Nivolumab and ipilimumab versus ipilimumab in untreated melanoma - PubMed (original) (raw)
Randomized Controlled Trial
. 2015 May 21;372(21):2006-17.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1414428. Epub 2015 Apr 20.
Jason Chesney, Anna C Pavlick, Caroline Robert, Kenneth Grossmann, David McDermott, Gerald P Linette, Nicolas Meyer, Jeffrey K Giguere, Sanjiv S Agarwala, Montaser Shaheen, Marc S Ernstoff, David Minor, April K Salama, Matthew Taylor, Patrick A Ott, Linda M Rollin, Christine Horak, Paul Gagnier, Jedd D Wolchok, F Stephen Hodi
Affiliations
- PMID: 25891304
- PMCID: PMC5744258
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1414428
Randomized Controlled Trial
Nivolumab and ipilimumab versus ipilimumab in untreated melanoma
Michael A Postow et al. N Engl J Med. 2015.
Erratum in
Abstract
Background: In a phase 1 dose-escalation study, combined inhibition of T-cell checkpoint pathways by nivolumab and ipilimumab was associated with a high rate of objective response, including complete responses, among patients with advanced melanoma.
Methods: In this double-blind study involving 142 patients with metastatic melanoma who had not previously received treatment, we randomly assigned patients in a 2:1 ratio to receive ipilimumab (3 mg per kilogram of body weight) combined with either nivolumab (1 mg per kilogram) or placebo once every 3 weeks for four doses, followed by nivolumab (3 mg per kilogram) or placebo every 2 weeks until the occurrence of disease progression or unacceptable toxic effects. The primary end point was the rate of investigator-assessed, confirmed objective response among patients with BRAF V600 wild-type tumors.
Results: Among patients with BRAF wild-type tumors, the rate of confirmed objective response was 61% (44 of 72 patients) in the group that received both ipilimumab and nivolumab (combination group) versus 11% (4 of 37 patients) in the group that received ipilimumab and placebo (ipilimumab-monotherapy group) (P<0.001), with complete responses reported in 16 patients (22%) in the combination group and no patients in the ipilimumab-monotherapy group. The median duration of response was not reached in either group. The median progression-free survival was not reached with the combination therapy and was 4.4 months with ipilimumab monotherapy (hazard ratio associated with combination therapy as compared with ipilimumab monotherapy for disease progression or death, 0.40; 95% confidence interval, 0.23 to 0.68; P<0.001). Similar results for response rate and progression-free survival were observed in 33 patients with BRAF mutation-positive tumors. Drug-related adverse events of grade 3 or 4 were reported in 54% of the patients who received the combination therapy as compared with 24% of the patients who received ipilimumab monotherapy. Select adverse events with potential immunologic causes were consistent with those in a phase 1 study, and most of these events resolved with immune-modulating medication.
Conclusions: The objective-response rate and the progression-free survival among patients with advanced melanoma who had not previously received treatment were significantly greater with nivolumab combined with ipilimumab than with ipilimumab monotherapy. Combination therapy had an acceptable safety profile. (Funded by Bristol-Myers Squibb; ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT01927419.).
Figures
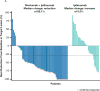
Fig 1. Clinical activities
(Panel A) Tumor burden change from baseline in the sum of reference diameters of target lesion among patients receiving combination nivolumab and ipilimumab (left) or ipilimumab monotherapy (right); Horizontal reference line indicates the 30% reduction in tumor burden consistent with a RECIST 1.1 response; (Panel B) Durability of tumor regressions in patients with advanced melanoma with BRAF wild-type tumors who had objective responses to combination nivolumab and ipilimumab or ipilimumab alone according to conventional RECIST criteria. Blue bars indicate the time to and duration of response while on treatment; red bars indicate duration of response after treatment discontinuation; open circles indicate first evidence of objective response; arrows indicate ongoing response at time of analysis. (Panel C) Kaplan-Meier curves for progression-free survival of patients with BRAF wild-type tumors treated with combination nivolumab and ipilimumab or ipilimumab alone.
Fig 1. Clinical activities
(Panel A) Tumor burden change from baseline in the sum of reference diameters of target lesion among patients receiving combination nivolumab and ipilimumab (left) or ipilimumab monotherapy (right); Horizontal reference line indicates the 30% reduction in tumor burden consistent with a RECIST 1.1 response; (Panel B) Durability of tumor regressions in patients with advanced melanoma with BRAF wild-type tumors who had objective responses to combination nivolumab and ipilimumab or ipilimumab alone according to conventional RECIST criteria. Blue bars indicate the time to and duration of response while on treatment; red bars indicate duration of response after treatment discontinuation; open circles indicate first evidence of objective response; arrows indicate ongoing response at time of analysis. (Panel C) Kaplan-Meier curves for progression-free survival of patients with BRAF wild-type tumors treated with combination nivolumab and ipilimumab or ipilimumab alone.
Fig 1. Clinical activities
(Panel A) Tumor burden change from baseline in the sum of reference diameters of target lesion among patients receiving combination nivolumab and ipilimumab (left) or ipilimumab monotherapy (right); Horizontal reference line indicates the 30% reduction in tumor burden consistent with a RECIST 1.1 response; (Panel B) Durability of tumor regressions in patients with advanced melanoma with BRAF wild-type tumors who had objective responses to combination nivolumab and ipilimumab or ipilimumab alone according to conventional RECIST criteria. Blue bars indicate the time to and duration of response while on treatment; red bars indicate duration of response after treatment discontinuation; open circles indicate first evidence of objective response; arrows indicate ongoing response at time of analysis. (Panel C) Kaplan-Meier curves for progression-free survival of patients with BRAF wild-type tumors treated with combination nivolumab and ipilimumab or ipilimumab alone.
Comment in
- Nivolumab + ipilimumab ups melanoma response.
[No authors listed] [No authors listed] Cancer Discov. 2015 Jun;5(6):OF2. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-NB2015-058. Epub 2015 Apr 21. Cancer Discov. 2015. PMID: 25898833 - Immunotherapy: Combined immunotherapy--a new standard in metastatic melanoma?
Hauschild A, Garbe C. Hauschild A, et al. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2015 Aug;12(8):439-40. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2015.118. Epub 2015 Jun 23. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26099985 No abstract available.
Similar articles
- Combined nivolumab and ipilimumab versus ipilimumab alone in patients with advanced melanoma: 2-year overall survival outcomes in a multicentre, randomised, controlled, phase 2 trial.
Hodi FS, Chesney J, Pavlick AC, Robert C, Grossmann KF, McDermott DF, Linette GP, Meyer N, Giguere JK, Agarwala SS, Shaheen M, Ernstoff MS, Minor DR, Salama AK, Taylor MH, Ott PA, Horak C, Gagnier P, Jiang J, Wolchok JD, Postow MA. Hodi FS, et al. Lancet Oncol. 2016 Nov;17(11):1558-1568. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(16)30366-7. Epub 2016 Sep 9. Lancet Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27622997 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Nivolumab plus ipilimumab or nivolumab alone versus ipilimumab alone in advanced melanoma (CheckMate 067): 4-year outcomes of a multicentre, randomised, phase 3 trial.
Hodi FS, Chiarion-Sileni V, Gonzalez R, Grob JJ, Rutkowski P, Cowey CL, Lao CD, Schadendorf D, Wagstaff J, Dummer R, Ferrucci PF, Smylie M, Hill A, Hogg D, Marquez-Rodas I, Jiang J, Rizzo J, Larkin J, Wolchok JD. Hodi FS, et al. Lancet Oncol. 2018 Nov;19(11):1480-1492. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30700-9. Epub 2018 Oct 22. Lancet Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30361170 Clinical Trial. - Overall Survival with Combined Nivolumab and Ipilimumab in Advanced Melanoma.
Wolchok JD, Chiarion-Sileni V, Gonzalez R, Rutkowski P, Grob JJ, Cowey CL, Lao CD, Wagstaff J, Schadendorf D, Ferrucci PF, Smylie M, Dummer R, Hill A, Hogg D, Haanen J, Carlino MS, Bechter O, Maio M, Marquez-Rodas I, Guidoboni M, McArthur G, Lebbé C, Ascierto PA, Long GV, Cebon J, Sosman J, Postow MA, Callahan MK, Walker D, Rollin L, Bhore R, Hodi FS, Larkin J. Wolchok JD, et al. N Engl J Med. 2017 Oct 5;377(14):1345-1356. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1709684. Epub 2017 Sep 11. N Engl J Med. 2017. PMID: 28889792 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Nivolumab: A Review in Advanced Melanoma.
Scott LJ. Scott LJ. Drugs. 2015 Aug;75(12):1413-24. doi: 10.1007/s40265-015-0442-6. Drugs. 2015. PMID: 26220912 Review. - Nivolumab (OPDIVOO) BRAF V600 mutation-negative metastatic or inoperable melanoma: survival advantage.
[No authors listed] [No authors listed] Prescrire Int. 2016 Dec;25(177):289-292. Prescrire Int. 2016. PMID: 30758924 Review.
Cited by
- 4E-BP3 deficiency impairs dendritic cell activation and CD4+ T cell differentiation and attenuates α-myosin-specific T cell-mediated myocarditis in mice.
Li S, Tajiri K, Yuan Z, Murakata Y, Song Z, Mizuno S, Xu D, Murakoshi N. Li S, et al. Basic Res Cardiol. 2024 Nov 9. doi: 10.1007/s00395-024-01089-3. Online ahead of print. Basic Res Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 39516410 - An insight into the role of innate immune cells in breast tumor microenvironment.
Garg S, Rai G, Singh S, Gauba P, Ali J, Dang S. Garg S, et al. Breast Cancer. 2024 Oct 26. doi: 10.1007/s12282-024-01645-8. Online ahead of print. Breast Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39460874 Review. - The many faces of autoimmune-mediated melanocyte destruction in melanoma.
Ungureanu L, Vasilovici AF, Halmágyi SR, Trufin II, Apostu AP, Şenilă SC. Ungureanu L, et al. Front Immunol. 2024 Oct 3;15:1417273. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1417273. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39421737 Free PMC article. Review. - Cold and hot tumors: from molecular mechanisms to targeted therapy.
Wu B, Zhang B, Li B, Wu H, Jiang M. Wu B, et al. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024 Oct 18;9(1):274. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-01979-x. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024. PMID: 39420203 Free PMC article. Review. - Machine learning-based identification of an immunotherapy-related signature to enhance outcomes and immunotherapy responses in melanoma.
Deng Z, Liu J, Yu YV, Jin YN. Deng Z, et al. Front Immunol. 2024 Sep 17;15:1451103. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1451103. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39355255 Free PMC article.
References
- Robert C, Thomas L, Bondarenko I, et al. Ipilimumab plus dacarbazine for previously untreated metastatic melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2011;364:2517–2526. - PubMed
- Larkin J, Ascierto PA, Dreno B, et al. Combined vemurafenib and cobimetinib in BRAF-mutated melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:1867–1876. - PubMed
- Long GV, Stroyakovsky D, Gogas H, et al. Combined BRAF and MEK inhibition versus BRAF inhibition alone in melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:1877–1888. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials