Non-Genomic Actions of the Androgen Receptor in Prostate Cancer - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Non-Genomic Actions of the Androgen Receptor in Prostate Cancer
Jacky K Leung et al. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2017.
Abstract
Androgen receptor (AR) is a validated drug target for prostate cancer based on its role in proliferation, survival, and metastases of prostate cancer cells. Unfortunately, despite recent improvements to androgen deprivation therapy and the advent of better antiandrogens with a superior affinity for the AR ligand-binding domain (LBD), most patients with recurrent disease will eventually develop lethal metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC). Expression of constitutively active AR splice variants that lack the LBD contribute toward therapeutic resistance by bypassing androgen blockade and antiandrogens. In the canonical pathway, binding of androgen to AR LBD triggers the release of AR from molecular chaperones which enable conformational changes and protein-protein interactions to facilitate its nuclear translocation where it regulates the expression of target genes. However, preceding AR function in the nucleus, initial binding of androgen to AR LBD in the cytoplasm may already initiate signal transduction pathways to modulate cellular proliferation and migration. In this article, we review the significance of signal transduction pathways activated by rapid, non-genomic signaling of the AR during the progression to metastatic CRPC and put into perspective the implications for current and novel therapies that target different domains of AR.
Keywords: AR antagonists; MAPK/ERK signaling; PI3K/Akt signaling; Src kinase; androgen receptor; non-genomic signaling; prostate cancer.
Figures
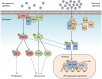
Figure 1
Integration of non-genomic signaling and canonical signaling of androgen receptor (AR). In the presence of low androgen levels (picomolar concentrations), AR interactions with Src kinase and p85α regulatory subunit of phosphoinositide 3-kinase activates mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and Akt pathways to enhance cell proliferation and survival in a non-genomic fashion. In the presence of high androgen levels (nanomolar concentrations), AR is activated in a canonical pathway to regulate the expression of target genes. Activation of MAPK and Akt by non-genomic signaling also enhances genomic AR signals by phosphorylating the AR or transcriptional coactivators.
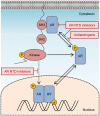
Figure 2
Targeting non-genomic actions of androgen receptor (AR). Non-genomic signaling of AR is activated by interactions between the polyproline domain of the AR N-terminal domain (NTD) and Src homology domain 3 of Src. Activated Src can enhance the transactivation of AR directly by phosphorylating AR Y534 or indirectly by stimulating alternate kinase pathways that modulate AR activity. AR NTD inhibitors may prevent non-genomic signals from AR by blocking Src interaction with the AR NTD and can block both ligand-dependent and ligand-independent transactivation of AR.
Similar articles
- Androgen receptors in hormone-dependent and castration-resistant prostate cancer.
Shafi AA, Yen AE, Weigel NL. Shafi AA, et al. Pharmacol Ther. 2013 Dec;140(3):223-38. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2013.07.003. Epub 2013 Jul 13. Pharmacol Ther. 2013. PMID: 23859952 Review. - Exploitation of the Androgen Receptor to Overcome Taxane Resistance in Advanced Prostate Cancer.
Martin SK, Kyprianou N. Martin SK, et al. Adv Cancer Res. 2015;127:123-58. doi: 10.1016/bs.acr.2015.03.001. Epub 2015 Mar 29. Adv Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 26093899 Review. - Regulation of androgen receptor variants in prostate cancer.
Zhu Y, Luo J. Zhu Y, et al. Asian J Urol. 2020 Jul;7(3):251-257. doi: 10.1016/j.ajur.2020.01.001. Epub 2020 Jan 25. Asian J Urol. 2020. PMID: 33024700 Free PMC article. Review. - Role of Androgen Receptor in Prostate Cancer: A Review.
Fujita K, Nonomura N. Fujita K, et al. World J Mens Health. 2019 Sep;37(3):288-295. doi: 10.5534/wjmh.180040. Epub 2018 Sep 10. World J Mens Health. 2019. PMID: 30209899 Free PMC article. Review. - Blocking GRP/GRP-R signaling decreases expression of androgen receptor splice variants and inhibits tumor growth in castration-resistant prostate cancer.
Case TC, Merkel A, Ramirez-Solano M, Liu Q, Sterling JA, Jin R. Case TC, et al. Transl Oncol. 2021 Nov;14(11):101213. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2021.101213. Epub 2021 Aug 27. Transl Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34461557 Free PMC article.
Cited by
- Decoding androgen receptor signalling: Genomic vs. non-genomic roles in prostate cancer.
Asim M. Asim M. Neoplasia. 2024 Dec;58:101066. doi: 10.1016/j.neo.2024.101066. Epub 2024 Oct 13. Neoplasia. 2024. PMID: 39405603 Free PMC article. - Therapy resistance in prostate cancer: mechanism, signaling and reversal strategies.
Thakur N, Singh P, Bagri A, Srivastava S, Dwivedi V, Singh A, Jaiswal SK, Dholpuria S. Thakur N, et al. Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2024;5(5):1110-1134. doi: 10.37349/etat.2024.00266. Epub 2024 Aug 29. Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2024. PMID: 39351434 Free PMC article. Review. - Androgen receptor monomers and dimers regulate opposing biological processes in prostate cancer cells.
Safi R, Wardell SE, Watkinson P, Qin X, Lee M, Park S, Krebs T, Dolan EL, Blattler A, Tsuji T, Nayak S, Khater M, Fontanillo C, Newlin MA, Kirkland ML, Xie Y, Long H, Fink EC, Fanning SW, Runyon S, Brown M, Xu S, Owzar K, Norris JD, McDonnell DP. Safi R, et al. Nat Commun. 2024 Sep 3;15(1):7675. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-52032-y. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39227594 Free PMC article. - Alterations in Tumor Aggression Following Androgen Receptor Signaling Restoration in Canine Prostate Cancer Cell Lines.
Vasilatis DM, Batra N, Lucchesi CA, Abria CJ, Packeiser EM, Murua Escobar H, Ghosh PM. Vasilatis DM, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 7;25(16):8628. doi: 10.3390/ijms25168628. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201315 Free PMC article. - Novel Plasma Membrane Androgen Receptor SLC39A9 Mediates Ovulatory Changes in Cells of the Monkey Ovarian Follicle.
Sage MAG, Duffy DM. Sage MAG, et al. Endocrinology. 2024 May 27;165(7):bqae071. doi: 10.1210/endocr/bqae071. Endocrinology. 2024. PMID: 38889246 Free PMC article.
References
- Ryan CJ, Smith MR, Fizazi K, Saad F, Mulders PF, Sternberg CN, et al. Abiraterone acetate plus prednisone versus placebo plus prednisone in chemotherapy-naive men with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (COU-AA-302): final overall survival analysis of a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol (2015) 16(2):152–60.10.1016/S1470-2045(14)71205-7 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous