Lymphocyte-Predominant Hodgkin's Disease in Children: A Case Study and Review of the Literature - PubMed (original) (raw)
Lymphocyte-Predominant Hodgkin's Disease in Children: A Case Study and Review of the Literature
James R Stier et al. Case Rep Oncol Med. 2015.
Abstract
A three-year-old boy presented with an enlarging neck mass. Biopsy demonstrated IgD-positive nodular lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin lymphoma (NLPHL), which was staged as IIa. The patient received cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (CHOP) with rituximab and had excellent results. NLPHL is a relatively rare disease that is biologically distinct from classic Hodgkin lymphoma (cHL). NLPHL is a B-cell malignancy likely of germinal center origin that has an overall good prognosis and favorable response to treatment. Unlike cHL, NLPHL is ubiquitously CD20-positive. Recent evidence supports the efficacy of targeted anti-CD20 therapy in NLPHL, though prospective data is limited. This case demonstrates several unique features of NLPHL and further supports the use of rituximab in front-line therapy. The clinical characteristics among patients at various ages are discussed with a special focus on the IgD-positive subtype. A thorough literature search demonstrates this to be the youngest patient with NLPHL yet described.
Figures
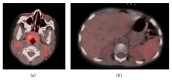
Figure 1
PET/CT demonstrates increased tracer uptake within bilateral cervical lymph nodes and the nasopharyngeal region (often normal in children). Slightly increased uptake in the spleen is seen in the image on the right with no apparent focal lesion.
Similar articles
- Minimising chemotherapy while optimising immune therapy for paediatric nodular lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin's lymphoma.
Farhan R, Alqarni NS, Algiraigri AH. Farhan R, et al. J Taibah Univ Med Sci. 2020 Sep 15;15(6):554-556. doi: 10.1016/j.jtumed.2020.08.004. eCollection 2020 Dec. J Taibah Univ Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 33318747 Free PMC article. - High relapse rate in children with non-advanced nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin's lymphoma (NLPHL or nodular paragranuloma) treated with chemotherapy only.
van Grotel M, Lam KH, de Man R, Beishuizen A, Pieters R, van den Heuvel-Eibrink MM. van Grotel M, et al. Leuk Lymphoma. 2006 Aug;47(8):1504-10. doi: 10.1080/10428190600573291. Leuk Lymphoma. 2006. PMID: 16966260 - Nodular lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin lymphoma (NLPHL) with CD30-positive lymphocyte-predominant (LP) cells.
Seliem RM, Ferry JA, Hasserjian RP, Harris NL, Zukerberg LR. Seliem RM, et al. J Hematop. 2011 Jul 23;4(3):175. doi: 10.1007/s12308-011-0104-x. eCollection 2011 Sep. J Hematop. 2011. PMID: 32288859 Free PMC article. - [Nodular lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin lymphoma in children: clinical course, biology, and management].
Gorde-Grosjean S, Guimard G, Lambilliotte A, Coulomb-Lhermine A, Montravers F, Landman-Parker J. Gorde-Grosjean S, et al. Bull Cancer. 2014 Sep;101(9):881-90. doi: 10.1684/bdc.2014.2021. Bull Cancer. 2014. PMID: 25296072 Review. French. - Modern principles in the management of nodular lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin lymphoma.
Spinner MA, Varma G, Advani RH. Spinner MA, et al. Br J Haematol. 2019 Jan;184(1):17-29. doi: 10.1111/bjh.15616. Epub 2018 Nov 28. Br J Haematol. 2019. PMID: 30485408 Review.
Cited by
- Minimising chemotherapy while optimising immune therapy for paediatric nodular lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin's lymphoma.
Farhan R, Alqarni NS, Algiraigri AH. Farhan R, et al. J Taibah Univ Med Sci. 2020 Sep 15;15(6):554-556. doi: 10.1016/j.jtumed.2020.08.004. eCollection 2020 Dec. J Taibah Univ Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 33318747 Free PMC article.
References
- Diehl V., Sextro M., Franklin J., et al. Clinical presentation, course, and prognostic factors in lymphocyte- predominant Hodgkin's disease and lymphocyte-rich classical Hodgkin's disease: report from the European Task Force on lymphoma project on lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin's disease. Journal of Clinical Oncology. 1999;17(3):776–783. - PubMed
- Biasoli I., Stamatoullas A., Meignin V., et al. Nodular, lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin lymphoma: a long-term study and analysis of transformation to diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in a cohort of 164 patients from the adult lymphoma study group. Cancer. 2010;116(3):631–639. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials