Regulation of DNA damage-induced apoptosis by the c-Abl tyrosine kinase - PubMed (original) (raw)
Regulation of DNA damage-induced apoptosis by the c-Abl tyrosine kinase
Z M Yuan et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997.
Abstract
Activation of the c-Abl protein tyrosine kinase by certain DNA-damaging agents contributes to downregulation of Cdk2 and G1 arrest by a p53-dependent mechanism. The present work investigates the potential role of c-Abl in apoptosis induced by DNA damage. Transient transfection studies with wild-type, but not kinase-inactive, c-Abl demonstrate induction of apoptosis. Cells that stably express inactive c-Abl exhibit resistance to ionizing radiation-induced loss of clonogenic survival and apoptosis. Cells null for c-abl are also impaired in the apoptotic response to ionizing radiation. We further show that cells deficient in p53 undergo apoptosis in response to expression of c-Abl and exhibit decreases in radiation-induced apoptosis when expressing inactive c-Abl. These findings suggest that c-Abl kinase regulates DNA damage-induced apoptosis.
Figures
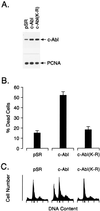
Figure 1
Overexpression of c-Abl induces apoptosis. MCF-7 cells were transfected with 8 μg of control pSRαMSVtkNeo, c-Abl, or c-Abl(K-R) vector. (A) Cell lysates were subjected to immunoblot analysis with anti-Abl and anti-proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA). (B) Cells were assayed for death by trypan blue exclusion at 48 h after transfection. Results are expressed as mean ± SEM of three independent transfections. Transfection efficiency as determined by cotransfection with a pSV-β-gal vector was 40–45%. Cell death for nontransfected MCF-7 cells was approximately 1%. (C) Cells were assayed for DNA content by flow cytometry at 48 h after transfection. Transfection with pSR, c-Abl, and c-Abl(K-R) resulted in 4.5% ± 0.9%, 29.4% ± 4.6%, and 4.1% ± 1.0% (mean ± SEM, three independent experiments) cells with sub-G1 DNA content, respectively.
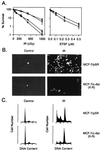
Figure 2
c-Abl(K-R) transfectants are resistant to ionizing radiation-induced apoptosis. (A) Wild-type MCF-7 (▪), MCF-7/pSR (•), and MCF-7/c-Abl(K-R) (clones a and b; □ and ○) cells (23) were exposed to the indicated doses of ionizing radiation (IR) and assayed for colony formation at 10 days (Left). MCF-7/pSR (•) and MCF-7/c-Abl(K-R) (□) cells were exposed to staurosporine (STSP) for 1 h, washed, and then assayed for colony formation at 10 days (Right). Results (mean ± SEM of three experiments) are expressed as the percentage clonogenic survival relative to untreated cells. (B) MCF-7/pSR and MCF-7/c-Abl(K-R) cells were treated with 5 Gy of ionizing radiation (IR). The cells were stained in TUNEL assays at 120 h after irradiation. (×400.) (C) DNA content was analyzed at 120 h after irradiation with 5 Gy.
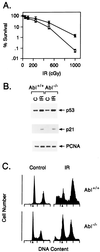
Figure 3
c-Abl kinase is involved in radiation-induced apoptosis. (A) Wild-type (Abl+/+; ○) and Abl−/− (•) MEFs (15) were exposed to the indicated doses of ionizing radiation (IR) and assayed for colony formation after 10 days. (B) Abl+/+ and Abl−/− MEFs were exposed to 0 or 5 Gy and collected at 3 h. Cell lysates were immunoblotted with anti-p53 and anti-p21 antibodies. (C) Abl+/+ and Abl−/− MEFs were exposed to 0 or 10 Gy and collected at 120 h for analysis of DNA content. Irradiation of the Abl+/+ and Abl−/− cells resulted in 17.3% ± 4.3% and 8.9% ± 2.1% with sub-G1 DNA, respectively.
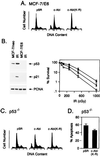
Figure 4
c-Abl kinase regulates irradiation-induced apoptosis by p53-dependent and -independent mechanisms. (A) MCF-7/E6 cells were transfected with 8 μg of pSR, c-Abl, or c-Abl(K-R) vector. Cells were harvested at 48 h and assessed for DNA content. Transfection efficiency as determined by cotransfection with pSV-β-gal vector was 40–45%. (B) (Left) MCF-7/pSR (lanes 1 and 2, counting from the left) and MCF-7/E6 (lanes 3 and 4) were irradiated with 5 Gy (lanes 2 and 4). Lysates prepared at 3 h were subjected to immunoblotting with anti-p53 (Ab-6; Oncogene Science) or anti-p21 (Ab-1; Oncogene Science). (Right) MCF-7/pSR (□), MCF-7/E6 (•), and MCF-7/E6/c-Abl(K-R) (▪) cells were irradiated with the indicated doses. Colony formation was assessed at 10 days. (C) p53−/− MEFs (33) were transfected with 8 μg of pSR, c-Abl, or c-Abl(K-R) vector. Transfection efficiency as determined by cotransfection of pSV-β-gal vector was 15–20%. Cells were harvested at 48 h and assessed for DNA content. (D) p53−/− MEFs stably tranfected with pSR vector or c-Abl(K-R) were treated with 10 Gy of ionizing radiation and collected at 120 h for assessment of DNA content. The results (mean ± SEM of three experiments) are expressed as the percentage of apoptotic cells with sub-G1 DNA.
Similar articles
- Role for c-Abl tyrosine kinase in growth arrest response to DNA damage.
Yuan ZM, Huang Y, Whang Y, Sawyers C, Weichselbaum R, Kharbanda S, Kufe D. Yuan ZM, et al. Nature. 1996 Jul 18;382(6588):272-4. doi: 10.1038/382272a0. Nature. 1996. PMID: 8717045 - Activation of the c-Abl tyrosine kinase in the stress response to DNA-damaging agents.
Kharbanda S, Ren R, Pandey P, Shafman TD, Feller SM, Weichselbaum RR, Kufe DW. Kharbanda S, et al. Nature. 1995 Aug 31;376(6543):785-8. doi: 10.1038/376785a0. Nature. 1995. PMID: 7651539 - Determination of cell fate by c-Abl activation in the response to DNA damage.
Kharbanda S, Yuan ZM, Weichselbaum R, Kufe D. Kharbanda S, et al. Oncogene. 1998 Dec 24;17(25):3309-18. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1202571. Oncogene. 1998. PMID: 9916993 Review. - The stress response to ionizing radiation involoves c-Abl-dependent phosphorylation of SHPTP1.
Kharbanda S, Bharti A, Pei D, Wang J, Pandey P, Ren R, Weichselbaum R, Walsh CT, Kufe D. Kharbanda S, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Jul 9;93(14):6898-901. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.14.6898. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996. PMID: 8692915 Free PMC article. - Regulation of cell death by the Abl tyrosine kinase.
Wang JY. Wang JY. Oncogene. 2000 Nov 20;19(49):5643-50. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1203878. Oncogene. 2000. PMID: 11114745 Review.
Cited by
- The functional role of cysteine residues for c-Abl kinase activity.
Leonberg AK, Chai YC. Leonberg AK, et al. Mol Cell Biochem. 2007 Oct;304(1-2):207-12. doi: 10.1007/s11010-007-9501-y. Epub 2007 Jun 22. Mol Cell Biochem. 2007. PMID: 17588140 - MUC1 oncoprotein regulates Bcr-Abl stability and pathogenesis in chronic myelogenous leukemia cells.
Kawano T, Ito M, Raina D, Wu Z, Rosenblatt J, Avigan D, Stone R, Kufe D. Kawano T, et al. Cancer Res. 2007 Dec 15;67(24):11576-84. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-2756. Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 18089786 Free PMC article. - RUNX Family Participates in the Regulation of p53-Dependent DNA Damage Response.
Ozaki T, Nakagawara A, Nagase H. Ozaki T, et al. Int J Genomics. 2013;2013:271347. doi: 10.1155/2013/271347. Epub 2013 Sep 3. Int J Genomics. 2013. PMID: 24078903 Free PMC article. Review. - MUC1 oncoprotein blocks nuclear targeting of c-Abl in the apoptotic response to DNA damage.
Raina D, Ahmad R, Kumar S, Ren J, Yoshida K, Kharbanda S, Kufe D. Raina D, et al. EMBO J. 2006 Aug 23;25(16):3774-83. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601263. Epub 2006 Aug 3. EMBO J. 2006. PMID: 16888623 Free PMC article. - Involvement of interferon-tau in the induction of apoptotic, pyroptotic, and autophagic cell death-related signaling pathways in the bovine uterine endometrium during early pregnancy.
Suzuki T, Sakumoto R, Hayashi KG, Ogiso T, Kunii H, Shirozu T, Kim SW, Bai H, Kawahara M, Kimura K, Takahashi M. Suzuki T, et al. J Reprod Dev. 2018 Dec 14;64(6):495-502. doi: 10.1262/jrd.2018-063. Epub 2018 Oct 8. J Reprod Dev. 2018. PMID: 30298824 Free PMC article.
References
- Wang J Y J. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1993;3:35–43. - PubMed
- Kipreos E T, Wang J Y J. Science. 1992;256:382–385. - PubMed
- McWhirter J R, Wang Y J. Mol Cell Biol. 1991;11:1785–1792. - PubMed
- Van Etten R A, Jackson P, Baltimore D. Cell. 1989;58:669–678. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous