FGFR1 is critical for the anti-endothelial mesenchymal transition effect of N-acetyl-seryl-aspartyl-lysyl-proline via induction of the MAP4K4 pathway - PubMed (original) (raw)
FGFR1 is critical for the anti-endothelial mesenchymal transition effect of N-acetyl-seryl-aspartyl-lysyl-proline via induction of the MAP4K4 pathway
Jinpeng Li et al. Cell Death Dis. 2017.
Abstract
Endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EndMT) has been shown to contribute to organ fibrogenesis, and we have reported that the anti-EndMT effect of N-acetyl-seryl-aspartyl-lysyl-proline (AcSDKP) is associated with restoring expression of diabetes-suppressed fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR), the key anti-EndMT molecule. FGFR1 is the key inhibitor of EndMT via the suppression of the transforming growth factor β (TGFβ) signaling pathway, and mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase kinase 4 (MAP4K4) inhibits integrin β1, a key factor in activating TGFβ signaling and EndMT. Here, we showed that the close proximity between AcSDKP and FGFR1 was essential for the suppression of TGFβ/smad signaling and EndMT associated with MAP4K4 phosphorylation (P-MAP4K4) in endothelial cells. In cultured human dermal microvascular endothelial cells (HMVECs), the anti-EndMT and anti-TGFβ/smad effects of AcSDKP were lost following treatment with a neutralizing FGFR1 antibody (N-FGFR1) or transfection of FRS2 siRNA. The physical interaction between FGFR1 and P-MAP4K4 in HMVECs was confirmed by proximity ligation analysis and an immunoprecipitation assay. AcSDKP induced P-MAP4K4 in HMVECs, which was significantly inhibited by treatment with either N-FGFR1 or FRS2 siRNA. Furthermore, MAP4K4 knockdown using specific siRNAs induced smad3 phosphorylation and EndMT in HMVECs, which was not suppressed by AcSDKP. Streptozotocin-induced diabetic CD-1 mice exhibited suppression of both FGFR1 and P-MAP4K4 expression levels associated with the induction of TGFβ/smad3 signaling and EndMT in their hearts and kidneys; those were restored by AcSDKP treatment. These data demonstrate that the AcSDKP-FGFR1-MAP4K4 axis has an important role in combating EndMT-associated fibrotic disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Figure 1
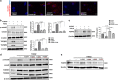
Proximity between AcSDKP and FGFR1 inhibits the TGF_β_/smad signaling pathway in HMVECs. (a) HMVECs were treated with N-FGFR1 (1.5 _μ_g/ml) for 48 h with or without preincubation with AcSDKP (100 nM) for 2 h, and the proximity between AcSDKP and FGFR1 was analyzed by the Duolink In Situ Assay. For each slide, images at a × 400 original magnification were obtained from six different areas. (b and c) HMVECs were treated with TGF_β_2 (5 ng/ml) for 15 min or 48 h with or without preincubation with AcSDKP for 2 h, and the p-smad3, TGF_β_R1, TGF_β_R2 and FGFR1 levels were analyzed by western blot. Densitometric analysis of the p-smad3/smad3, TGF_β_R1/_β_-actin, TGF_β_R2/_β_-actin and FGFR1/_β_-actin levels from each group (_n_=6) were analyzed. (d and e) HMVECs were incubated with TGF_β_2 for 15 min or 48 h with or without preincubation with AcSDKP or its mutants (Ac
DSPK
, AcSDK
A
, Ac
A
DKP) (100 nM) for 2 h. The p-smad3/smad3, TGF_β_R1/_β_-actin, TGF_β_R2/_β_-actin and FGFR1/_β_-actin protein levels were analyzed by western blot
Figure 2
AcSDKP suppresses TGF_β_/smad signaling and EndMT through the FGFR1/FRS2 pathway. (a) HMVECs were treated with N-FGFR1 for 48 h, and the FGFR1, TGF_β_R1 and TGF_β_R2 protein levels were analyzed by western blot. (b) HMVECs were treated with TGF_β_2 in the presence or absence of N-FGFR1 for 15 min with or without AcSDKP preincubation. The p-smad3 and TGF_β_R1 protein levels were analyzed by western blot. Densitometric analysis of the p-smad3/smad3 and TGF_β_R1/β_-actin levels (n_=3) in each group was performed. (c) HMVECs were incubated with either N-FGFR1 in the presence or absence of TGF_β_2 for 48 h with or without preincubation with AcSDKP for 2 h or with N-FGFR1 in the presence or absence of TGF_β_2 for 48 h with or without 24 h of incubation with FGF2 (50 ng/ml). The CD31, SM22_α, FSP1 and α_-SMA protein levels were analyzed by western blot. (d) HMVECs were transfected with FRS2 siRNA (100 nM) for 48 h with or without AcSDKP preincubation. The VE-cadherin, FSP1, vimentin, SM22_α and p-smad3 levels were analyzed by western blot. (e) HMVECs were treated with N-FGFR1 for 48 h or 15 min in the presence or absence of N-TGF_β (1, 2, 3) (1.0 μ_g/ml). The CD31, VE-cadherin, SM22_α, FSP1, TGF_β_R1, TGF_β_R2 and p-smad3 levels were analyzed by western blot
Figure 3
FGF2/FGFR1 mediates MAP4K4 signaling in endothelial cells. (a) Immunofluorescence microscopy analysis of P-MAP4K4 expression following FRS2 siRNA or TGF_β_2 treatment. For each slide, images of six different fields of view at × 400 magnification were evaluated. The scale bar is 60 _μ_m in each panel. (b and c) HMVECs were treated with N-FGFR1 for 48 h or FGF2 for 24 h. The P-MAP4K4 levels were analyzed by western blot
Figure 4
The proximity between FGFR1 and P-MAP4K4 decreases in FGFR1-deficient cells. (a) HMVECs were treated with N-FGFR1 or TGF_β_2 for 48 h. The proximity between FGFR1 and P-MAP4K4 was analyzed using the Duolink In Situ Assay. For each slide, images at × 400 original magnification were obtained from six different areas. (b) immunoprecipitation analysis with either a P-MAP4K4 or a FGFR1 antibody was performed and analyzed by western blot. Then, the FGFR1 and P-MAP4K4 levels with N-FGFR1 or TGF_β_2 treatment were analyzed by western blot in endothelial cells
Figure 5
MAP4K4 signaling is mediated by AcSDKP in a FGFR1/FRS2-dependent manner. (a and b) HMVECs were treated with N-FGFR1 for 48 h in the presence or absence of FGF2 or AcSDKP. P-MAP4K4 levels were analyzed by western blot. Densitometric analysis of P-MAP4K4 levels normalized to MAP4K4. For each group, _n_=3 were analyzed. (c and d) HMVECs were transfected with FRS2 siRNA for 48 h with or without FGF2 or AcSDKP treatment. P-MAP4K4 levels were analyzed by western blot. Densitometric analysis of P-MAP4K4 levels, normalized to MAP4K4. A total of _n_=3 from each group were analyzed
Figure 6
MAP4K4 deficiency induces TGF_β_/smad signaling and EndMT via activation of integrin _β_1. (a) HMVECs were transfected with MAP4K4 siRNA (100 nM) for 48 h. Next, the cells were treated with or without AcSDKP for 2 h. The p-smad3/smad3 pathway was analyzed by western blot. Densitometric analysis of the p-smad3/smad3 levels was performed, with n_=3 for each group. (b) HMVECs were treated with MAP4K4 siRNA for 48 h with or without AcSDKP treatment. The VE-cadherin, CD31, FSP1, SM22_α and vimentin protein levels were analyzed by western blot. (c) HMVECs were transfected with MAP4K4 siRNA for 48 h in the presence or absence of TGF_β_2 with or without AcSDKP. The integrin _β_1 level was analyzed by western blot
Figure 7
AcSDKP inhibits TGF_β_/smad signaling and EndMT and restores the FGFR1 and P-MAP4K4 levels in diabetic hearts. (a) Immunofluorescence microscopy analysis of CD31/FGFR1 and CD31/P-MAP4K4 in the heart tissues from each group of mice. The scale bar is 60 _μ_m in each panel. The CD31 and FGFR1 double-labeled cells and the CD31 and P-MAP4K4 double-labeled cells in each visual field were assessed by fluorescence microscopy and quantified. For each section, images from six different fields of view at × 400 magnification were evaluated. (b and c) Immunofluorescence microscopy analysis of CD31/α_-SMA, VE-cadherin /SM22_α and CD31/p-smad3 expression levels in the heart tissues from each group of mice. The scale bar is 60 _μ_m in each panel. The CD31 and α_-SMA double-labeled cells, the VE-cadherin and SM22_α double-labeled cells and the CD31 and p-smad3 double-labeled cells in each visual field were analyzed by fluorescence microscopy and quantified. For each section, images from six different fields of view at × 400 magnification were evaluated. Four mice from each group were analyzed. (d) Western blot analysis of the FGFR1, P-MAP4K4, TGF_β_1, TGF_β_2 and TGF_β_3 levels in cardiac tissues. A representative blot from four independent experiments was shown. The densitometric analysis of western blot data was presented (_n_=4). The diabetic mice are abbreviated as DM in the figure
Figure 8
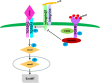
Schematic of the AcSDKP/FGFR1/MAP4K4 pathway suppression of TGF_β_/smad signaling and EndMT. In endothelial cells, the close proximity between AcSDKP and FGFR1 increased FGFR1 and induced its phosphorylation levels. Interacting with co-factor FRS2, FGFR1 recruited MAP4K4 and induced its phosphorylation. Subsequently, p-MAP4K4 suppressed integrin_β_1 (integrin_β_1 should be localized on the cell surface interacted with some of α integrins). Integrin_β_1 was a potent activator of TGF-β signaling and also EndMT. Therefore, AcSDKP could inhibit EndMT through FGFR1-MAP4K4-dependent manner
References
- He J, Xu Y, Koya D, Kanasaki K. Role of the endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition in renal fibrosis of chronic kidney disease. Clin Exp Nephrol 2013; 17: 488–497. - PubMed
- Zeisberg EM, Tarnavski O, Zeisberg M, Dorfman AL, McMullen JR, Gustafsson E et al. Endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition contributes to cardiac fibrosis. Nat Med 2007; 13: 952–961. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous