pRB plays an essential role in cell cycle arrest induced by DNA damage - PubMed (original) (raw)
pRB plays an essential role in cell cycle arrest induced by DNA damage
E A Harrington et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998.
Abstract
To maintain genome stability, cells with damaged DNA must arrest to allow repair of mutations before replication. Although several key components required to elicit this arrest have been discovered, much of the pathway remains elusive. Here we report that pRB acts as a central mediator of the proliferative block induced by a diverse range of DNA damaging stimuli. Rb-/- mouse embryo fibroblasts are defective in arrest after gamma-irradiation, UV irradiation, and treatment with a variety of chemotherapeutic drugs. In contrast, the pRB related proteins p107 and p130 do not play an essential part in the DNA damage response. pRB is required specifically for the G1/S phase checkpoint induced by gamma-irradiation. Despite a defect in G1/S phase arrest, levels of p53 and p21 are increased normally in Rb-/- cells in response to gamma-irradiation. These results lead us to propose a model in which pRB acts as an essential downstream target of the DNA damage-induced arrest pathway. The ability of pRB to prevent replication of damaged DNA is likely to inhibit the propagation of carcinogenic mutations and may therefore contribute to its role as a tumor suppressor. Furthermore, because many cancer therapies act by damaging DNA, these findings also have implications for the treatment of tumors in which pRB is inactivated.
Figures
Figure 1
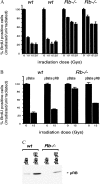
_Rb_−/− MEFs are defective in cell cycle arrest after γ-irradiation. (A) Asynchronous cultures of _Rb_−/− and wild-type littermate control MEFs were γ-irradiated at the indicated doses. Twenty-four hours after treatment, cells were labeled with BrdUrd for 8 hr. BrdUrd incorporation was then assessed by immunocytochemistry. Data from three independent samples are presented as the percentage of cells that incorporated BrdUrd in irradiated vs. unirradiated cultures. (B)Rb_−/− and wild-type MEFs infected with pBabe or pBabe pRB retroviruses were treated as in A. (C) Expression of pRB in infected cells from_B was confirmed by Western blotting.
Figure 2
p107 and p130 do not play an essential role in γ-irradiation induced arrest. Asynchronous cultures of wild type,_Rb_−/−, p107−/− and p130−/− (A) or p107−/−; p130−/− (B) and littermate control MEFs were γ-irradiated at the indicated doses. Twenty-four hours after irradiation, cells were given an 8-hr BrdUrd pulse, and BrdUrd incorporation was assessed by immunocytochemistry. Data from three independent samples are presented as the percentage of cells that incorporated BrdUrd in irradiated vs. unirradiated cultures.
Figure 3
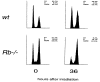
pRB is required for G1/S phase arrest after γ-irradiation. Zero or 36 hr after γ-irradiation the cell cycles profile of _Rb_−/− and wild-type MEFs were examined by FACs analysis.
Figure 4
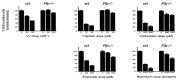
_Rb_−/− cells are impaired in cell cycle arrest after treatment with a diverse range of DNA-damaging agents. Twenty-four hours after treatment with the indicated DNA-damaging agents, BrdUrd incorporation in wild-type and_Rb_−/− MEFs was assessed by immunocytochemistry. The mean percentage of BrdUrd positive cells in treated vs. untreated cultures from three independent samples is presented.
Figure 5
Response of _Rb_−/−cells to treatment with vincristine or vinblastine. (A) Asynchronous cultures of wild-type and_Rb_−/− MEFs were treated for 24 hr with the indicated doses of vincristine or vinblastine. BrdUrd incorporation over the next 8 hr was then assessed by immunocytochemistry. The percentage of BrdUrd positive cells in treated vs. untreated cultures from three independent samples is shown. (B) Asynchronous cultures of wild-type and _Rb_−/− MEFs at passage 4 were treated with 1 μM of vincristine or vinblastine. The percentage of cells with >4N DNA content was assessed by FACs analysis.
Figure 6
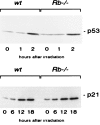
p53 and p21 levels are increased normally in_Rb_−/− cells after γ-irradiation. Lysates from _Rb_−/− and wild-type MEFs were made at the indicated time points after γ-irradiation (15 Gy). Levels of p53 (A) and p21 (B) were assessed by Western blotting.
References
- Cox L S, Lane D P. BioEssays. 1995;17:501–508. - PubMed
- Levine A J. Cell. 1997;88:323–331. - PubMed
- Morgan S E, Kastan M B. Adv Cancer Res. 1997;71:1–25. - PubMed
- Kastan M B, Onyekwere O, Sidransky D, Vogelstein B, Craig R W. Cancer Res. 1991;51:6304–6311. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous