In vitro whole blood clot lysis for fibrinolytic activity study using d-dimer and confocal microscopy - PubMed (original) (raw)
In vitro whole blood clot lysis for fibrinolytic activity study using d-dimer and confocal microscopy
Abuzar Elnager et al. Adv Hematol. 2014.
Abstract
This study aimed to evaluate in vitro whole blood (WB) clot lysis method for the assessment of fibrinolytic activity. Standardized unresected (uncut) retracted WB clot was incubated in pool platelet poor plasma (PPP) for varying incubation times and in streptokinase (SK) at different concentrations. The fibrinolytic activity was assessed by D-dimer (DD), confocal microscopy, and clot weight. DD was measured photometrically by immunoturbidimetric method. There was a significant difference in mean DD levels according to SK concentrations (P = 0.007). The mean DD ± SD according to the SK concentrations of 5, 30, 50, and 100 IU/mL was: 0.69 ± 0.12, 0.78 ± 0.14, 1.04 ± 0.14 and 2.40 ± 1.09 μ g/mL. There were no significant changes of clot weight at different SK concentrations. Gradual loss and increased branching of fibrin in both PPP and SK were observed. Quantitation of DD and morphology of fibrin loss as observed by the imaging features are in keeping with fibrinolytic activity. Combination of DD levels and confocal microscopic features was successfully applied to evaluate the in vitro WB clot lysis method described here.
Figures
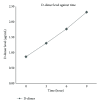
Figure 1
Line graph of D-dimer level against time of whole blood clot lysis in plasma.
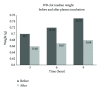
Figure 2
The difference in clot median weight between before and after pool PPP incubation.
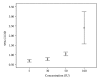
Figure 3
D-dimer level (_μ_g/mL) against various concentrations (IU/mL) of streptokinase using Box-and-Whisker plot.
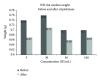
Figure 4
The difference in clot median weight between before and after SK induced fibrinolysis.
Figure 5
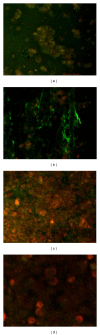
Confocal images for retracted WB clot incubated in pool PPP. (a) showed confocal image of normal retracted WB clot. (b), (c), and (d) showed retracted WB clot after 3, 6, and 9 hrs incubation in pool PPP, respectively. (a) shows confocal images of normal retracted WB clot showing fibrin mass surrounded and covered by RBCs (control untreated). (b) demonstrates a clear separation of fibrin from the RBCs after 3 hrs of WB clot incubation in PPP. (c) shows fibrin separation from the RBCs and a gradual loss of fibrin fibres after 6 hrs of incubation. (d) shows at 9 hrs of incubation in PPP minimal fibrin fibres with some remaining RBCs.
Figure 6
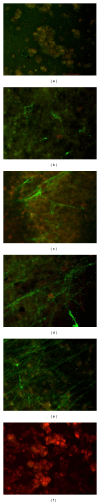
Confocal images for retracted WB clot treated with SK. (a) showed image of normal retracted WB clot. (b), (c), (d), (e) and (f) showed retracted WB clot treated with 5 IU/mL, 30 IU/mL, 50 IU/mL, 100 IU/mL, and 1500,000 IU (stock) of SK concentrations after 1-hour incubation, respectively. (a) demonstrates fibrin integrated with RBCs in retracted WB clot (control untreated). (b) shows 5 IU/mL concentration of SK where the fibrin started to separate from the RBCs. (c) depicts 30 IU/mL concentration of SK showing the fibrin that separated from the RBCs and a gradual thinning of fibrin fibres. (d) shows 50 IU/mL concentration of SK demonstrating fibrin separation from the RBCs and the fibrin fibres became much thinner and increased branching than 30 IU/mL. (e) shows 100 IU/mL concentration of SK where the fibrin almost separated from the RBCs and fibrin fibres became much thinner and increased branching than the 50 IU/mL SK. (f) shows 1500,000 IU (stock) of SK showing complete disappearance of fibrin from the RBCs.
Similar articles
- Quantitation of venous clot lysis with the D-dimer immunoassay during fibrinolytic therapy requires correction for soluble fibrin degradation.
Brenner B, Francis CW, Totterman S, Kessler CM, Rao AK, Rubin R, Kwaan HC, Gabriel KR, Marder VJ. Brenner B, et al. Circulation. 1990 Jun;81(6):1818-25. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.81.6.1818. Circulation. 1990. PMID: 2111742 - Fibrinolytic activity and dose-dependent effect of incubating human blood clots in caffeic acid phenethyl ester: in vitro assays.
Elnager A, Hassan R, Idris Z, Mustafa Z, Wan-Arfah N, Sulaiman SA, Gan SH, Abdullah WZ. Elnager A, et al. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:627471. doi: 10.1155/2015/627471. Epub 2015 Jan 15. Biomed Res Int. 2015. PMID: 25664321 Free PMC article. - Rearrangements of the fibrin network and spatial distribution of fibrinolytic components during plasma clot lysis. Study with confocal microscopy.
Sakharov DV, Nagelkerke JF, Rijken DC. Sakharov DV, et al. J Biol Chem. 1996 Jan 26;271(4):2133-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.4.2133. J Biol Chem. 1996. PMID: 8567670 - Turbulent axially directed flow of plasma containing rt-PA promotes thrombolysis of non-occlusive whole blood clots in vitro.
Tratar G, Blinc A, Strukelj M, Mikac U, Sersa I. Tratar G, et al. Thromb Haemost. 2004 Mar;91(3):487-96. doi: 10.1160/TH03-07-0447. Thromb Haemost. 2004. PMID: 14983224 - Thrombolysis using liposomal-encapsulated streptokinase: an in vitro study.
Nguyen PD, O'Rear EA, Johnson AE, Lu R, Fung BM. Nguyen PD, et al. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1989 Dec;192(3):261-9. doi: 10.3181/00379727-192-42995. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1989. PMID: 2602391
Cited by
- Fibrin Network Changes in Neonates after Cardiopulmonary Bypass.
Brown AC, Hannan RT, Timmins LH, Fernandez JD, Barker TH, Guzzetta NA. Brown AC, et al. Anesthesiology. 2016 May;124(5):1021-31. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000001058. Anesthesiology. 2016. PMID: 26914227 Free PMC article. - Comparative Analysis of Blood Clot, Plasma Rich in Growth Factors and Platelet-Rich Fibrin Resistance to Bacteria-Induced Fibrinolysis.
Puidokas T, Kubilius M, Nomeika D, Januzis G, Skrodeniene E. Puidokas T, et al. Microorganisms. 2019 Sep 7;7(9):328. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms7090328. Microorganisms. 2019. PMID: 31500263 Free PMC article. - Computer-aided engineering of staphylokinase toward enhanced affinity and selectivity for plasmin.
Nikitin D, Mican J, Toul M, Bednar D, Peskova M, Kittova P, Thalerova S, Vitecek J, Damborsky J, Mikulik R, Fleishman SJ, Prokop Z, Marek M. Nikitin D, et al. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022 Mar 12;20:1366-1377. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2022.03.004. eCollection 2022. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022. PMID: 35386102 Free PMC article. - Effect of Apixaban Pretreatment on Alteplase-Induced Thrombolysis: An In Vitro Study.
Thalerová S, Pešková M, Kittová P, Gulati S, Víteček J, Kubala L, Mikulík R. Thalerová S, et al. Front Pharmacol. 2021 Sep 15;12:740930. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.740930. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34603054 Free PMC article. - Spectrophotometric analysis of thrombolytic activity: SATA assay.
Zamanlu M, Eskandani M, Mohammadian R, Entekhabi N, Rafi M, Farhoudi M. Zamanlu M, et al. Bioimpacts. 2018;8(1):31-38. doi: 10.15171/bi.2018.05. Epub 2017 Nov 1. Bioimpacts. 2018. PMID: 29713600 Free PMC article.
References
- Weisel JW. Structure of fibrin: impact on clot stability. Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis. 2007;5(1):116–124. - PubMed
- Carroll RC, Gerrard JM, Gilliam JM. Clot retraction facilitates clot lysis. Blood. 1981;57(1):44–48. - PubMed
- Couto LT, Donato JL, de Nucci G. Analysis of five streptokinase formulations using the euglobulin lysis test and the plasminogen activation assay. Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research. 2004;37(12):1889–1894. - PubMed
- Tratar G, Blinc A, Štrukelj M, Mikac U, Serša I. Turbulent axially directed flow of plasma containing rt-PA promotes thrombolysis of non-occlusive whole blood clots in vitro . Thrombosis and Haemostasis. 2004;91(3):487–496. - PubMed
- Bruinstroop E, van de Ree MA, Huisman MV. The use of D-dimer in specific clinical conditions: a narrative review. European Journal of Internal Medicine. 2009;20(5):441–446. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials