Interactions of the Brain Renin-Angiotensin-System (RAS) and Inflammation in the Sensitization of Hypertension - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Interactions of the Brain Renin-Angiotensin-System (RAS) and Inflammation in the Sensitization of Hypertension
Baojian Xue et al. Front Neurosci. 2020.
Abstract
Mounting evidence indicates that the renin-angiotensin (RAS) and immune systems interact with one another in the central nervous system (CNS) and that they are importantly involved in the pathogenesis of hypertension. Components comprising the classic RAS were first identified in the periphery, and subsequently, similar factors were found to be generated de novo in many different organs including the brain. There is humoral-neural coupling between the systemic and brain RASs, which is important for controlling sympathetic tone and the release of endocrine factors that collectively determine blood pressure (BP). Similar to the interactions between the systemic and brain RASs is the communication between the peripheral and brain immune systems. Systemic inflammation activates the brain's immune response. Importantly, the RAS and inflammatory factors act synergistically in brain regions involved in the regulation of BP. This review presents evidence of how such interactions between the brain RAS and central immune mechanisms contribute to the pathogenesis of hypertension. Emphasis focuses on the role of these interactions to induce neuroplastic changes in a central neural network resulting in hypertensive response sensitization (HTRS). Neuroplasticity and HTRS can be induced by challenges (stressors) presented earlier in life such as a low-dose of angiotensin II or high fat diet (HFD) feeding in adults. Similarly, the offspring of mothers with gestational hypertension or of mothers ingesting a HFD during pregnancy are reprogrammed and manifest HTRS when exposed to new stressors as adults. Consideration of the actions and interactions of the brain RAS and inflammatory mediators in the context of the induction and expression of HTRS will provide insights into the etiology of high BP that may lead to new strategies for the prevention and treatment of hypertension.
Keywords: CNS; RAS; hypertension; inflammation; perinatal programming.
Copyright © 2020 Xue, Zhang and Johnson.
Figures
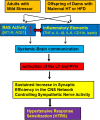
FIGURE 1
Central cascade of factors mediating hypertensive response sensitization (HTRS). In adult animals challenged with mild physiological or psychological stress or in offspring from dams with maternal hypertension (HT) or high fat diet (HFD) feeding, both the renin-angiotensin system (RAS) and inflammatory elements will be upregulated and act on brain nuclei involved in blood pressure regulation through systemic-brain communication. These central RAS and inflammatory mechanisms will synergistically induce a HTRS. (ACE1, angiotensin converting enzyme 1; AT1-R, angiotensin II type 1 receptor; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α; IL-1β, interleukin-1β; IL-6, interleukin-6; CD11b, cluster of differentiation molecule 11b; LT, the lamina terminalis; PVN, the paraventricular nucleus of hypothalamus).
Similar articles
- Sensitization of Hypertension: The Impact of Earlier Life Challenges: Excellence Award for Hypertension Research 2021.
Xue B, Johnson AK. Xue B, et al. Hypertension. 2023 Jan;80(1):1-12. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.122.18550. Epub 2022 Sep 7. Hypertension. 2023. PMID: 36069195 Review. - Central Renin-Angiotensin System Activation and Inflammation Induced by High-Fat Diet Sensitize Angiotensin II-Elicited Hypertension.
Xue B, Thunhorst RL, Yu Y, Guo F, Beltz TG, Felder RB, Johnson AK. Xue B, et al. Hypertension. 2016 Jan;67(1):163-70. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.115.06263. Epub 2015 Nov 16. Hypertension. 2016. PMID: 26573717 Free PMC article. - Leptin Mediates High-Fat Diet Sensitization of Angiotensin II-Elicited Hypertension by Upregulating the Brain Renin-Angiotensin System and Inflammation.
Xue B, Yu Y, Zhang Z, Guo F, Beltz TG, Thunhorst RL, Felder RB, Johnson AK. Xue B, et al. Hypertension. 2016 May;67(5):970-6. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.115.06736. Epub 2016 Mar 28. Hypertension. 2016. PMID: 27021010 Free PMC article. - Central nervous system neuroplasticity and the sensitization of hypertension.
Johnson AK, Xue B. Johnson AK, et al. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2018 Dec;14(12):750-766. doi: 10.1038/s41581-018-0068-5. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2018. PMID: 30337707 Free PMC article. Review. - The roles of sensitization and neuroplasticity in the long-term regulation of blood pressure and hypertension.
Johnson AK, Zhang Z, Clayton SC, Beltz TG, Hurley SW, Thunhorst RL, Xue B. Johnson AK, et al. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2015 Dec 1;309(11):R1309-25. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00037.2015. Epub 2015 Aug 19. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26290101 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- The Role of Furin in the Pathogenesis of COVID-19-Associated Neurological Disorders.
Ayyubova G, Gychka SG, Nikolaienko SI, Alghenaim FA, Teramoto T, Shults NV, Suzuki YJ. Ayyubova G, et al. Life (Basel). 2024 Feb 19;14(2):279. doi: 10.3390/life14020279. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38398788 Free PMC article. - μ-Opioid Receptor-Mediated AT1R-TLR4 Crosstalk Promotes Microglial Activation to Modulate Blood Pressure Control in the Central Nervous System.
Sun GC, Tse J, Hsu YH, Ho CY, Tseng CJ, Cheng PW. Sun GC, et al. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Nov 8;10(11):1784. doi: 10.3390/antiox10111784. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34829655 Free PMC article. - Exercise Training Attenuates Hypertension via Suppressing ROS/MAPK/NF-κB/AT-1R Pathway in the Hypothalamic Paraventricular Nucleus.
Qi J, Li RJ, Fu LY, Liu KL, Qiao JA, Yang Y, Yu XJ, Yu JY, Li Y, Tan H, Kang YM. Qi J, et al. Nutrients. 2022 Sep 24;14(19):3968. doi: 10.3390/nu14193968. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36235619 Free PMC article. - Gestational Intermittent Hypoxia Impairs AT2R-Mediated Vascular Protection in Female Offspring on a High-Fat, High-Sucrose Diet.
Song R, Yadav P, Mishra JS, Dangudubiyyam SV, Kumar S. Song R, et al. J Biotechnol Biomed. 2024;7(2):264-276. doi: 10.26502/jbb.2642-91280150. Epub 2024 Jun 14. J Biotechnol Biomed. 2024. PMID: 39036336 Free PMC article. - Pregnancy, Preeclampsia, and COVID-19: Susceptibility and Mechanisms: A Review Study.
Sayad B, Mohseni Afshar Z, Mansouri F, Salimi M, Miladi R, Rahimi S, Rahimi Z, Shirvani M. Sayad B, et al. Int J Fertil Steril. 2022 Apr;16(2):64-69. doi: 10.22074/IJFS.2022.539768.1194. Epub 2022 May 8. Int J Fertil Steril. 2022. PMID: 35639648 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Akira S. (2003). Toll-like receptor signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 278 38105–38108. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources