Whole-Exome Sequencing in Familial Parkinson Disease - PubMed (original) (raw)
doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2015.3266.
Laurie A Robak 2, Kurt Hetrick 3, Kevin Bowling 4, Eric Boerwinkle 5, Zeynep H Coban-Akdemir 6, Tomasz Gambin 6, Richard A Gibbs 7, Shen Gu 6, Preti Jain 8, Joseph Jankovic 9, Shalini Jhangiani 7, Kaveeta Kaw 10, Dongbing Lai 1, Hai Lin 11, Hua Ling 3, Yunlong Liu 1, James R Lupski 12, Donna Muzny 7, Paula Porter 10, Elizabeth Pugh 3, Janson White 6, Kimberly Doheny 3, Richard M Myers 4, Joshua M Shulman 13, Tatiana Foroud 1
Affiliations
- PMID: 26595808
- PMCID: PMC4946647
- DOI: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2015.3266
Whole-Exome Sequencing in Familial Parkinson Disease
Janice L Farlow et al. JAMA Neurol. 2016 Jan.
Abstract
Importance: Parkinson disease (PD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disease for which susceptibility is linked to genetic and environmental risk factors.
Objective: To identify genetic variants contributing to disease risk in familial PD.
Design, setting, and participants: A 2-stage study design that included a discovery cohort of families with PD and a replication cohort of familial probands was used. In the discovery cohort, rare exonic variants that segregated in multiple affected individuals in a family and were predicted to be conserved or damaging were retained. Genes with retained variants were prioritized if expressed in the brain and located within PD-relevant pathways. Genes in which prioritized variants were observed in at least 4 families were selected as candidate genes for replication in the replication cohort. The setting was among individuals with familial PD enrolled from academic movement disorder specialty clinics across the United States. All participants had a family history of PD.
Main outcomes and measures: Identification of genes containing rare, likely deleterious, genetic variants in individuals with familial PD using a 2-stage exome sequencing study design.
Results: The 93 individuals from 32 families in the discovery cohort (49.5% [46 of 93] female) had a mean (SD) age at onset of 61.8 (10.0) years. The 49 individuals with familial PD in the replication cohort (32.6% [16 of 49] female) had a mean (SD) age at onset of 50.1 (15.7) years. Discovery cohort recruitment dates were 1999 to 2009, and replication cohort recruitment dates were 2003 to 2014. Data analysis dates were 2011 to 2015. Three genes containing a total of 13 rare and potentially damaging variants were prioritized in the discovery cohort. Two of these genes (TNK2 and TNR) also had rare variants that were predicted to be damaging in the replication cohort. All 9 variants identified in the 2 replicated genes in 12 families across the discovery and replication cohorts were confirmed via Sanger sequencing.
Conclusions and relevance: TNK2 and TNR harbored rare, likely deleterious, variants in individuals having familial PD, with similar findings in an independent cohort. To our knowledge, these genes have not been previously associated with PD, although they have been linked to critical neuronal functions. Further studies are required to confirm a potential role for these genes in the pathogenesis of PD.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest Disclosures: None reported.
Figures
Figure 1. Study Design and Discovery Cohort Variant Filtering
Shown is the overall design for the 2-stage study and variant counts at each stage of filtering. GO indicates Gene Ontology (annotations listed in the Filtering subsection of the Methods section); Indels, insertions or deletions; MAF, minor allele frequency; and SNVs, single-nucleotide variants.
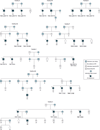
Figure 2. Pedigrees Segregating TNK2 and TNR Variants
PD indicates Parkinson disease. A square indicates a male individual; a circle, a female individual. Below each symbol is a subject number. For sequenced, affected individuals, the age at disease onset is below the subject number. A question mark indicates an unknown age at onset.
Comment in
- Exome Variant Mining in Familial Parkinson Disease: Will Replication Find the Gold?
Toft M, Ross OA. Toft M, et al. JAMA Neurol. 2016 Jan;73(1):21-2. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2015.3536. JAMA Neurol. 2016. PMID: 26595415 No abstract available.
Similar articles
- Exome Variant Mining in Familial Parkinson Disease: Will Replication Find the Gold?
Toft M, Ross OA. Toft M, et al. JAMA Neurol. 2016 Jan;73(1):21-2. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2015.3536. JAMA Neurol. 2016. PMID: 26595415 No abstract available. - Identification of sixteen novel candidate genes for late onset Parkinson's disease.
Gialluisi A, Reccia MG, Modugno N, Nutile T, Lombardi A, Di Giovannantonio LG, Pietracupa S, Ruggiero D, Scala S, Gambardella S; International Parkinson’s Disease Genomics Consortium (IPDGC); Iacoviello L, Gianfrancesco F, Acampora D, D'Esposito M, Simeone A, Ciullo M, Esposito T. Gialluisi A, et al. Mol Neurodegener. 2021 Jun 21;16(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s13024-021-00455-2. Mol Neurodegener. 2021. PMID: 34148545 Free PMC article. - Exome Sequencing of Familial Bipolar Disorder.
Goes FS, Pirooznia M, Parla JS, Kramer M, Ghiban E, Mavruk S, Chen YC, Monson ET, Willour VL, Karchin R, Flickinger M, Locke AE, Levy SE, Scott LJ, Boehnke M, Stahl E, Moran JL, Hultman CM, Landén M, Purcell SM, Sklar P, Zandi PP, McCombie WR, Potash JB. Goes FS, et al. JAMA Psychiatry. 2016 Jun 1;73(6):590-7. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2016.0251. JAMA Psychiatry. 2016. PMID: 27120077 Free PMC article. - Rare and Coding Region Genetic Variants Associated With Risk of Ischemic Stroke: The NHLBI Exome Sequence Project.
Auer PL, Nalls M, Meschia JF, Worrall BB, Longstreth WT Jr, Seshadri S, Kooperberg C, Burger KM, Carlson CS, Carty CL, Chen WM, Cupples LA, DeStefano AL, Fornage M, Hardy J, Hsu L, Jackson RD, Jarvik GP, Kim DS, Lakshminarayan K, Lange LA, Manichaikul A, Quinlan AR, Singleton AB, Thornton TA, Nickerson DA, Peters U, Rich SS; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Exome Sequencing Project. Auer PL, et al. JAMA Neurol. 2015 Jul;72(7):781-8. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2015.0582. JAMA Neurol. 2015. PMID: 25961151 Free PMC article. - Spontaneous preterm birth: advances toward the discovery of genetic predisposition.
Strauss JF 3rd, Romero R, Gomez-Lopez N, Haymond-Thornburg H, Modi BP, Teves ME, Pearson LN, York TP, Schenkein HA. Strauss JF 3rd, et al. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2018 Mar;218(3):294-314.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2017.12.009. Epub 2017 Dec 14. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2018. PMID: 29248470 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Genetic Analysis of FBXO2, FBXO6, FBXO12, and FBXO41 Variants in Han Chinese Patients with Sporadic Parkinson's Disease.
Yuan L, Song Z, Deng X, Yang Z, Yang Y, Guo Y, Lu H, Deng H. Yuan L, et al. Neurosci Bull. 2017 Oct;33(5):510-514. doi: 10.1007/s12264-017-0122-5. Epub 2017 Mar 24. Neurosci Bull. 2017. PMID: 28341977 Free PMC article. - The Rostock International Parkinson's Disease (ROPAD) Study: Protocol and Initial Findings.
Skrahina V, Gaber H, Vollstedt EJ, Förster TM, Usnich T, Curado F, Brüggemann N, Paul J, Bogdanovic X, Zülbahar S, Olmedillas M, Skobalj S, Ameziane N, Bauer P, Csoti I, Koleva-Alazeh N, Grittner U, Westenberger A, Kasten M, Beetz C, Klein C, Rolfs A; ROPAD Study Group. Skrahina V, et al. Mov Disord. 2021 Apr;36(4):1005-1010. doi: 10.1002/mds.28416. Epub 2020 Dec 14. Mov Disord. 2021. PMID: 33314351 Free PMC article. - Structure of Tau filaments in Prion protein amyloidoses.
Hallinan GI, Hoq MR, Ghosh M, Vago FS, Fernandez A, Garringer HJ, Vidal R, Jiang W, Ghetti B. Hallinan GI, et al. Acta Neuropathol. 2021 Aug;142(2):227-241. doi: 10.1007/s00401-021-02336-w. Epub 2021 Jun 14. Acta Neuropathol. 2021. PMID: 34128081 Free PMC article. - CRISPR-mediated gene correction links the ATP7A M1311V mutations with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis pathogenesis in one individual.
Yun Y, Hong SA, Kim KK, Baek D, Lee D, Londhe AM, Lee M, Yu J, McEachin ZT, Bassell GJ, Bowser R, Hales CM, Cho SR, Kim J, Pae AN, Cheong E, Kim S, Boulis NM, Bae S, Ha Y. Yun Y, et al. Commun Biol. 2020 Jan 20;3(1):33. doi: 10.1038/s42003-020-0755-1. Commun Biol. 2020. PMID: 31959876 Free PMC article. - Structure-based classification of tauopathies.
Shi Y, Zhang W, Yang Y, Murzin AG, Falcon B, Kotecha A, van Beers M, Tarutani A, Kametani F, Garringer HJ, Vidal R, Hallinan GI, Lashley T, Saito Y, Murayama S, Yoshida M, Tanaka H, Kakita A, Ikeuchi T, Robinson AC, Mann DMA, Kovacs GG, Revesz T, Ghetti B, Hasegawa M, Goedert M, Scheres SHW. Shi Y, et al. Nature. 2021 Oct;598(7880):359-363. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03911-7. Epub 2021 Sep 29. Nature. 2021. PMID: 34588692 Free PMC article.
References
- Bonifati V, Rizzu P, van Baren MJ, et al. Mutations in the DJ-1 gene associated with autosomal recessive early-onset parkinsonism. Science. 2003;299(5604):256–259. - PubMed
- Zimprich A, Biskup S, Leitner P, et al. Mutations in LRRK2 cause autosomal-dominant parkinsonism with pleomorphic pathology. Neuron. 2004;44(4):601–607. - PubMed
- Polymeropoulos MH, Lavedan C, Leroy E, et al. Mutation in the alpha-synuclein gene identified in families with Parkinson’s disease. Science. 1997;276(5321):2045–2047. - PubMed
- Kitada T, Asakawa S, Hattori N, et al. Mutations in the parkin gene cause autosomal recessive juvenile parkinsonism. Nature. 1998;392(6676):605–608. - PubMed
- Valente EM, Abou-Sleiman PM, Caputo V, et al. Hereditary early-onset Parkinson’s disease caused by mutations in PINK1. Science. 2004;304(5674):1158–1160. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U54HG003273/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U54HG006542/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- C06RR029965/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100011I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HG003273/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001108/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM077229/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS037167/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM008307/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R21NS089854/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HG006542/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007526/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100011C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- TL1 TR000162/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- C06 RR029965/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM07526-37/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS037167/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS089854/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- 1X01HG006236/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous