Immune epitope database analysis resource - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2012 Jul;40(Web Server issue):W525-30.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gks438. Epub 2012 May 18.
Julia Ponomarenko, Zhanyang Zhu, Dorjee Tamang, Peng Wang, Jason Greenbaum, Claus Lundegaard, Alessandro Sette, Ole Lund, Philip E Bourne, Morten Nielsen, Bjoern Peters
Affiliations
- PMID: 22610854
- PMCID: PMC3394288
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gks438
Immune epitope database analysis resource
Yohan Kim et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Jul.
Abstract
The immune epitope database analysis resource (IEDB-AR: http://tools.iedb.org) is a collection of tools for prediction and analysis of molecular targets of T- and B-cell immune responses (i.e. epitopes). Since its last publication in the NAR webserver issue in 2008, a new generation of peptide:MHC binding and T-cell epitope predictive tools have been added. As validated by different labs and in the first international competition for predicting peptide:MHC-I binding, their predictive performances have improved considerably. In addition, a new B-cell epitope prediction tool was added, and the homology mapping tool was updated to enable mapping of discontinuous epitopes onto 3D structures. Furthermore, to serve a wider range of users, the number of ways in which IEDB-AR can be accessed has been expanded. Specifically, the predictive tools can be programmatically accessed using a web interface and can also be downloaded as software packages.
Figures
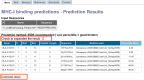
Figure 1.
Screenshot of the peptide:MHC-I binding predictive tool results page generated using the ‘IEDB recommended’ option. The first highlighted area at the top indicates a checkbox with which the user can expand the table to display method-specific predictions. The second highlighted area at the bottom allows the user to download the prediction results as a text file.
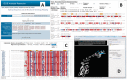
Figure 2.
Screenshots of the homology modeling tool. (A) The input page. (B) The output page: a pair-wise sequence alignment of the source protein and one of the PDB hits. Epitope residues are shown in orange. Solvent exposed residues (with a relative solvent accessibility of side chain atoms, RSA, above 40%) are shown in red and buried (RSA below 7%), in blue (these cut-offs can be changed as shown in C). In the annotation for secondary structures (34), ‘H’ denotes an alpha-helix; ‘G’, a 3-10 helix; ‘E’, a beta-strand; ‘T’, a turn; ‘X’, no structure. (C) The output page: a fragment of a multiple sequence alignment of the source protein and all PDB hits (at the Blast _E_-value < 1.0E-3). (D) Default view of the protein source and epitope (colored in blue) in EpitopeViewer. The view can be changed using the EpitopeViewer’s tools and shortcuts accessible on the right top panel.
Similar articles
- Immune epitope database analysis resource (IEDB-AR).
Zhang Q, Wang P, Kim Y, Haste-Andersen P, Beaver J, Bourne PE, Bui HH, Buus S, Frankild S, Greenbaum J, Lund O, Lundegaard C, Nielsen M, Ponomarenko J, Sette A, Zhu Z, Peters B. Zhang Q, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008 Jul 1;36(Web Server issue):W513-8. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn254. Epub 2008 May 31. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008. PMID: 18515843 Free PMC article. - IEDB-AR: immune epitope database-analysis resource in 2019.
Dhanda SK, Mahajan S, Paul S, Yan Z, Kim H, Jespersen MC, Jurtz V, Andreatta M, Greenbaum JA, Marcatili P, Sette A, Nielsen M, Peters B. Dhanda SK, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Jul 2;47(W1):W502-W506. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz452. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. PMID: 31114900 Free PMC article. - IEDB-3D: structural data within the immune epitope database.
Ponomarenko J, Papangelopoulos N, Zajonc DM, Peters B, Sette A, Bourne PE. Ponomarenko J, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011 Jan;39(Database issue):D1164-70. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq888. Epub 2010 Oct 28. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011. PMID: 21030437 Free PMC article. - Applications for T-cell epitope queries and tools in the Immune Epitope Database and Analysis Resource.
Kim Y, Sette A, Peters B. Kim Y, et al. J Immunol Methods. 2011 Nov 30;374(1-2):62-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jim.2010.10.010. Epub 2010 Oct 31. J Immunol Methods. 2011. PMID: 21047510 Free PMC article. Review. - An introduction to epitope prediction methods and software.
Yang X, Yu X. Yang X, et al. Rev Med Virol. 2009 Mar;19(2):77-96. doi: 10.1002/rmv.602. Rev Med Virol. 2009. PMID: 19101924 Review.
Cited by
- Designing of Peptide Based Multi-Epitope Vaccine Construct against Gallbladder Cancer Using Immunoinformatics and Computational Approaches.
Dar MA, Kumar P, Kumar P, Shrivastava A, Dar MA, Chauhan R, Trivedi V, Singh A, Khan E, Velayutham R, Dhingra S. Dar MA, et al. Vaccines (Basel). 2022 Oct 31;10(11):1850. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10111850. Vaccines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36366359 Free PMC article. - Fusion peptide constructs from antigens of M. tuberculosis producing high T-cell mediated immune response.
Arif S, Akhter M, Khaliq A, Akhtar MW. Arif S, et al. PLoS One. 2022 Sep 29;17(9):e0271126. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0271126. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36174012 Free PMC article. - Adult Memory T Cell Responses to the Respiratory Syncytial Virus Fusion Protein During a Single RSV Season (2018-2019).
Blunck BN, Angelo LS, Henke D, Avadhanula V, Cusick M, Ferlic-Stark L, Zechiedrich L, Gilbert BE, Piedra PA. Blunck BN, et al. Front Immunol. 2022 Mar 29;13:823652. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.823652. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35422803 Free PMC article. - Identification of an immunogenic DKK1 long peptide for immunotherapy of human multiple myeloma.
Li R, Zheng C, Wang Q, Bi E, Yang M, Hou J, Fu W, Yi Q, Qian J. Li R, et al. Haematologica. 2021 Mar 1;106(3):838-846. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2019.236836. Haematologica. 2021. PMID: 32079700 Free PMC article. - Immunization with full-length Plasmodium falciparum merozoite surface protein 1 is safe and elicits functional cytophilic antibodies in a randomized first-in-human trial.
Blank A, Fürle K, Jäschke A, Mikus G, Lehmann M, Hüsing J, Heiss K, Giese T, Carter D, Böhnlein E, Lanzer M, Haefeli WE, Bujard H. Blank A, et al. NPJ Vaccines. 2020 Jan 31;5(1):10. doi: 10.1038/s41541-020-0160-2. eCollection 2020. NPJ Vaccines. 2020. PMID: 32025341 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials