The Caregiver Burden Questionnaire for Heart Failure (CBQ-HF): face and content validity - PubMed (original) (raw)
Multicenter Study
The Caregiver Burden Questionnaire for Heart Failure (CBQ-HF): face and content validity
Louise Humphrey et al. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2013.
Abstract
Background: A new caregiver burden questionnaire for heart failure (CBQ-HF v1.0) was developed based on previously conducted qualitative interviews with HF caregivers and with input from HF clinical experts. Version 1.0 of the CBQ-HF included 41 items measuring the burden associated with caregiving in the following domains: physical, emotional/psychological, social, and impact on caregiver's life. Following initial development, the next stage was to evaluate caregivers' understanding of the questionnaire items and their conceptual relevance.
Methods: To evaluate the face and content validity of the new questionnaire, cognitive interviews were conducted with caregivers of heart failure patients. The cognitive interviews included a "think aloud" exercise as the patient completed the CBQ-HF, followed by more specific probing questions to better understand caregivers' understanding, interpretation and the relevance of the instructions, items, response scales and recall period.
Results: Eighteen caregivers of heart failure patients were recruited. The mean age of the caregivers was 50 years (SD = 10.2). Eighty-three percent of caregivers were female and most commonly the patient was either a spouse (44%) or a parent (28%). Among the patients 55% were NYHA Class 2 and 45% were NYHA Class 3 or 4. The caregiver cognitive interviews demonstrated that the CBQ-HF was well understood, relevant and consistently interpreted. From the initial 41 item questionnaire, fifteen items were deleted due to conceptual overlap and/or item redundancy. The final 26-item CBQ-HF (v3.0) uses a 5-point Likert severity scale, assessing 4 domains of physical, emotional/psychological, social and lifestyle burdens using a 4-week recall period.
Conclusions: The CBQ-HF (v3.0) is a comprehensive and relevant measure of subjective caregiver burden with strong content validity. This study has established that the CBQ-HF (v3.0) has strong face and content validity and should be valuable as an outcomes measure to help understand and monitor the relationship between patient heart failure severity and caregiver burden. A Translatability AssessmentSM of the measure has since been performed confirming the cultural appropriateness of the measure and psychometric validation is planned for the future to further explore the reliability, and validity of the new questionnaire in a larger caregiver sample.
Figures
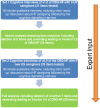
Figure 1
Flow diagram of process of face and content validity testing of CBQ-HF.
Similar articles
- Psychometric Validation of the Heart Failure Caregiver Questionnaire (HF-CQ®).
Strömberg A, Bonner N, Grant L, Bennett B, Chung ML, Jaarsma T, Luttik ML, Lewis EF, Calado F, Deschaseaux C. Strömberg A, et al. Patient. 2017 Oct;10(5):579-592. doi: 10.1007/s40271-017-0228-x. Patient. 2017. PMID: 28343292 - [Caregiver burden in relatives of persons with schizophrenia: an overview of measure instruments].
Reine G, Lancon C, Simeoni MC, Duplan S, Auquier P. Reine G, et al. Encephale. 2003 Mar-Apr;29(2):137-47. Encephale. 2003. PMID: 14567165 Review. French. - Impact of Alzheimer's Disease on Caregiver Questionnaire: internal consistency, convergent validity, and test-retest reliability of a new measure for assessing caregiver burden.
Cole JC, Ito D, Chen YJ, Cheng R, Bolognese J, Li-McLeod J. Cole JC, et al. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2014 Sep 4;12:114. doi: 10.1186/s12955-014-0114-3. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2014. PMID: 25186634 Free PMC article. - Assessing the Impact of Caring for a Person with Schizophrenia: Development of the Schizophrenia Caregiver Questionnaire.
Gater A, Rofail D, Marshall C, Tolley C, Abetz-Webb L, Zarit SH, Berardo CG. Gater A, et al. Patient. 2015 Dec;8(6):507-20. doi: 10.1007/s40271-015-0114-3. Patient. 2015. PMID: 25680337 Free PMC article. - Tools to measure the burden on informal caregivers of cancer patients: A literature review.
Zhong M, Sun S, Long J, Yuan M, Wang M, Zhang Z. Zhong M, et al. J Clin Nurs. 2024 Aug;33(8):2949-2970. doi: 10.1111/jocn.17112. Epub 2024 Mar 25. J Clin Nurs. 2024. PMID: 38528583 Review.
Cited by
- Comparative Effectiveness of Psychotherapy vs Antidepressants for Depression in Heart Failure: A Randomized Clinical Trial.
IsHak WW, Hamilton MA, Korouri S, Diniz MA, Mirocha J, Hedrick R, Chernoff R, Black JT, Aronow H, Vanle B, Dang J, Edwards G, Darwish T, Messineo G, Collier S, Pasini M, Tessema KK, Harold JG, Ong MK, Spiegel B, Wells K, Danovitch I. IsHak WW, et al. JAMA Netw Open. 2024 Jan 2;7(1):e2352094. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.52094. JAMA Netw Open. 2024. PMID: 38231511 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Measuring Quality of Life in Parents or Caregivers of Children and Adolescents with Celiac Disease: Development and Content Validation of the Questionnaire.
Abreu Paiva LM, Gandolfi L, Pratesi R, Harumi Uenishi R, Puppin Zandonadi R, Nakano EY, Pratesi CB. Abreu Paiva LM, et al. Nutrients. 2019 Sep 27;11(10):2302. doi: 10.3390/nu11102302. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 31569610 Free PMC article. - Validation and preliminary data from a health-related quality of life questionnaire for owners of dogs with cardiac disease.
Freeman LM, Rush JE, Clark MA, Bulmer BJ. Freeman LM, et al. J Vet Intern Med. 2020 May;34(3):1119-1126. doi: 10.1111/jvim.15791. Epub 2020 May 12. J Vet Intern Med. 2020. PMID: 32396234 Free PMC article. - International REgistry to assess medical Practice with lOngitudinal obseRvation for Treatment of Heart Failure (REPORT-HF): rationale for and design of a global registry.
Filippatos G, Khan SS, Ambrosy AP, Cleland JG, Collins SP, Lam CS, Angermann CE, Ertl G, Dahlström U, Hu D, Dickstein K, Perrone SV, Ghadanfar M, Bermann G, Noe A, Schweizer A, Maier T, Gheorghiade M. Filippatos G, et al. Eur J Heart Fail. 2015 May;17(5):527-33. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.262. Epub 2015 Mar 10. Eur J Heart Fail. 2015. PMID: 25754836 Free PMC article. - Rehabilitation Enablement in Chronic Heart Failure-a facilitated self-care rehabilitation intervention in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (REACH-HFpEF) and their caregivers: rationale and protocol for a single-centre pilot randomised controlled trial.
Eyre V, Lang CC, Smith K, Jolly K, Davis R, Hayward C, Wingham J, Abraham C, Green C, Warren FC, Britten N, Greaves CJ, Doherty P, Austin J, Van Lingen R, Singh S, Buckingham S, Paul K, Taylor RS, Dalal HM; REACH-HF investigators. Eyre V, et al. BMJ Open. 2016 Oct 25;6(10):e012853. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2016-012853. BMJ Open. 2016. PMID: 27798024 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
- McMurray JJ, Adamopoulos S, Anker SD, Auricchio A, Bohm M, Dickstein K. ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure 2012: the task force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure 2012 of the european society of cardiology. Developed in collaboration with the heart failure association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur Heart J. 2012;33:1787–1847. - PubMed
- Bolger AP, Gatzoulis MA. Towards defining heart failure in adults with congenital heart disease. Int J Cardiol. 2004;97:15–23. - PubMed
- National Clinical Guideline Centre. Chronic heart failure: the management of chronic heart failure in adults in primary and secondary care. London: National Clinical Guideline Centre; 2010.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous