Protective Effects of Total Flavones of Elaeagnus rhamnoides (L.) A. Nelson against Vascular Endothelial Injury in Blood Stasis Model Rats - PubMed (original) (raw)
Protective Effects of Total Flavones of Elaeagnus rhamnoides (L.) A. Nelson against Vascular Endothelial Injury in Blood Stasis Model Rats
Zhicheng Wei et al. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017.
Abstract
The aim was to evaluate the protective effects of total flavones of Elaeagnus rhamnoides (L.) A. Nelson (TFE) against vascular endothelial injury in blood stasis model rats and explore the potential mechanisms preliminarily. The model of blood stasis rat model with vascular endothelial injury was induced by subcutaneous injection of adrenaline combined with ice-water bath. Whole blood viscosity (WBV), histological examination, and prothrombin time (PT), activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT), and fibrinogen (FIB) were measured. Meanwhile, the levels of Thromboxane B2 (TXB2), 6-keto-PGF1_α_ , von Willebrand factor (vWF), and thrombomodulin (TM) were detected. In addition, Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qPCR) was performed to identify PI3K, Erk2, Bcl-2, and caspase-3 gene expression. The results showed that TFE can relieve WBV, increase PT and APTT, and decrease FIB content obviously. Moreover, TFE might significantly downregulate the levels of TXB2, vWF, and TM in plasma and upregulate the level of 6-keto-PGF1_α_ in plasma. Expressions of PI3K and Bcl-2 were increased and the expression of caspase-3 was decreased by TFE pretreatment in the rat model. Consequently, the study suggested that TFE may have the potential against vascular endothelial injury in blood stasis model rats induced by a high dose of adrenaline with ice-water bath.
Figures
Figure 1
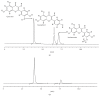
Typical high-performance liquid chromatography profile of three known standards (a) and total flavonoid aglycones obtained by hydrolyzing (b) at an absorbance of 370 nm.
Figure 2
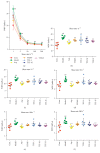
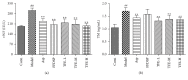
Effects of TFE on whole blood viscosity (WBV) at various shear rates. n = 6, ##P < 0.01 compared with control group. ∗ P < 0.05, ∗∗ P < 0.01 compared with model group. Highly significant change (P < 0.01) was recorded at all shear (ranging from 1 to 200 s−1), rates between control and model group (a). WBV at 1, 5, 50, 100, and 200 s−1 rates (b–f).
Figure 3
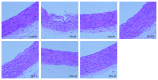
Effect of TFE in pathological photomicrograph of rats aorta: pathological photomicrograph of rats stained by hematoxylin and eosin (H.E. ×400).
Figure 4
Effect of TFE on PT (a), APTT (b), and FIB (c). n = 6, ##P < 0.01 compared with control group. ∗ P < 0.05, ∗∗ P < 0.01 compared with model group.
Figure 5
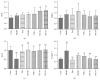
Determination of vWF (a) and TM (b) in the plasma. n = 6, ##P < 0.01 compared with control group; ∗∗ P < 0.01 compared with model group.
Figure 6
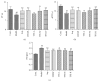
The mRNA expressions of PI3K (a), Erk2 (b), Bcl-2 (c), and caspase-3 (d). n = 6, ##P < 0.01 compared with control group. n = 6, ∗ P < 0.05, ∗∗ P < 0.01 compared with model group.
Similar articles
- The antithrombotic effect of RSNK in blood-stasis model rats.
Dang X, Miao JJ, Chen AQ, Li P, Chen L, Liang JR, Xie RM, Zhao Y. Dang X, et al. J Ethnopharmacol. 2015 Sep 15;173:266-72. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.06.030. Epub 2015 Jul 26. J Ethnopharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26216512 - [Effects of the effective components group of xiaoshuantongluo formula on rat acute blood stasis model].
Zhao Y, Yu X, Shi LL, Chen BN, Wang SH, Du GH. Zhao Y, et al. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2012 May;47(5):604-8. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2012. PMID: 22812003 Chinese. - Improvement and Application of Acute Blood Stasis Rat Model Aligned with the 3Rs (Reduction, Refinement and Replacement) of Humane Animal Experimentation.
Huang S, Xu F, Wang YY, Shang MY, Wang CQ, Wang X, Cai SQ. Huang S, et al. Chin J Integr Med. 2020 Apr;26(4):292-298. doi: 10.1007/s11655-014-2008-y. Epub 2014 Dec 23. Chin J Integr Med. 2020. PMID: 25537151 - Coagulation Testing in the Core Laboratory.
Winter WE, Flax SD, Harris NS. Winter WE, et al. Lab Med. 2017 Nov 8;48(4):295-313. doi: 10.1093/labmed/lmx050. Lab Med. 2017. PMID: 29126301 Review. - HEMORHEOLOGY INDEX CHANGES IN A RAT ACUTE BLOOD STASIS MODEL: A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW AND META-ANALYSIS.
Zhang JX, Feng Y, Zhang Y, Liu Y, Li SD, Yang MH. Zhang JX, et al. Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med. 2017 Jun 5;14(4):96-107. doi: 10.21010/ajtcam.v14i4.12. eCollection 2017. Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med. 2017. PMID: 28638872 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Identification of the Antithrombotic Mechanism of Leonurine in Adrenalin Hydrochloride-Induced Thrombosis in Zebrafish via Regulating Oxidative Stress and Coagulation Cascade.
Liao L, Zhou M, Wang J, Xue X, Deng Y, Zhao X, Peng C, Li Y. Liao L, et al. Front Pharmacol. 2021 Nov 4;12:742954. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.742954. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34803688 Free PMC article. - Effect of cold stress on ovarian & uterine microcirculation in rats and the role of endothelin system.
Wang D, Cheng X, Fang H, Ren Y, Li X, Ren W, Xue B, Yang C. Wang D, et al. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2020 Apr 14;18(1):29. doi: 10.1186/s12958-020-00584-1. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2020. PMID: 32290862 Free PMC article. - Phytochemistry and pharmacology of sea buckthorn (Elaeagnus rhamnoides; syn. Hippophae rhamnoides): progress from 2010 to 2021.
Żuchowski J. Żuchowski J. Phytochem Rev. 2023;22(1):3-33. doi: 10.1007/s11101-022-09832-1. Epub 2022 Aug 11. Phytochem Rev. 2023. PMID: 35971438 Free PMC article. Review. - Total flavonoids of hawthorn leaves promote motor function recovery via inhibition of apoptosis after spinal cord injury.
Zhang Q, Xiong Y, Li B, Deng GY, Fu WW, Cao BC, Zong SH, Zeng GF. Zhang Q, et al. Neural Regen Res. 2021 Feb;16(2):350-356. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.286975. Neural Regen Res. 2021. PMID: 32859797 Free PMC article.
References
- Berry C. N., Girard D., Lochot S., Lecoffre C. Antithrombotic actions of argatroban in rat models of venous, ‘mixed’ and arterial thrombosis, and its effects on the tail transection bleeding time. British Journal of Pharmacology. 1994;113(4):1209–1214. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb17126.x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Rosendaal F. R. Risk factors for venous thrombotic disease. Thromb Haemost. 1999;82(2):610–619. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous