IL-6 signaling contributes to cisplatin resistance in non-small cell lung cancer via the up-regulation of anti-apoptotic and DNA repair associated molecules - PubMed (original) (raw)
IL-6 signaling contributes to cisplatin resistance in non-small cell lung cancer via the up-regulation of anti-apoptotic and DNA repair associated molecules
Shanzhou Duan et al. Oncotarget. 2015.
Abstract
Cisplatin-based chemotherapy is currently the most effective treatment regimen for non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), but eventually tumor resistance develops which limits its success. The potential implication of IL-6 signaling in the cisplatin resistance of NSCLC was explored by testing whether NSCLC cells with different levels of intracellular IL-6 show different responses to the cytotoxic treatment of cisplatin. When the cisplatin cytotoxicity of the IL-6 knocked down human NSCLC cells (A549IL-6si and H157IL-6si) were compared with their corresponding scramble control cells (A549sc and H157sc), higher cisplatin cytotoxicity was found in IL-6 si cells than sc cells. Subcutaneous xenograft mouse models were developed using a pair of A549sc and A549IL-6si cells. When the tumor grew to about 400 mm2, mice were treated with cisplatin and tumor regression was monitored. Higher tumor regression was detected in the A549IL-6si xenografts compared to A549sc xenografts following cisplatin treatment. Immunostaining study results from tumor tissues also supported this finding. Expression of anti-apoptotic proteins Bcl-2 and Mcl-1 and DNA repair associated molecules ATM, CHK1, TP73, p53, and ERCC1 were significantly up regulated in cisplatin-treated A549sc and H157sc cells, but no increase was detected in A549IL-6si and H157IL-6si cells. Further inhibitor studies revealed that up regulation of these molecules by IL-6 may be through activation of IL-6 downstream signaling pathways like Akt, MAPK, Stat3, and Erk. These results provide potential for combining cisplatin and inhibitors of IL-6 signaling or its downstream signaling pathway as a future therapeutic approach in preventing development of cisplatin resistant NSCLC tumors.
Keywords: DNA repair; IL-6; apoptosis; cisplatin resistance; non-small cell lung cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
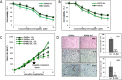
Figure 1. IL-6 knockdown in NSCLC cells increased in vitro and in vivo sensitivity to cisplatin
A. Cisplatin cytotoxicity tests of A549IL-6si/sc cells upon various concentrations of cisplatin for 2 days. B. Cisplatin cytotoxicity tests of H157IL-6si/sc cells upon various concentrations of cisplatin for 2 days. C. Tumor regression analyses of A549IL-6si and A549sc cells-derived xenografts in nude mice on cisplatin treatments. Xenografts were developed by subcutaneously injecting 1 × 106 A549IL-6si or A549sc cells into flanks of 8 week old female nude mice. When tumor volumes reached 400 mm3, cisplatin (3 mg/kg, i.p. two times per week) treatment started. Tumor growth was monitored twice per week and at the end of three weeks of treatment, mice were sacrificed. D. H&E and IHC staining of tumor tissues. Tumor tissues of A549IL-6si/sc xenografts were processed and subjected to H&E and IHC staining. Upper panels show H&E staining, middle panels present IHC staining with IL-6 antibody, and lower panels are the IHC staining results using antibody against Ki67 (magnification, 100x). Quantitation of IL-6 and Ki67 IHC staining is shown on right. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.
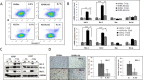
Figure 2. IL-6 protected A549 and H157 cells from apoptotic death after cisplatin treatment via up regulation of Bcl-2 and Mcl-1
A. Analysis of apoptosis following cisplatin treatment. A549IL-6si/sc and H157IL-6si/sc cells were treated with cisplatin (5 μM) for 48 hours and subjected into Annexin V based-flow cytometric analysis according to the manufacturer's instruction. The % of apoptotic cell is indicated in each graph. B. qPCR results of analyzing mRNA expressions of anti-apoptotic molecules in A549IL-6si/sc and H157IL-6si/sc cells after cisplatin treatment (5 μM, 48 hours). C. Western blot results showing expression of anti-apoptotic proteins in A549IL-6si/sc and H157IL-6si/sc cells following cisplatin treatment (5 μM, 48 hours). D. IHC staining of tumor tissues of A549IL-6si/sc xenografts showing expression of Bcl-2 and Mcl-1(Magnification, 100x). Quantitation of Bcl-2 and Mcl-1 IHC staining is shown on right. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.
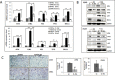
Figure 3. IL-6 expressing A549sc and H157sc cells showed higher expression of DNA repair molecules upon cisplatin treatment compared to A549IL-6si and H157IL-6si cells
A. qPCR results of mRNA expressions of DNA repair associated molecules in A549IL-6si/sc and H157IL-6si/sc cells after cisplatin treatment (5 μM, 48 hours). B. Western blot analyses results showing expression of the DNA repair-associated molecules in A549IL-6si/sc and H157IL-6si/sc cells on cisplatin treatment (5 μM, 48 hours). C. IHC staining of tumor tissues of A549IL-6si/sc xenografts investigating expression of ATM and CHK1 (Magnification, 100x). Quantitation of positively stained cells is shown on right. *p < 0.05 **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.
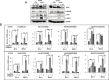
Figure 4. Activation of IL-6 downstream signaling pathways on cisplatin treatment
A. Western blot analysis analyzing activations of several signaling pathways in A549IL-6si/sc and H157IL-6si/sc cells 48 hours after cisplatin treatments (5 μM). B. Analyses of qPCR results showing expression of Bcl-2 and ERCC1 in A549sc and H157sc cells, with or without cisplatin treatment, in the absence and presence of inhibitors of each signaling pathway. *p < 0.05 **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.
Similar articles
- IL-6 promotes growth and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of CD133+ cells of non-small cell lung cancer.
Lee SO, Yang X, Duan S, Tsai Y, Strojny LR, Keng P, Chen Y. Lee SO, et al. Oncotarget. 2016 Feb 9;7(6):6626-38. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6570. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26675547 Free PMC article. - Simultaneous targeting of ATM and Mcl-1 increases cisplatin sensitivity of cisplatin-resistant non-small cell lung cancer.
Zhang F, Shen M, Yang L, Yang X, Tsai Y, Keng PC, Chen Y, Lee SO, Chen Y. Zhang F, et al. Cancer Biol Ther. 2017 Aug 3;18(8):606-615. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2017.1345391. Epub 2017 Jul 7. Cancer Biol Ther. 2017. PMID: 28686074 Free PMC article. - IL-6 signaling promotes DNA repair and prevents apoptosis in CD133+ stem-like cells of lung cancer after radiation.
Chen Y, Zhang F, Tsai Y, Yang X, Yang L, Duan S, Wang X, Keng P, Lee SO. Chen Y, et al. Radiat Oncol. 2015 Nov 14;10:227. doi: 10.1186/s13014-015-0534-1. Radiat Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26572130 Free PMC article. Retracted. - DNA repair and cisplatin resistance in non-small-cell lung cancer.
Rosell R, Lord RV, Taron M, Reguart N. Rosell R, et al. Lung Cancer. 2002 Dec;38(3):217-27. doi: 10.1016/s0169-5002(02)00224-6. Lung Cancer. 2002. PMID: 12445742 Review. - Pharmacogenomics in lung cancer: an analysis of DNA repair gene expression in patients treated with platinum-based chemotherapy.
García-Campelo R, Alonso-Curbera G, Antón Aparicio LM, Rosell R. García-Campelo R, et al. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2005 Oct;6(12):2015-26. doi: 10.1517/14656566.6.12.2015. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2005. PMID: 16197356 Review.
Cited by
- Interleukin-6 mediates resistance to PI3K-pathway-targeted therapy in lymphoma.
Kim JH, Kim WS, Park C. Kim JH, et al. BMC Cancer. 2019 Oct 10;19(1):936. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-6057-7. BMC Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31601188 Free PMC article. - Inflammation-induced DNA damage, mutations and cancer.
Kay J, Thadhani E, Samson L, Engelward B. Kay J, et al. DNA Repair (Amst). 2019 Nov;83:102673. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2019.102673. Epub 2019 Jul 25. DNA Repair (Amst). 2019. PMID: 31387777 Free PMC article. Review. - Long Non-Coding RNA SLC25A21-AS1 Promotes Multidrug Resistance in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma by Regulating miR-324-3p/IL-6 Axis.
Wang X, Wang C, Xu H, Xie H. Wang X, et al. Cancer Manag Res. 2020 May 26;12:3949-3957. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S251820. eCollection 2020. Cancer Manag Res. 2020. PMID: 32547230 Free PMC article. - IL-22 Confers EGFR-TKI Resistance in NSCLC via the AKT and ERK Signaling Pathways.
Wang X, Xu J, Chen J, Jin S, Yao J, Yu T, Wang W, Guo R. Wang X, et al. Front Oncol. 2019 Nov 5;9:1167. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.01167. eCollection 2019. Front Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31750252 Free PMC article. - PD-0332991 combined with cisplatin inhibits nonsmall cell lung cancer and reversal of cisplatin resistance.
Liu M, Cui L, Li X, Xia C, Li Y, Wang R, Ren F, Liu H, Chen J. Liu M, et al. Thorac Cancer. 2021 Mar;12(6):924-931. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.13866. Epub 2021 Feb 3. Thorac Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33534964 Free PMC article.
References
- Cersosimo RJ. Lung cancer: a review. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2002;59:611–642. - PubMed
- Galluzzi L, Senovilla L, Vitale I, Michels J, Martins I, Kepp O, Castedo M, Kroemer G. Molecular mechanisms of cisplatin resistance. Oncogene. 2012;31:1869–1883. - PubMed
- The role of DNA repair pathways in cisplatin resistant lung cancer. Cancer Treat Rev. 2014;40:1161–1170. - PubMed
- Lai SL, Hwang J, Perng RP, Whang-Peng J. Modulation of cisplatin resistance in acquired-resistant nonsmall cell lung cancer cells. Oncology Res. 1995;7:31–38. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous