Search for inhibitors of endocytosis: Intended specificity and unintended consequences - PubMed (original) (raw)
Search for inhibitors of endocytosis: Intended specificity and unintended consequences
Dipannita Dutta et al. Cell Logist. 2012.
Abstract
We discuss here the variety of approaches that have been taken to inhibit different forms of endocytosis. Typically, both non-specific and specific chemical inhibitors of endocytosis are tried in order to "classify" entry of a new plasma membrane protein into one of the various types of endocytosis. This classification can be confirmed through genetic approaches of protein depletion or overexpression of mutants of known endocytosis machinery components. Although some new compounds have been designed to be selective in biochemical assays, we caution investigators to be alert to the unintended consequences that sometimes arise when these compounds are applied to intact cells.
Keywords: chemical inhibitor; clathrin-independent endocytosis; clathrin-mediated endocytosis; endocytosis; inhibitor; phagocytosis; pinocytosis.
Figures
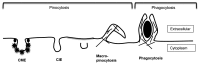
Figure 1. Different types of endocytosis. Endocytosis can be broadly classified into pinocytosis and phagocytosis. Phagocytosis involves the internalization of large particles like bacteria whereas macropinocytosis involves the internalization of enlarged fluid-filled endosomes; both processes are driven by actin (shown as hatched lines). Clathrin-mediated endocytosis (CME) is a selective mechanism whereby cell surface proteins containing specific sorting sequences are gathered into membrane depressions by associating with adaptor proteins which recruit clathrin (*). CME endosomes pinch off from the cell surface by recruiting the dynamin GTPase (•) to the bud neck. Clathrin-independent endocytosis (CIE) is shown here as one form, although there are reports of distinct variations of CIE. Most CIE is clathrin- and dynamin-independent and cholesterol-dependent and includes both the CLIC/GEEC and Arf6-associated forms of CIE. In addition other CIE modes (caveolae- and RhoA-dependent) are dynamin-dependent.
Similar articles
- Endocytosis and signal transduction: basic science update.
Liu J, Shapiro JI. Liu J, et al. Biol Res Nurs. 2003 Oct;5(2):117-28. doi: 10.1177/1099800403256860. Biol Res Nurs. 2003. PMID: 14531216 Review. - Pharmacological inhibition of endocytic pathways: is it specific enough to be useful?
Ivanov AI. Ivanov AI. Methods Mol Biol. 2008;440:15-33. doi: 10.1007/978-1-59745-178-9_2. Methods Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 18369934 Review. - Fluid phase endocytosis and galactosyl receptor-mediated endocytosis employ different early endosomes.
Synnes M, Prydz K, Løvdal T, Brech A, Berg T. Synnes M, et al. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1999 Oct 15;1421(2):317-28. doi: 10.1016/s0005-2736(99)00134-0. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1999. PMID: 10518701 - Pitstop 2 is a potent inhibitor of clathrin-independent endocytosis.
Dutta D, Williamson CD, Cole NB, Donaldson JG. Dutta D, et al. PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e45799. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0045799. Epub 2012 Sep 21. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23029248 Free PMC article. - Virus entry by endocytosis.
Mercer J, Schelhaas M, Helenius A. Mercer J, et al. Annu Rev Biochem. 2010;79:803-33. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biochem-060208-104626. Annu Rev Biochem. 2010. PMID: 20196649 Review.
Cited by
- Contributions of the Four Essential Entry Glycoproteins to HSV-1 Tropism and the Selection of Entry Routes.
Hilterbrand AT, Daly RE, Heldwein EE. Hilterbrand AT, et al. mBio. 2021 Mar 2;12(2):e00143-21. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00143-21. mBio. 2021. PMID: 33653890 Free PMC article. - Insight into the role of clathrin-mediated endocytosis inhibitors in SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Alkafaas SS, Abdallah AM, Ghosh S, Loutfy SA, Elkafas SS, Abdel Fattah NF, Hessien M. Alkafaas SS, et al. Rev Med Virol. 2023 Jan;33(1):e2403. doi: 10.1002/rmv.2403. Epub 2022 Nov 7. Rev Med Virol. 2023. PMID: 36345157 Free PMC article. Review. - Combination Approach of YSA Peptide Anchored Docetaxel Stealth Liposomes with Oral Antifibrotic Agent for the Treatment of Lung Cancer.
Patel K, Doddapaneni R, Sekar V, Chowdhury N, Singh M. Patel K, et al. Mol Pharm. 2016 Jun 6;13(6):2049-58. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.6b00187. Epub 2016 Apr 26. Mol Pharm. 2016. PMID: 27070720 Free PMC article. - Inhibiting nucleolin reduces inflammation induced by mitochondrial DNA in cardiomyocytes exposed to hypoxia and reoxygenation.
Mariero LH, Torp MK, Heiestad CM, Baysa A, Li Y, Valen G, Vaage J, Stensløkken KO. Mariero LH, et al. Br J Pharmacol. 2019 Nov;176(22):4360-4372. doi: 10.1111/bph.14830. Epub 2019 Oct 27. Br J Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31412132 Free PMC article. - Cellular Uptake of Gold Nanorods in Breast Cancer Cell Lines.
White BE, White MK, Nima Alsudani ZA, Watanabe F, Biris AS, Ali N. White BE, et al. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022 Mar 12;12(6):937. doi: 10.3390/nano12060937. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35335749 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources