 Free PMC article. Review. - Serial analysis of binding elements for transcription factors.
Chen J. Chen J. Methods Mol Biol. 2009;567:113-32. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60327-414-2_8. Methods Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19588089 Review.
Cited by
- Single-cell sequencing to multi-omics: technologies and applications.
Wu X, Yang X, Dai Y, Zhao Z, Zhu J, Guo H, Yang R. Wu X, et al. Biomark Res. 2024 Sep 27;12(1):110. doi: 10.1186/s40364-024-00643-4. Biomark Res. 2024. PMID: 39334490 Free PMC article. Review. - Gene regulatory dynamics during the development of a paleopteran insect, the mayfly Cloeon dipterum.
Pallarès-Albanell J, Ortega-Flores L, Senar-Serra T, Ruiz A, Abril JF, Rossello M, Almudi I. Pallarès-Albanell J, et al. Development. 2024 Oct 15;151(20):dev203017. doi: 10.1242/dev.203017. Epub 2024 Oct 10. Development. 2024. PMID: 39324209 Free PMC article. - Century-old chromatin architecture revealed in formalin-fixed vertebrates.
Hahn EE, Stiller J, Alexander MR, Grealy A, Taylor JM, Jackson N, Frere CH, Holleley CE. Hahn EE, et al. Nat Commun. 2024 Jul 29;15(1):6378. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-50668-4. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39075073 Free PMC article. - Recent advances in exploring transcriptional regulatory landscape of crops.
Huo Q, Song R, Ma Z. Huo Q, et al. Front Plant Sci. 2024 Jun 5;15:1421503. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1421503. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 38903438 Free PMC article. Review. - Emerging Approaches to Profile Accessible Chromatin from Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded Sections.
Sunitha Kumary VUN, Venters BJ, Raman K, Sen S, Estève PO, Cowles MW, Keogh MC, Pradhan S. Sunitha Kumary VUN, et al. Epigenomes. 2024 May 12;8(2):20. doi: 10.3390/epigenomes8020020. Epigenomes. 2024. PMID: 38804369 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources