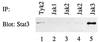Constitutive activation of a slowly migrating isoform of Stat3 in mycosis fungoides: tyrphostin AG490 inhibits Stat3 activation and growth of mycosis fungoides tumor cell lines - PubMed (original) (raw)
Constitutive activation of a slowly migrating isoform of Stat3 in mycosis fungoides: tyrphostin AG490 inhibits Stat3 activation and growth of mycosis fungoides tumor cell lines
M Nielsen et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997.
Abstract
Mycosis fungoides (MF) is a low-grade cutaneous T cell lymphoma of unknown etiology. In this report, the Jak/Stat (Janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription) signaling pathway was investigated in tumor cell lines established from skin biopsy specimens from a patient with MF. Jaks link cytokine receptors to Stats, and abnormal Jak/Stat signaling has been observed in some hemopoietic cancers. In MF tumor cells, a slowly migrating isoform of Stat3, Stat3(sm), was found to be constitutively activated, i.e., (i) Stat3(sm) was constitutively phosphorylated on tyrosine residues, and tyrosine phosphorylation was not enhanced by growth factor stimulation; (ii) band shift assays and immunoprecipitations of DNA/Stat complexes showed constitutive DNA-binding properties of Stat3(sm); and (iii) Stat3(sm) was constitutively associated with Jak3. The abnormal activation of Stat3(sm) was highly specific. Thus, neither the fast migrating isoform of Stat3 (Stat3(fm)) nor other Stats (Stat1, Stat2, and Stat4 through Stat6) were constitutively activated. The Jak kinase inhibitor, tyrphostin AG490, blocked the constitutive activation of Stat3(sm) and inhibited spontaneous as well as interleukin 2-induced growth of MF tumor cells. In conclusion, we have provided evidence for an abnormal Jak/Stat signaling and growth regulation in tumor cells obtained from affected skin of an MF patient.
Figures
Figure 1
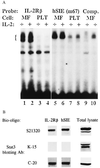
(A) Stat3sm (Upper) is constitutively tyrosine-phosphorylated in MF cells. Cytoplasmic extracts from IL-2-starved cells were analyzed by immunoprecipitation with anti-phosphotyrosine mAb (4G10) and subsequent blotting with use of mAbs against Stat1 through Stat6. Tyrosine phosphorylation of Stat3sm cannot be further induced in My-la cells (Lower). Three MF cell lines and a nonmalignant T cell line (PLT) were IL-2-starved before stimulation with IL-2 (500 units/ml) for 10 min. The cytoplasmic lysates were analyzed by immunoprecipitation with an anti-phosphotyrosine mAb and by subsequent blotting with a Stat3 mAb. (B) After IL-2 starvation, MF cells were stimulated with IL-2 (500 units/ml) for 30 min. Nuclear extracts were analyzed by immunoprecipitation with an anti-phosphotyrosine mAb (4G10) and by subsequent blotting with a Stat3 mAb (Left). The blot was stripped and reprobed with an antibody against Stat5 (Right).
Figure 2
(A) Constitutive tyrosine phosphorylation of Stat3sm correlates with constitutive binding to DNA. MF cells or nonmalignant T cells (PLT) were starved in medium without IL-2 before band-shift analysis of nuclear extracts. DNA binding was determined by using 32P-labeled IL-2Rβ and hSIE m67 probes. The position of Stat-related proteins is indicated by a bracket. Binding was competed out by using a 50-fold excess of unlabeled probe (not shown). (B) A specific form of Stat3 binds to DNA. Cytoplasmic extracts from IL-2-starved MF cells were analyzed by affinity purification of Stat proteins by using biotinylated probes (hSIE and IL-2Rβ). Stat/DNA complexes were analyzed by Western blotting with use of Stat3 antibodies directed against different parts of Stat3 (S21320, amino acids 1–178; K-15, amino acids 626–640; C-20, amino acids 750–769). The same panel of Stat3 antibodies was used for blotting of total cell lysates.
Figure 3
Stat5 activation is inducible, whereas Stat3sm cannot be further induced. Cells were starved for 4 hr in IL-2-free medium before stimulation with medium or IL-2 (500 units/ml) for 15 min. DNA-binding Stats were affinity-purified by using biotinylated hSIE and IL-2Rβ probes and were subjected to Western blotting with the Stat3sm mAb (upper bands). The membrane was stripped and reprobed with the Stat5 mAb (lower band).
Figure 4
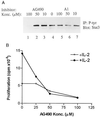
Tyrphostin AG490 inhibits constitutive Stat3sm activation and growth of MF cells. (A) Cells were incubated for 16 hr in culture medium without inhibitor (lane 4), medium containing the indicated amounts of the Jak inhibitor AG490 (lanes 1–3), or the inactive control tyrphostin A1 (lanes 5–7). The cells were then starved for 4 hr in IL-2-free medium containing the relevant inhibitor before cytoplasmic lysates were prepared. Tyrosine-phosphorylated proteins were immunoprecipitated with an anti-phosphotyrosine mAb (4G10), resolved on a polyacrylamide gel, and immunoblotted with the Stat3sm mAb. (B) Cells were cultured for 16 hr with or without the indicated concentrations of Jak inhibitor AG490, and then [3H]thymidine uptake was measured.
Figure 5
Stat3sm is associated with Jak3 and Tyk2. Cells were starved for 4 hr in IL-2-free medium before they were lysed. The different members of the Jak family were immunoprecipitated by using the antibodies indicated on the figure. Association with Stat3sm was determined by immunoblotting with the Stat3sm mAb.
Similar articles
- Inhibition of constitutively activated Stat3 correlates with altered Bcl-2/Bax expression and induction of apoptosis in mycosis fungoides tumor cells.
Nielsen M, Kaestel CG, Eriksen KW, Woetmann A, Stokkedal T, Kaltoft K, Geisler C, Röpke C, Odum N. Nielsen M, et al. Leukemia. 1999 May;13(5):735-8. doi: 10.1038/sj.leu.2401415. Leukemia. 1999. PMID: 10374878 - Constitutive activation of STAT transcription factors in acute myelogenous leukemia.
Spiekermann K, Biethahn S, Wilde S, Hiddemann W, Alves F. Spiekermann K, et al. Eur J Haematol. 2001 Aug;67(2):63-71. Eur J Haematol. 2001. PMID: 11722592 - STAT proteins as novel targets for cancer drug discovery.
Turkson J. Turkson J. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2004 Oct;8(5):409-22. doi: 10.1517/14728222.8.5.409. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2004. PMID: 15469392 Review. - The role of STATs in inflammation and inflammatory diseases.
Pfitzner E, Kliem S, Baus D, Litterst CM. Pfitzner E, et al. Curr Pharm Des. 2004;10(23):2839-50. doi: 10.2174/1381612043383638. Curr Pharm Des. 2004. PMID: 15379672 Review.
Cited by
- Histamine affects STAT6 phosphorylation via its effects on IL-4 secretion: role of H1 receptors in the regulation of IL-4 production.
Kharmate G, Liu Z, Patterson E, Khan MM. Kharmate G, et al. Int Immunopharmacol. 2007 Mar;7(3):277-86. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2006.10.006. Epub 2006 Nov 20. Int Immunopharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17276885 Free PMC article. - Cerulein pancreatitis: oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis.
Kim H. Kim H. Gut Liver. 2008 Sep;2(2):74-80. doi: 10.5009/gnl.2008.2.2.74. Epub 2008 Sep 30. Gut Liver. 2008. PMID: 20485614 Free PMC article. - The expression and the tumor suppressor role of CLDN6 in colon cancer.
Qu H, Wang M, Wang M, Liu Y, Quan C. Qu H, et al. Mol Cell Biochem. 2022 Dec;477(12):2883-2893. doi: 10.1007/s11010-022-04450-z. Epub 2022 Jun 14. Mol Cell Biochem. 2022. PMID: 35701678 - Interleukin-1beta mediates human airway epithelial cell migration via NF-kappaB.
White SR, Fischer BM, Marroquin BA, Stern R. White SR, et al. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2008 Dec;295(6):L1018-27. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00065.2008. Epub 2008 Oct 10. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18849440 Free PMC article. - Gamma c-signaling cytokines induce a regulatory T cell phenotype in malignant CD4+ T lymphocytes.
Kasprzycka M, Zhang Q, Witkiewicz A, Marzec M, Potoczek M, Liu X, Wang HY, Milone M, Basu S, Mauger J, Choi JK, Abrams JT, Hou JS, Rook AH, Vonderheid E, Woetmann A, Odum N, Wasik MA. Kasprzycka M, et al. J Immunol. 2008 Aug 15;181(4):2506-12. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.181.4.2506. J Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18684941 Free PMC article.
References
- Hansen E R. Arch Dermatol. 1996;132:554–561. - PubMed
- Kaltoft K, Hansen B H, Thestrup-Pedersen K. Dermatol Clin. 1994;12:295–304. - PubMed
- Kaltoft K, Bisballe S, Dyrberg T, Boel E, Rasmussen P B, Thestrup-Pedersen K. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. 1992;28A:161–167. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous