Sufentanil, morphine, met-enkephalin, and kappa-agonist (U-50,488H) inhibit substance P release from primary sensory neurons: a model for presynaptic spinal opioid actions - PubMed (original) (raw)
Sufentanil, morphine, met-enkephalin, and kappa-agonist (U-50,488H) inhibit substance P release from primary sensory neurons: a model for presynaptic spinal opioid actions
H M Chang et al. Anesthesiology. 1989 Apr.
Abstract
An in vitro model system for analysis of presynaptic inhibitory actions of spinal opioids has been applied. Embryonic sensory neurons derived from chick dorsal root ganglia were grown in primary cell culture, and the release of substance P was evoked by electrical field stimulation during exposure to drugs with well-demonstrated affinity for opioid receptors. This allowed a pharmacologic characterization of the inhibitory actions of specific opioid agonists on the release of substance P as measured by radioimmunoassay (RIA). Sufentanil (0.5 microM), a high affinity mu receptor agonist, U-50,488H (25 microM), a selective kappa receptor agonist, and morphine (10 microM), an agonist with high affinity for mu and delta receptors, inhibited the evoked release of substance P by approximately 60%, 40%, and 50%, respectively. For sufentanil the response was demonstrated to be dose-dependent. As is the case for its analgesic action in vivo, morphine was approximately 50-fold less potent than sufentanil on a molar basis in this assay. The actions of sufentanil, U-50-488H and morphine were mimicked by the endogenous opioid peptide met-enkephalin, and its stable synthetic analog D-ala2-met5-enkephalinamide (DAME). Naloxone (25 microM), an opioid receptor antagonist, blocked the inhibitory action of sufentanil (0.5 microM), morphine (5 microM), and DAME (5 microM), but not U-50,488H (10 microM). The action of U-50,488H was partially blocked by the antagonist naltrexone (25 microM). Stereo-selectivity of agonist action was confirmed by the failure of dextrorphan (50 microM), an inactive opioid isomer, to inhibit the release of substance P.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Figures
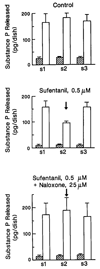
FIG. 1.
Substance P release during three phases of electrical field stimulation: Diagrams showing the result of a typical experiment. Nine cultures from a single plating were divided into three groups of three as shown in table 1. Each culture was stimulated for 3 min at 1 Hz. Baseline (shaded bars) and evoked (blanked bars) levels of substance P immunoreactivity were determined by direct RIA of the release buffer for three repeated phases of stimulation. S1, 2, and 3 stand for the amount of substance P released in Phases 1, 2, and 3, respectively. The upper diagram shows results for the external control group. In the absence of any drug, the amount of evoked substance P release was not significantly different for the three repeated phases. The middle diagram shows the result of the agonist-treated (sufentanil 0.5 µ
m
) group. The presence of sufentanil during Phase 2 inhibited the evoked substance P release by 54% (P < 0.05) as compared with Phase 1 and 3 of the same group. The lower diagram shows the result of the agonist/antagonist-treated (sufentanil 0.5 µ
m
and naloxone 25 µ
m
) group. Naloxone completely blocked the inhibitory effect of sufentanil. Error bars indicate the mean ± SD (n = 3) for released substance P as determined for three cultures of a single group.
Similar articles
- Roles of mu, delta and kappa opioid receptors in spinal and supraspinal mediation of gastrointestinal transit effects and hot-plate analgesia in the mouse.
Porreca F, Mosberg HI, Hurst R, Hruby VJ, Burks TF. Porreca F, et al. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1984 Aug;230(2):341-8. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1984. PMID: 6086883 - Mu antagonist properties of kappa agonists in a model of rat urinary bladder motility in vivo.
Sheldon RJ, Nunan L, Porreca F. Sheldon RJ, et al. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 Oct;243(1):234-40. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987. PMID: 2822899 - Opioidergic control of the spinal release of neuropeptides. Possible significance for the analgesic effects of opioids.
Bourgoin S, Benoliel JJ, Collin E, Mauborgne A, Pohl M, Hamon M, Cesselin F. Bourgoin S, et al. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 1994;8(4):307-21. doi: 10.1111/j.1472-8206.1994.tb00809.x. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 1994. PMID: 7851837 Review. - Narcotic analgesics, their detection and pain measurement in the horse: a review.
Kamerling S, Wood T, DeQuick D, Weckman TJ, Tai C, Blake JW, Tobin T. Kamerling S, et al. Equine Vet J. 1989 Jan;21(1):4-12. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-3306.1989.tb02081.x. Equine Vet J. 1989. PMID: 2563969 Review.
Cited by
- Sufentanil inhibits Pin1 to attenuate renal tubular epithelial cell ischemia-reperfusion injury by activating the PI3K/AKT/FOXO1 pathway.
Liu C, Wang Q, Niu L. Liu C, et al. Int Urol Nephrol. 2023 Aug;55(8):1903-1916. doi: 10.1007/s11255-023-03651-9. Epub 2023 Jun 10. Int Urol Nephrol. 2023. PMID: 37300758 - Pain management of nalbuphine and sufentanil in patients admitted intensive care unit of different ages.
Ji K, Gong X, Luan T, Gao X, Zang B. Ji K, et al. BMC Emerg Med. 2022 Mar 26;22(1):50. doi: 10.1186/s12873-022-00592-x. BMC Emerg Med. 2022. PMID: 35346051 Free PMC article. - Endogenous analgesia, dependence, and latent pain sensitization.
Taylor BK, Corder G. Taylor BK, et al. Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2014;20:283-325. doi: 10.1007/7854_2014_351. Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25227929 Free PMC article. - Regulation of spinal substance p release by intrathecal calcium channel blockade.
Takasusuki T, Yaksh TL. Takasusuki T, et al. Anesthesiology. 2011 Jul;115(1):153-64. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0b013e31821950c2. Anesthesiology. 2011. PMID: 21577088 Free PMC article. - Capsaicin-evoked iCGRP release from human dental pulp: a model system for the study of peripheral neuropeptide secretion in normal healthy tissue.
Fehrenbacher JC, Sun XX, Locke EE, Henry MA, Hargreaves KM. Fehrenbacher JC, et al. Pain. 2009 Aug;144(3):253-261. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2009.03.027. Epub 2009 May 9. Pain. 2009. PMID: 19428185 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
- Schenker C, Mroz EA, Leeman SE. Release of substance P from isolated nerve endings. Nature. 1976;264:790–792. - PubMed
- Lembeck F, Gamse R. Substance P in peripheral sensory processes. Ciba Found Symp. 1982;91:35–54. - PubMed
- Henry JL. In: Substance P Pain: A possible relation in afferent transmission, Substance P. von Euler US, Pernow B, editors. New York: Raven Press; 1977. pp. 231–240.
- Henry JL. Relation of substance P to pain transmission: Neurophysiological evidence. Ciba Found Symp. 1982;91:206–224. - PubMed
- Jessel TM. Substance P in nociceptive sensory neurons. Ciba Found Symp. 1982;91:225–248. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous