NK Cell Function Regulation by TGF-β-Induced Epigenetic Mechanisms - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
NK Cell Function Regulation by TGF-β-Induced Epigenetic Mechanisms
Stefano Regis et al. Front Immunol. 2020.
Abstract
TGF-β is a potent immunosuppressive cytokine that severely affects the function of NK cells. Tumor cells can take advantage of this ability, enriching their surrounding microenvironment with TGF-β. TGF-β can alter the expression of effector molecules and of activating and chemokine receptors, influence metabolism, induce the NK cell conversion toward the less cytolytic ILC1s. These and other changes possibly occur by the induction of complex gene expression programs, involving epigenetic mechanisms. While most of these programs are at present unexplored, the role of certain transcription factors, microRNAs and chromatin changes determined by TGF-β in NK cells start to be elucidated in human and/or mouse NK cells. The deep understanding of these mechanisms will be useful to design therapies contributing to restore the full NK function.
Keywords: NK cells; TGF-β; epigenetic; microRNAs; transcription factors.
Copyright © 2020 Regis, Dondero, Caliendo, Bottino and Castriconi.
Figures
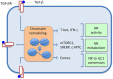
Figure 1
TGF-β induces changes in the expression of several transcription factors, and, consequently, in sets of controlled genes. Effects, often accompanied by chromatin alterations, range from inhibition of NK cell activity, to depression of cell metabolism, up to the induced conversion of NK cells to ILC1s.
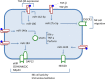
Figure 2
Under the influence of TGF-β, levels of expression of some miRNAs are increased, down-regulating the expression of surface molecules and transcription factors involved in NK cell activity. Conversely, miRNA-186 level decreases, thus preventing the down-regulation of the TGF-β receptor expression, and maintaining the NK cells responsiveness to the immunomodulatory cytokine. miR-142-3p down-regulates TGFBR1, thus modulating the TGF-β signaling.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources