A Single Dose of 5-MeO-DMT Stimulates Cell Proliferation, Neuronal Survivability, Morphological and Functional Changes in Adult Mice Ventral Dentate Gyrus - PubMed (original) (raw)
A Single Dose of 5-MeO-DMT Stimulates Cell Proliferation, Neuronal Survivability, Morphological and Functional Changes in Adult Mice Ventral Dentate Gyrus
Rafael Vitor Lima da Cruz et al. Front Mol Neurosci. 2018.
Erratum in
- Corrigendum: A Single Dose of 5-MeO-DMT Stimulates Cell Proliferation, Neuronal Survivability, Morphological and Functional Changes in Adult Mice Ventral Dentate Gyrus.
Lima da Cruz RV, Moulin TC, Petiz LL, Leão RN. Lima da Cruz RV, et al. Front Mol Neurosci. 2019 Apr 4;12:79. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2019.00079. eCollection 2019. Front Mol Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31019450 Free PMC article.
Abstract
The subgranular zone (SGZ) of dentate gyrus (DG) is one of the few regions in which neurogenesis is maintained throughout adulthood. It is believed that newborn neurons in this region encode temporal information about partially overlapping contextual memories. The 5-Methoxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamine (5-MeO-DMT) is a naturally occurring compound capable of inducing a powerful psychedelic state. Recently, it has been suggested that DMT analogs may be used in the treatment of mood disorders. Due to the strong link between altered neurogenesis and mood disorders, we tested whether 5-MeO-DMT is capable of increasing DG cell proliferation. We show that a single intracerebroventricular (ICV) injection of 5-MeO-DMT increases the number of Bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU+) cells in adult mice DG. Moreover, using a transgenic animal expressing tamoxifen-dependent Cre recombinase under doublecortin promoter, we found that 5 Meo-DMT treated mice had a higher number of newborn DG Granule cells (GC). We also showed that these DG GC have more complex dendritic morphology after 5-MeO-DMT. Lastly, newborn GC treated with 5-MeO-DMT, display shorter afterhyperpolarization (AHP) potentials and higher action potential (AP) threshold compared. Our findings show that 5-MeO-DMT affects neurogenesis and this effect may contribute to the known antidepressant properties of DMT-derived compounds.
Keywords: 5-MeO-DMT; adult neurogenesis; dentate gyrus granule cells; patch clamp; psychedelics.
Figures
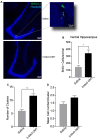
Figure 1
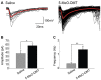
Single dose of5-Methoxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamine (5-MeO-DMT) increases cell proliferation within the dentate gyrus (DG) of adult mice. (A) Photomicrography showing representative hippocampal sections Bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU+) cells in green and hoechst 33342 in blue. (B) Average number of BrdU+ cells in the adult mice ventral DG. (C) Mean number of cells per clusters. (D) Mean number of clusters in each group. *p = 0.0029, **p = 0.0002.
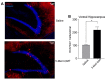
Figure 2
Single dose of 5-MeO-DMT increase the number of new DG granule cells (GC) 21 days after injection. (A) Photomicrography showing representative hippocampal sections (DCX::tdTom+ cells in red and hoechst 33342 in blue). (B) Average number of DCX::tdTom+ cells per group. *p = 0.0006.
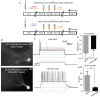
Figure 3
5-Meo-DMT injection alters afterhyperpolarization (AHP) duration and action potential (AP) threshold in immature hippocampus GC. (A) Animals received a dose of 100 μg of 5-MeO-DMT, followed by 100 μg/g of tamoxifen i.p. diluted in sesame oil 3 days after, daily for 3 days to allow cre recombination. Experiments were performed on day 21. (B) Photomicrography of a recorded tdTomato+ cells from control and 5-MeO-DMT-treated mouse. (C) Membrane potential changes in response to current steps, the black line denotes the trace in which the first AP was elicited, red dotted line denote AP threshold for that step. (D) Mean AP threshold. (E) Mean AHP duration. *p = 0.0216, **p = 0.0062.
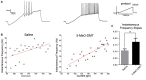
Figure 4
Young GC in 5-MeO-DMT-treated mice show a greater capacity for high frequency firing. (A) Membrane potential recording in response to a current ramp. (B) Linear regressions (ramp current vs. instantaneous AP frequency). (C) Average slopes (ramp current vs. instantaneous AP frequency relationship). **p = 0.0036.
Figure 5
Young GC in 5-MeO-DMT-treated show a higher frequency of spontaneous excitatory postsynaptic potentials. (A) Examples of detectedspontaneous excitatory postsynaptic currents (sEPSCs; in 2 min recordings) cells from saline- and 5-MeO-DMT-treated mice. (B) Mean absolute sEPSC amplitude for saline- and 5-MeO-DMT-treated mice. *p = 0.03. (C) Average slopes (ramp current vs. instantaneous AP frequency relationship). **p = 0.001.
Figure 6
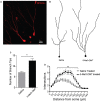
Single dose of 5-MeO-DMT increases dendritic complexity in young DG GC. (A) Sample image showing a tdTomato+ (CreERT2/tdTomlox/lox mouse) granule cell with visible dendritic processes. (B) Vectorial reconstruction of tdTomato+ granule cell. (C) Mean number of branch tips of GC across treatments. (D) Sholl analysis comparing the dendritic complexity between two treatments with increasing radial distance from soma. *p = 0.0001, **p < 0.05.
Similar articles
- Corrigendum: A Single Dose of 5-MeO-DMT Stimulates Cell Proliferation, Neuronal Survivability, Morphological and Functional Changes in Adult Mice Ventral Dentate Gyrus.
Lima da Cruz RV, Moulin TC, Petiz LL, Leão RN. Lima da Cruz RV, et al. Front Mol Neurosci. 2019 Apr 4;12:79. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2019.00079. eCollection 2019. Front Mol Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31019450 Free PMC article. - Serotonergic psychedelic 5-MeO-DMT alters plasticity-related gene expression and generates anxiolytic effects in stressed mice.
Nogueira M, Ferreira Golbert DC, Menezes R, Nóbrega de Almeida R, Galvão-Coelho NL, Siroky AN, Lima TZ, Maia H, Leão KE, Leão RN. Nogueira M, et al. Mol Psychiatry. 2025 Jan;30(1):50-60. doi: 10.1038/s41380-024-02655-w. Epub 2024 Jul 5. Mol Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 38969716 - A case report SPECT study and theoretical rationale for the sequential administration of ibogaine and 5-MeO-DMT in the treatment of alcohol use disorder.
Barsuglia JP, Polanco M, Palmer R, Malcolm BJ, Kelmendi B, Calvey T. Barsuglia JP, et al. Prog Brain Res. 2018;242:121-158. doi: 10.1016/bs.pbr.2018.08.002. Epub 2018 Oct 25. Prog Brain Res. 2018. PMID: 30471678 - The clinical pharmacology and potential therapeutic applications of 5-methoxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamine (5-MeO-DMT).
Reckweg JT, Uthaug MV, Szabo A, Davis AK, Lancelotta R, Mason NL, Ramaekers JG. Reckweg JT, et al. J Neurochem. 2022 Jul;162(1):128-146. doi: 10.1111/jnc.15587. Epub 2022 Mar 8. J Neurochem. 2022. PMID: 35149998 Free PMC article. Review. - A narrative synthesis of research with 5-MeO-DMT.
Ermakova AO, Dunbar F, Rucker J, Johnson MW. Ermakova AO, et al. J Psychopharmacol. 2022 Mar;36(3):273-294. doi: 10.1177/02698811211050543. Epub 2021 Oct 19. J Psychopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34666554 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Divergent Effects of Ketamine and the Serotoninergic Psychedelic 2,5-Dimethoxy-4-Iodoamphetamine on Hippocampal Plasticity and Metaplasticity.
Zahid Z, Sultan ZW, Krause BM, Wenthur CJ, Pearce RA, Banks MI. Zahid Z, et al. Psychedelic Med (New Rochelle). 2024 Sep;2(3):166-177. doi: 10.1089/psymed.2023.0061. Epub 2024 Sep 4. Psychedelic Med (New Rochelle). 2024. PMID: 39669671 Free PMC article. - Ketamine and Serotonergic Psychedelics: Common Mechanisms Underlying the Effects of Rapid-Acting Antidepressants.
Kadriu B, Greenwald M, Henter ID, Gilbert JR, Kraus C, Park LT, Zarate CA. Kadriu B, et al. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2021 Jan 20;24(1):8-21. doi: 10.1093/ijnp/pyaa087. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33252694 Free PMC article. Review. - N,N-dimethyltryptamine compound found in the hallucinogenic tea ayahuasca, regulates adult neurogenesis in vitro and in vivo.
Morales-Garcia JA, Calleja-Conde J, Lopez-Moreno JA, Alonso-Gil S, Sanz-SanCristobal M, Riba J, Perez-Castillo A. Morales-Garcia JA, et al. Transl Psychiatry. 2020 Sep 28;10(1):331. doi: 10.1038/s41398-020-01011-0. Transl Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 32989216 Free PMC article. - Effects of psychedelics on neurogenesis and broader neuroplasticity: a systematic review.
Lima da Cruz RV, Leão RN, Moulin TC. Lima da Cruz RV, et al. Mol Med. 2024 Dec 19;30(1):244. doi: 10.1186/s10020-024-01013-4. Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 39701927 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Canales J. J. (2016). Adult Neurogenesis in the Hippocampus. 1st Edn. New York, NY: Academic Press.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous