Experimental Drugs for the Treatment of Hepatitis D - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
. 2021 Apr 16:13:461-468.
doi: 10.2147/JEP.S235550. eCollection 2021.
Affiliations
- PMID: 33889032
- PMCID: PMC8057838
- DOI: 10.2147/JEP.S235550
Review
Experimental Drugs for the Treatment of Hepatitis D
Lisa Sandmann et al. J Exp Pharmacol. 2021.
Abstract
Chronic hepatitis D virus infection is the most severe form of viral hepatitis. Antiviral treatment is urgently needed to prevent patients from developing end stage liver disease or hepatocellular carcinoma. Treatment options were limited to off-label use of pegylated interferon alfa until conditional approval of bulevirtide by the EMA (European Medicines Agency) in July 2020. However, several other antiviral compounds are currently investigated and represent promising agents for the treatment of chronic HDV infection.
Keywords: HBV/HDV coinfection; bulevirtide; hepatitis delta; interferon; lonafarnib.
© 2021 Sandmann and Cornberg.
Conflict of interest statement
MC has received personal fees from AbbVie, Gilead Sciences, GSK, Janssen-Cilag, MSD Sharp & Dohme, Novartis, Spring Bank Pharmaceuticals, Swedish Orphan Biovitrum AB (SOBI). The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Figure 1
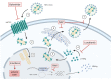
Therapeutic approaches for the treatment of chronic HDV infection are depicted in relation to the viral life cycle. (1) HDV virions attachment to heparan sulfate proteoglycans and binding of L-HBsAg pre-S1 region to the HBV/HDV specific receptor, hNTCP. Viral particles enter the cell through endocytosis and the viral ribonucleoprotein (RNP) is released in the cytoplasm. (2) Viral RNP translocation to the nucleus. (3) HDAg mRNA transcription and replication of HDV RNA. (4) L-HDAg contains a prenylation site that is farnesylated by a cellular farnesyltransferase before being re-translocated to the nucleus. (5) Both forms of HDAg interact with the newly synthesized genomic RNA to form new viral (RNP) that are exported to the cytoplasm. (6) Viral RNPs interact with the cytosolic part of HBsAg at the endoplasmic reticulum surface inducing their envelopment. (7) HDV virions are secreted form the infected cell. The different steps targeted by antiviral treatments are depicted. HBV co-infection is represented by presence of HBV cccDNA and integrated HBV DNA. The figure was created with BioRender.com.
Similar articles
- New Treatments for Chronic Hepatitis B Virus/Hepatitis D Virus Infection.
Sandmann L, Wedemeyer H. Sandmann L, et al. Clin Liver Dis. 2021 Nov;25(4):831-839. doi: 10.1016/j.cld.2021.06.011. Epub 2021 Aug 8. Clin Liver Dis. 2021. PMID: 34593156 Review. - Beyond bulevirtide: Alternative therapeutic options for the management of hepatitis delta virus.
Asselah T. Asselah T. J Viral Hepat. 2023 Apr;30 Suppl 1:33-38. doi: 10.1111/jvh.13789. Epub 2023 Jan 5. J Viral Hepat. 2023. PMID: 36529713 Review. - Bulevirtide for HBV and HDV infections.
Yardeni D, Koh C. Yardeni D, et al. Drugs Today (Barc). 2021 Jul;57(7):433-448. doi: 10.1358/dot.2021.57.7.3283861. Drugs Today (Barc). 2021. PMID: 34268531 - Bulevirtide with or without pegIFNα for patients with compensated chronic hepatitis delta: From clinical trials to real-world studies.
Lampertico P, Roulot D, Wedemeyer H. Lampertico P, et al. J Hepatol. 2022 Nov;77(5):1422-1430. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2022.06.010. Epub 2022 Jun 22. J Hepatol. 2022. PMID: 35752223 Review. - Emerging drugs for hepatitis D.
Keskin O, Yurdaydin C. Keskin O, et al. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. 2023 Dec;28(2):55-66. doi: 10.1080/14728214.2023.2205639. Epub 2023 Apr 27. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. 2023. PMID: 37096555
Cited by
- Epidemiologic and clinical updates on viral infections in Saudi Arabia.
Alshiban NM, Aleyiydi MS, Nassar MS, Alhumaid NK, Almangour TA, Tawfik YMK, Damiati LA, Almutairi AS, Tawfik EA. Alshiban NM, et al. Saudi Pharm J. 2024 Jul;32(7):102126. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2024.102126. Epub 2024 Jun 8. Saudi Pharm J. 2024. PMID: 38966679 Free PMC article. - A hitchhiker's guide through the COVID-19 galaxy.
Felsenstein S, Reiff AO. Felsenstein S, et al. Clin Immunol. 2021 Nov;232:108849. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2021.108849. Epub 2021 Sep 24. Clin Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34563684 Free PMC article. Review. - [Diagnosis and treatment of viral hepatitis B and D in 2024].
Souleiman R, Cornberg M. Souleiman R, et al. Inn Med (Heidelb). 2024 Apr;65(4):296-307. doi: 10.1007/s00108-024-01671-w. Epub 2024 Feb 28. Inn Med (Heidelb). 2024. PMID: 38418664 Review. German. - Global burden of hepatitis B virus: current status, missed opportunities and a call for action.
Hsu YC, Huang DQ, Nguyen MH. Hsu YC, et al. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023 Aug;20(8):524-537. doi: 10.1038/s41575-023-00760-9. Epub 2023 Apr 6. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023. PMID: 37024566 Review. - Review article: emerging insights into the immunopathology, clinical and therapeutic aspects of hepatitis delta virus.
Usai C, Gill US, Riddell AC, Asselah T, Kennedy PT. Usai C, et al. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2022 Apr;55(8):978-993. doi: 10.1111/apt.16807. Epub 2022 Mar 16. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2022. PMID: 35292991 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials