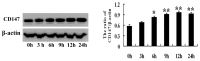CD147 modulates autophagy through the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in human prostate cancer PC-3 cells - PubMed (original) (raw)
CD147 modulates autophagy through the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in human prostate cancer PC-3 cells
Fang Fang et al. Oncol Lett. 2015 Mar.
Abstract
The multifunctional glycoprotein cluster of differentiation (CD)147 is highly expressed on the cell surface of the majority of cancer cells, and promotes tumor invasion, metastasis and growth. However, the role of CD147 in autophagy has not yet been explored in prostrate cancer cells. In the present study, prostate cancer PC-3 cells were cultured under starvation conditions, and the expression level of CD147 gradually increased. Therefore, RNA interference was used to inhibit CD147 expression, in order to investigate the biological role of this glycoprotein in autophagy progression. Autophagic activity was monitored by the changes in green fluorescent protein-light chain 3 (GFP-LC3) location and the expression of the autophagy-associated protein LC3-II. It was found that downregulation of CD147 significantly promoted GFP-LC3 puncta formation and the expression of LC3-II. Furthermore, the levels of phosphorylated serine/threonine protein kinase B (p-Akt) and phosphorylated mammalian target of rapamycin (p-mTOR) were significantly decreased, and the level of LC3-II was inversely associated with levels of p-Akt and p-mTOR in cells with downregulated expression of CD147. The results of a trypan blue exclusion assay revealed that starvation-induced cell death was increased in PC-3/shCD147 cells compared with control PC-3/Scramble cells (37.7±6.4 vs. 21.7±5.5%). Together, these results indicate that CD147 may be important in the inhibition of autophagy via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway, which prevents cell death from unrestrained autophagy.
Keywords: PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway; autophagy; cluster of differentiation 147; prostate cancer.
Figures
Figure 1
Change in CD147 expression in starvation-induced autophagy in PC-3 cells. CD147 expression was assayed by western blotting. *P<0.05 vs. 0 h, **P<0.01 vs. 0 h. CD147, cluster of differentiation 147.
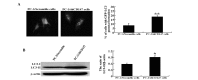
Figure 2
CD147 expression was detected in transfected cells. (A) Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction analysis of the CD147 gene level. (B) Western blot analysis of the CD147 protein level. CD147, cluster of differentiation 147; shCD147, short hairpin CD147 RNA.
Figure 3
CD147-mediated inhibition of starvation-induced autophagy in PC-3 cells. (A) The autophagosomes in the cells were visualized by observing LC3 puncta under fluroesence microscopy. (B) Quantitated levels of LC3-II from western blot analysis. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs. control cells. CD147, cluster of differentiation 147; shCD147, short hairpin CD147 RNA; GFP, green fluorescence protein; LC3, light chain 3.
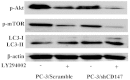
Figure 4
Analysis of the signaling pathway involved in the downregulation of atophagy by CD147. The cells were cultured for 12 h in EBSS medium with or without 20 μM LY294002. Western blot analysis was performed to observe the expression level of p-Akt, p-mTOR and LC3-II. p-Akt, phosphorylated protein kinase B; p-mTOR, phosphorylated mammalian target of rapamycin; LC3, light chain 3; CD147, cluster of differentiation 147; shCD147, short hairpin CD147 RNA.
Similar articles
- CD147 modulates androgen receptor activity through the Akt/Gsk-3β/β-catenin/AR pathway in prostate cancer cells.
Fang F, Qin Y, Hao F, Li Q, Zhang W, Zhao C, Chen S, Zhao L, Wang L, Cai J. Fang F, et al. Oncol Lett. 2016 Aug;12(2):1124-1128. doi: 10.3892/ol.2016.4684. Epub 2016 Jun 7. Oncol Lett. 2016. PMID: 27446405 Free PMC article. - Antitumor activity of curcumin by modulation of apoptosis and autophagy in human lung cancer A549 cells through inhibiting PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway.
Liu F, Gao S, Yang Y, Zhao X, Fan Y, Ma W, Yang D, Yang A, Yu Y. Liu F, et al. Oncol Rep. 2018 Mar;39(3):1523-1531. doi: 10.3892/or.2018.6188. Epub 2018 Jan 4. Oncol Rep. 2018. PMID: 29328421 - Hexabromocyclododecanes promoted autophagy through the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in L02 cells.
Jin Y, Shang Y, Zhang D, An J, Pan D. Jin Y, et al. J Environ Manage. 2019 Aug 15;244:77-82. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.05.031. Epub 2019 May 17. J Environ Manage. 2019. PMID: 31108313 - [Sunitinib induces autophagy via suppressing Akt/mTOR pathway in renal cell carcinoma].
Cao P, Jiang XJ, Xi ZJ. Cao P, et al. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2016 Aug 18;48(4):584-589. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2016. PMID: 29263493 Chinese. - Molecular pathogenesis, mechanism and therapy of Cav1 in prostate cancer.
Bian Q, Li B, Zhang L, Sun Y, Zhao Z, Ding Y, Yu H. Bian Q, et al. Discov Oncol. 2023 Nov 1;14(1):196. doi: 10.1007/s12672-023-00813-0. Discov Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37910338 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Thapsigargin induces apoptosis of prostate cancer through cofilin-1 and paxillin.
Huang F, Wang P, Wang X. Huang F, et al. Oncol Lett. 2018 Aug;16(2):1975-1980. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.8833. Epub 2018 May 30. Oncol Lett. 2018. PMID: 30008891 Free PMC article. - Influence and mechanism of miR-99a suppressing development of colorectal cancer (CRC) with diabetes mellitus (DM).
Zhu P, Liu J, Lu M, Wu G, Lin X, Cai L, Zhang X. Zhu P, et al. Onco Targets Ther. 2019 Nov 27;12:10311-10321. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S190998. eCollection 2019. Onco Targets Ther. 2019. PMID: 31819515 Free PMC article. - The Network of Pro-Inflammatory Factors CD147, DcR3, and IL33 in the Development of Kawasaki Disease.
Qi Y, Xu J, Lin Z, Tao Y, Zheng F, Wang Y, Sun Y, Fu S, Wang W, Xie C, Zhang Y, Gong F. Qi Y, et al. J Inflamm Res. 2021 Nov 19;14:6043-6053. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S338763. eCollection 2021. J Inflamm Res. 2021. PMID: 34824540 Free PMC article. - Expression and clinical significance of CD147 in renal cell carcinoma: a meta-analysis.
Li H, Wu D, Shi S, Xu Y, Wei L, Liu J, Liu Y. Li H, et al. Oncotarget. 2017 Apr 10;8(31):51331-51344. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.17376. eCollection 2017 Aug 1. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28881651 Free PMC article. - Statins: Could an old friend help in the fight against COVID-19?
Rodrigues-Diez RR, Tejera-Muñoz A, Marquez-Exposito L, Rayego-Mateos S, Santos Sanchez L, Marchant V, Tejedor Santamaria L, Ramos AM, Ortiz A, Egido J, Ruiz-Ortega M. Rodrigues-Diez RR, et al. Br J Pharmacol. 2020 Nov;177(21):4873-4886. doi: 10.1111/bph.15166. Epub 2020 Jul 15. Br J Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32562276 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous